Transpiration Drawing
Transpiration Drawing - Research the climatic conditions and types of plants in various biomes. But how does that work? Web this plastic bag transpiration demonstration shows that water was released from the leaf while it was covered up. Transpiration is the movement of water up the stem of a plant from root to leaf when water is lost from the plant due to evaporation and diffusion of water from a plant’s surface. But air that is not fully saturated with water vapor (100% relative humidity) will dry the surfaces of cells with which it comes in contact. Negative water potential draws water into the root hairs. Web cohesion and adhesion draw water up the xylem. Stomatal, lenticular and cuticular transpiration | plants botany , plant water relations , relationship , transpiration and absorption difference between transpiration and evaporation | plants Or draw a picture of a plant and label all these parts on the drawing. Drawing machine collaged with an analytical drawing of the machine and fragments of the drawing produced by it. But air that is not fully saturated with water vapor (100% relative humidity) will dry the surfaces of cells with which it comes in contact. The transpiration ratio of crops tends to fall between 200 and 1000 (i.e., crop plants. Web transpiration—the loss of water vapor to the atmosphere through stomata—is a passive process, meaning that metabolic energy in the. Polythene bag or bell jar experiment. Explain how photosynthates are transported in plants. Or draw a picture of a plant and label all these parts on the drawing. Web point out the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers of plants around you. It is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. It gets rid of the excess water absorbed by roots and returns it back to the atmosphere. Drawing machine collaged with an analytical drawing of the machine and fragments of the drawing produced by it. “transpiration is the biological process by which water is lost in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plants.” table of. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. Web during the daytime, the transpiration dominates but during the nighttime because there is no transpiration, root pressure is the only force. Water potential decreases from the roots to the top of the plant. Transpiration helps keep the water balance in the plant body through the loss of water. Web how to. But how does that work? Transpiration helps keep the water balance in the plant body through the loss of water. The energy driving transpiration is the difference in energy between the water in the soil and the water in the atmosphere. It is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. This dyed celery experiment is a classic science. Web cohesion and adhesion draw water up the xylem. Describe how water potential, evapotranspiration, and stomatal regulation influence how water is transported in plants. Explain how photosynthates are transported in plants. Most of the water absorbed by the roots of a plant—as much as 99.5 percent—is not used for growth or metabolism; This dyed celery experiment is a classic science. Transpiration is the movement of water up the stem of a plant from root to leaf when water is lost from the plant due to evaporation and diffusion of water from a plant’s surface. Transpiration rates vary widely depending on weather and other conditions, such as. But air that is not fully saturated with water vapor (100% relative humidity) will. Research the climatic conditions and types of plants in various biomes. Have the students relate transpiration to the hydrologic cycle and draw pictures showing transpiration as part of the hydrologic cycle. Web point out the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers of plants around you. Drawing machine collaged with an analytical drawing of the machine and fragments of the drawing produced. Demonstration of transpiration through the stomatal pores of the leaves. It occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of co 2 and o 2 during photosynthesis. Or draw a picture of a plant and label all these parts on the drawing. Web define transpiration and identify how environmental factors affect transpiration rate. Web plants. The energy driving transpiration is the difference in energy between the water in the soil and the water in the atmosphere. How is transpiration involved in capillary action? It occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of co 2 and o 2 during photosynthesis. “transpiration is the biological process by which water is lost. Describe how water potential, evapotranspiration, and stomatal regulation influence how water is transported in plants. Web transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. Well, to quickly give you an overview, here we have zoomed in to the tip of one of the tiny root hairs. “transpiration is the biological process by which water is lost in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plants.” table of contents. Most of the water absorbed by the roots of a plant—as much as 99.5 percent—is not used for growth or metabolism; It occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of co 2 and o 2 during photosynthesis. Web during the daytime, the transpiration dominates but during the nighttime because there is no transpiration, root pressure is the only force. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. Plants transpire water at different rates. Web point out the roots, stems, leaves, and flowers of plants around you. Web draw and label your observations, making sure to label each sketch with the plant species. Transpiration helps keep the water balance in the plant body through the loss of water. Transpiration draws water from the leaf. Have the students conduct the same investigation with various plants such as geraniums and cactuses. Web learn about how transpiration works in plants with this classic dyed celery experiment for kids! Or draw a picture of a plant and label all these parts on the drawing.
