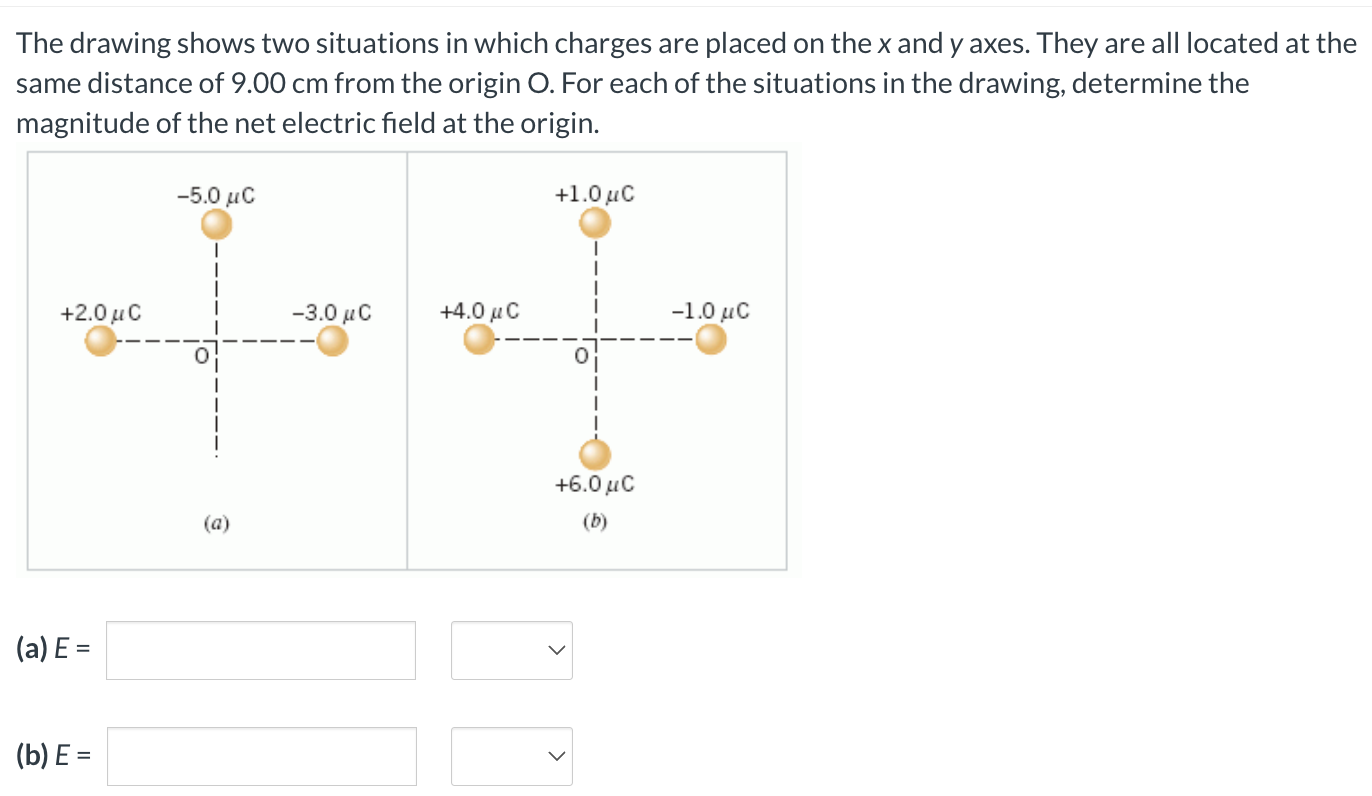
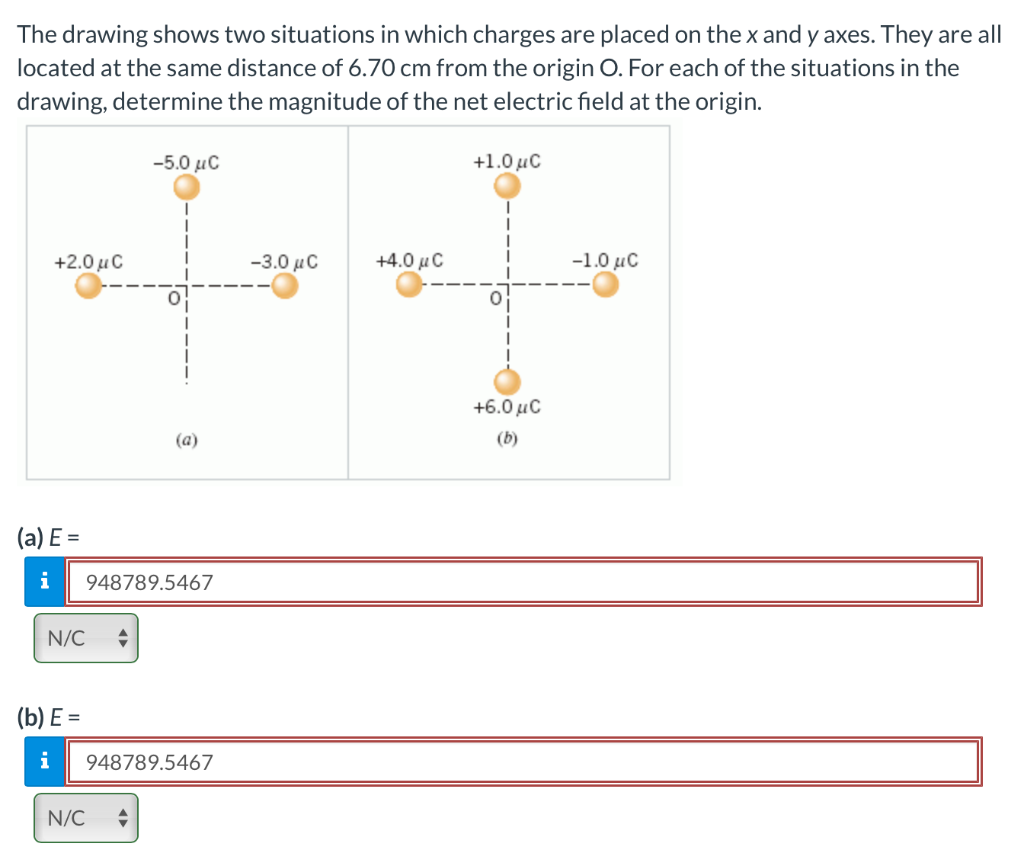
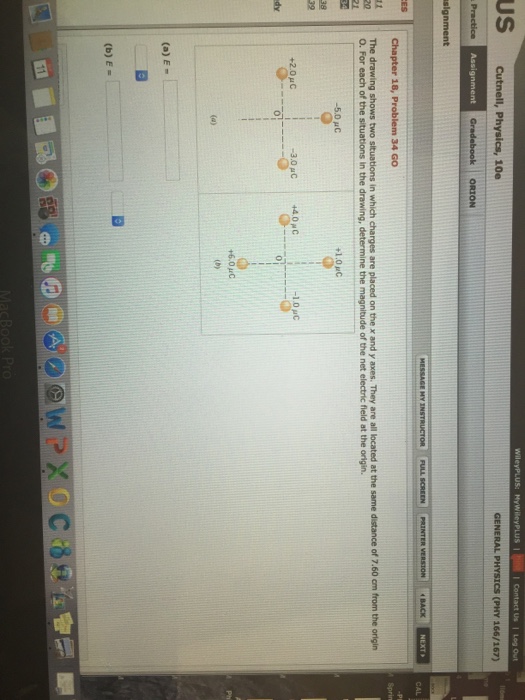
The Drawing Shows Two Situations In Which Charges Are Placed
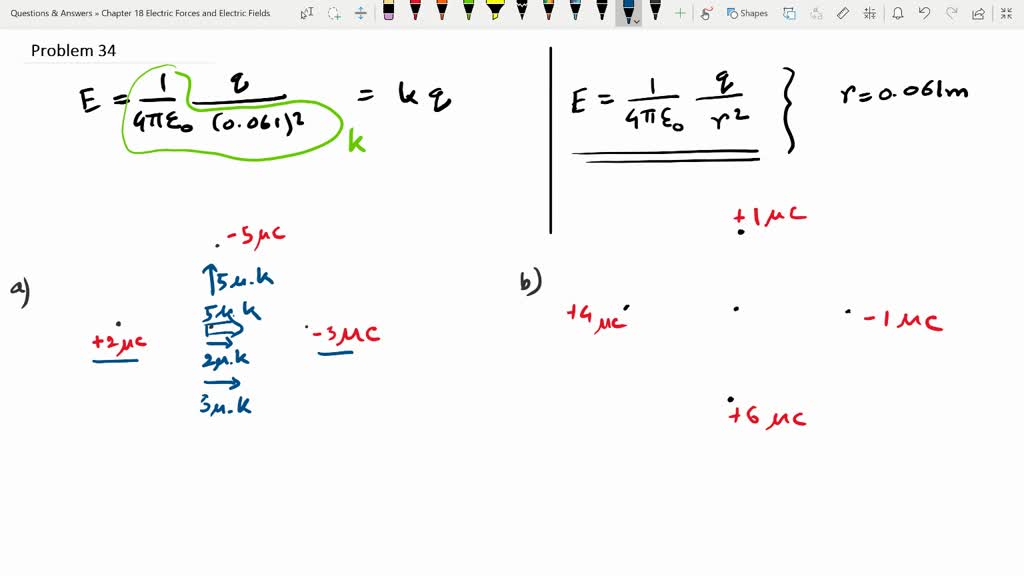
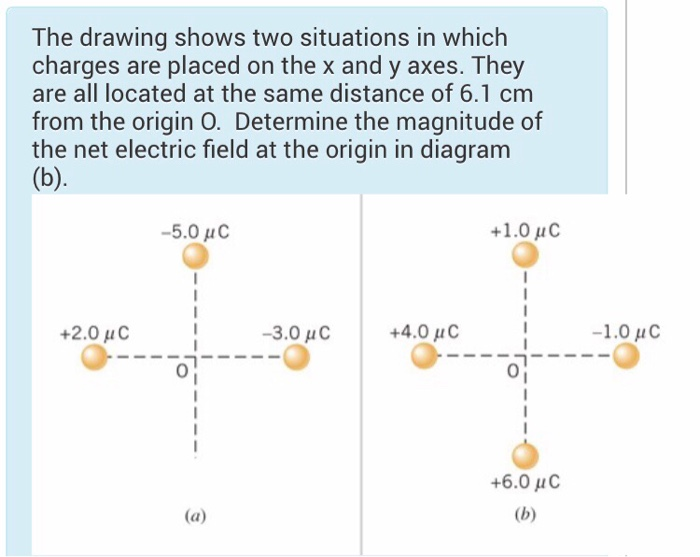
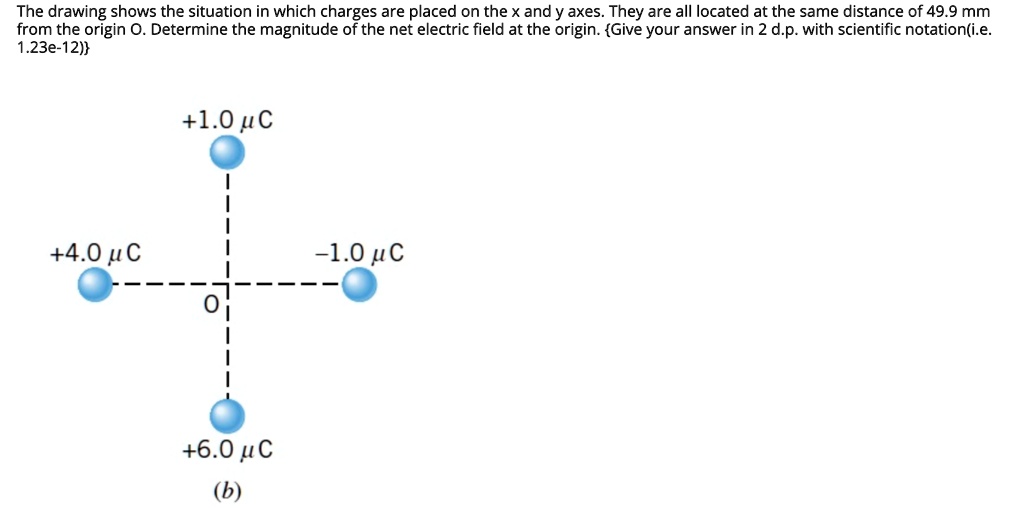
The Drawing Shows Two Situations In Which Charges Are Placed - They are all located at the same distance of 7.30 cm from the origin. They are all located at the same distance of 5.30 cm from the origin o. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. @ the drawing shows two situations in which. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. For each of the situations in the drawing, determine the magnitude of the net electric field at the. Let's say we have a spinning ball and a spelling ball, and the spelling ball starts rotating from rest, and the. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. They are all located at the same distance of 6.1 cm from the origin o. There is a spinning ball here. They are all located at the same distance of 8.20 cm from the. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. @ the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. The drawing shows. By the end of this section, you will be able to: In this situation, charges are placed in a uniform electric field, which means that the electric field has the same magnitude. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. They are all located at the same distance of 6.1 cm from. They are all located at the same distance of 6.1 cm c m from the. Question asked by filo student. The other two charges have identical magnitudes, but. The distance from the origin to where three or four charges are situated is given a 0.61 meters. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and. Calculate the total force (magnitude and direction) exerted on a test charge from. They are all located at the same distance of 8.20 cm from the. Let's say we have a spinning ball and a spelling ball, and the spelling ball starts rotating from rest, and the. Web @ @ the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed. They are all located at the same distance of 5.80 cm from the origin o. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The. The spinning ball was given to us here. Let's say we have a spinning ball with a spelling ball, and the spelling ball starts rotating from rest, and. Calculate the total force (magnitude and direction) exerted on a test charge from. They are all located at the same distance of 6.1 cm c m from the. @ the drawing shows. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. Calculate the total force (magnitude and direction) exerted on a test charge from. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. The spinning ball was given to us here. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. The other two. Web @ @ the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x x and y y axes. In order to solve this problem, we will be using a formula that is. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. For situation (a) net charge e = e₊₂. Let's say we have a spinning ball with a spelling ball, and the spelling ball starts rotating from rest, and. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. For situation (a) net charge e = e₊₂ + e₋₅ + e₋₃. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. They are all located at the same distance of. There is a spinning ball here. Q 1 is the charge minus 3.0 micro coulomb, which is kept on the x axis, and q2 is the charge minus 5.0 micro coulomb, which is kept on the y axis. For situation (a) net charge e = e₊₂ + e₋₅ + e₋₃. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. Hello to all of you. They are all located at the same distance of 8.20 cm from the. They are all located at the same distance of 6.1 cm from the origin o. By the end of this section, you will be able to: They are all located at the same distance of 5.30 cm from the origin o. The spinning ball was given to us here. They are all located at the same distance of 6.1 cm c m from the. Web the drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x x and y y axes. The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on the x and y axes. @ the drawing shows two situations in which.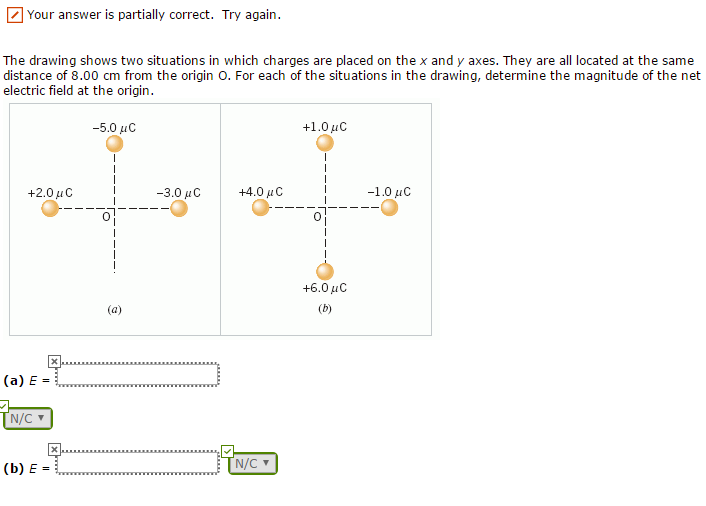
Solved The drawing shows two situations in which charges are
⏩SOLVED The drawing shows two situations in which charges are… Numerade