Diagram showing transpiration in plant illustration Stock Vector Image

Diagram showing transpiration plant 6466285 Vector Art at Vecteezy
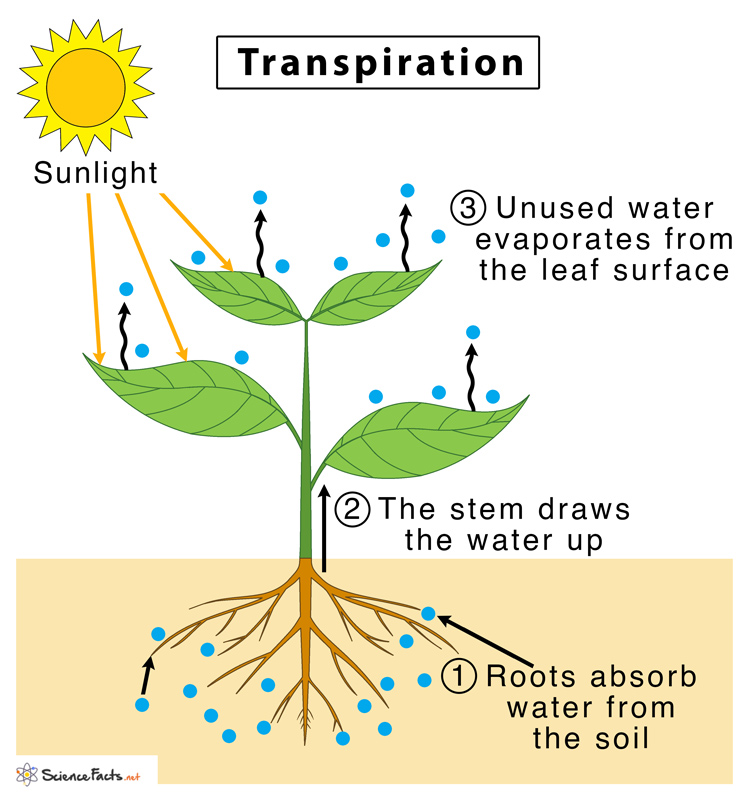
Transpiration Definition, Factors, Types, and Importance
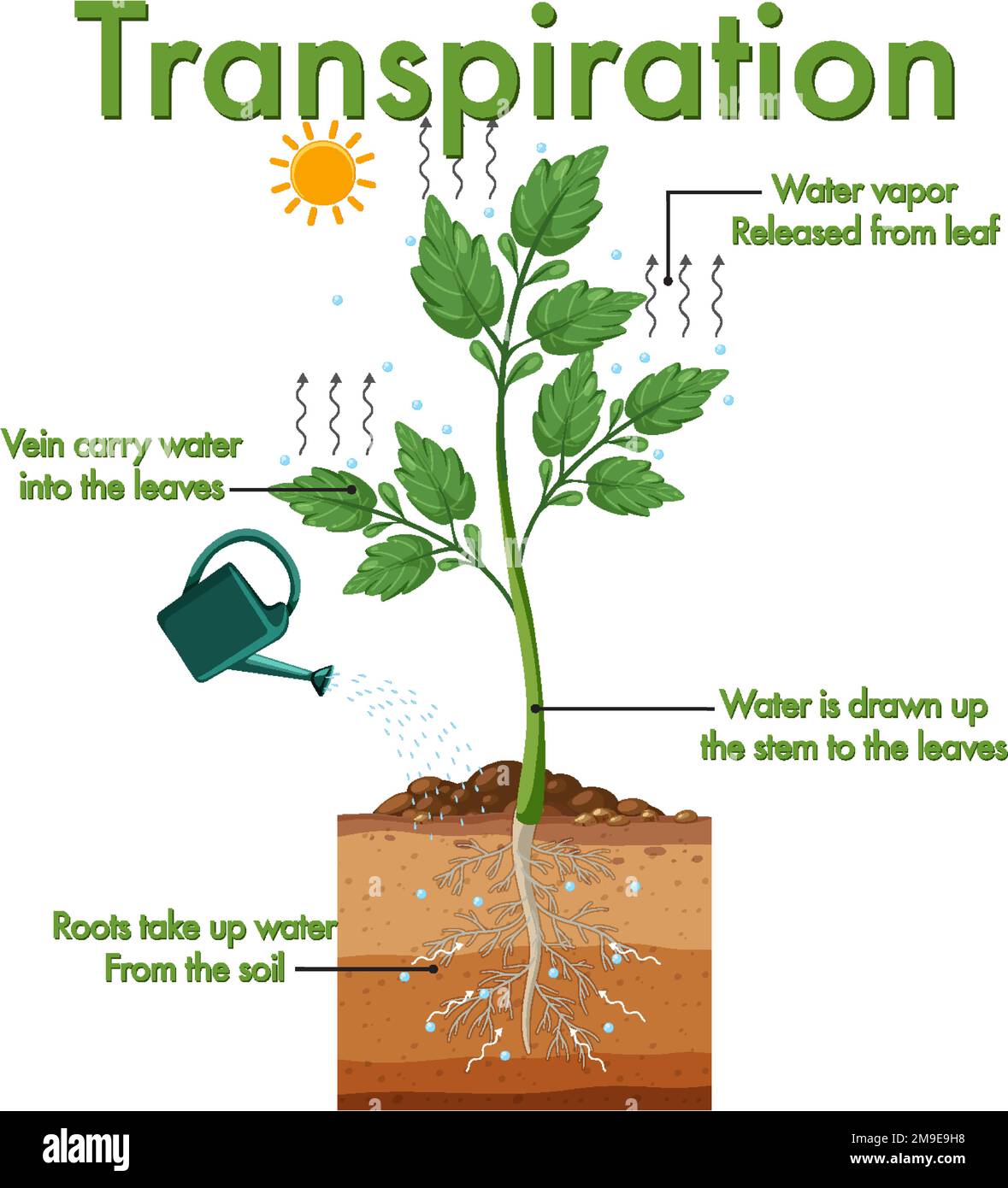
Diagram showing plant transpiration illustration Stock Vector Image

Diagram Showing Transpiration of Plant Stock Vector Illustration of
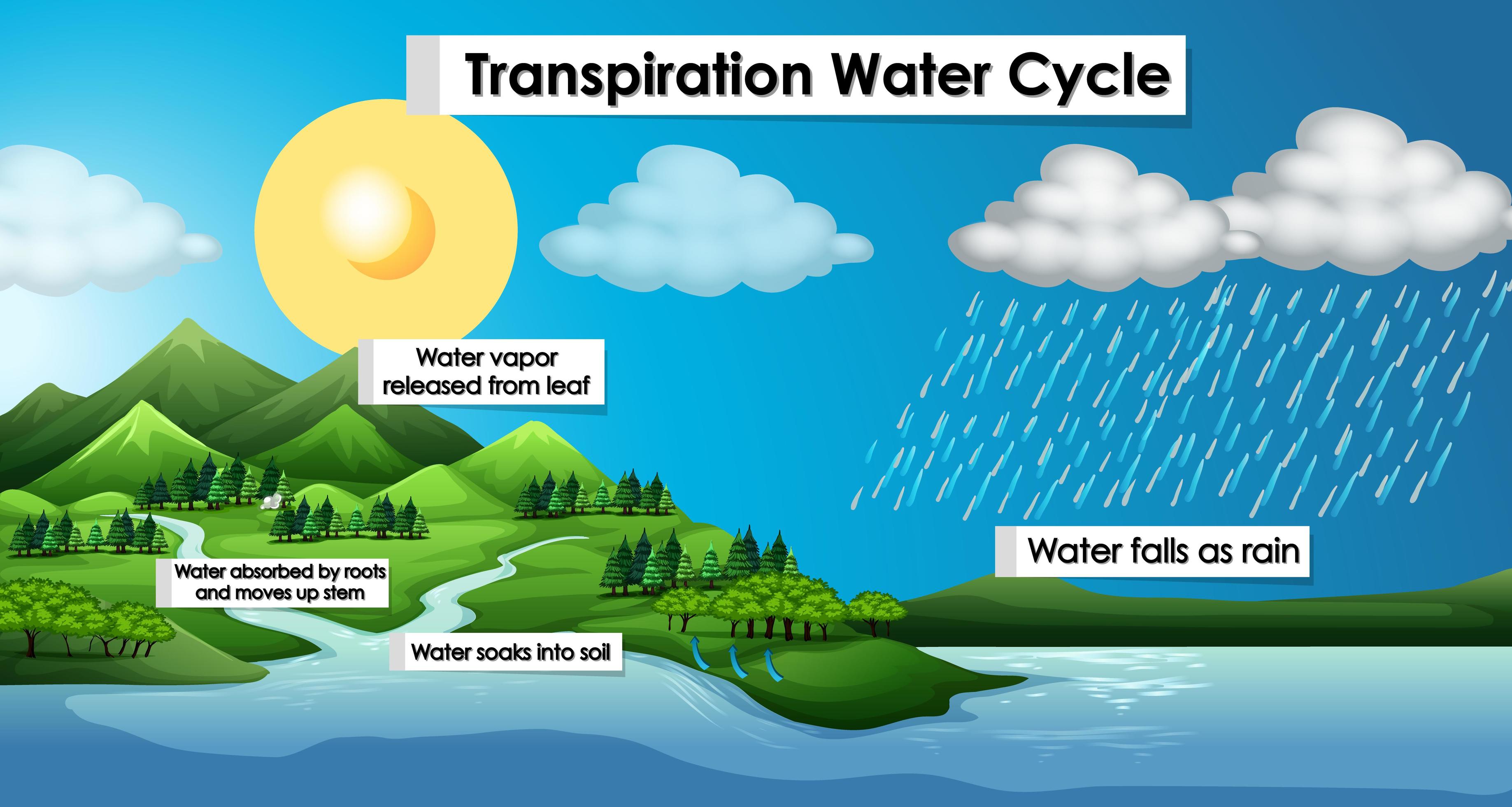
Diagram showing transpiration water cycle 1235130 Vector Art at Vecteezy
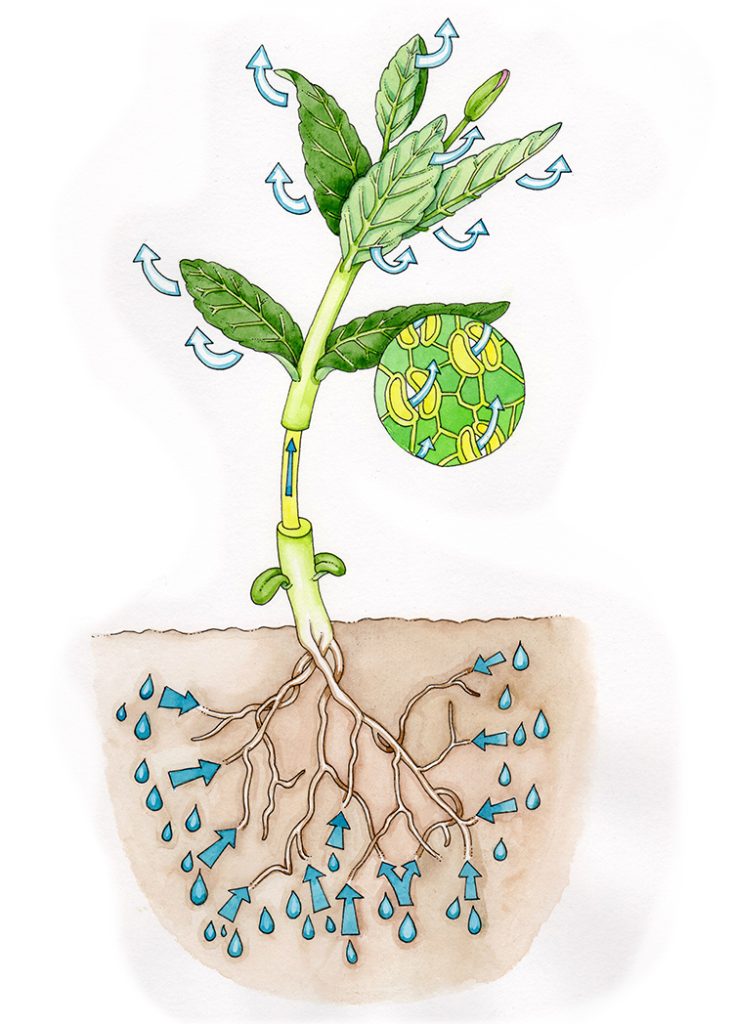
Transpiration diagram Lizzie Harper
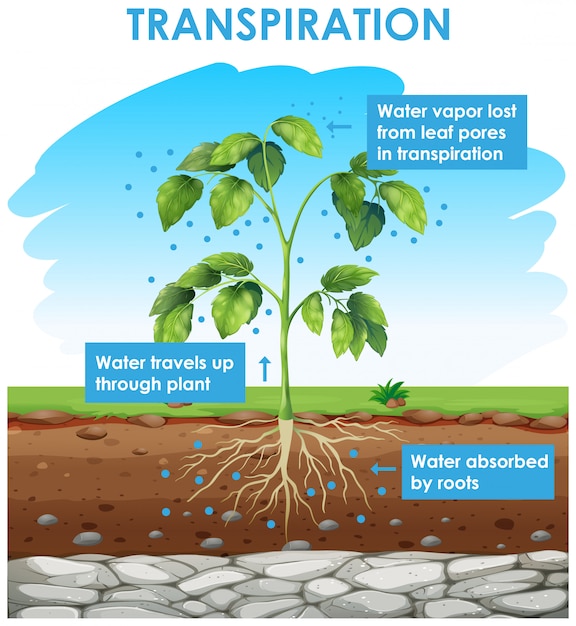
Free Vector Diagram showing transpiration in plant

Diagram showing transpiration in plant Royalty Free Vector

How to draw diagram of transpiration in plant // easy drawing grow
You Should Perform This Count A Total Of Four Times In Four Different Areas Of The Leaf Impression, And Then Determine The Average Number Of Stomata Per Counted Area On The Leaf.
Stomatal, Lenticular And Cuticular Transpiration | Plants Botany , Plant Water Relations , Relationship , Transpiration And Absorption Difference Between Transpiration And Evaporation | Plants
How Is Transpiration Involved In Capillary Action?
Transpiration Draws Water From The Leaf.
Related Post: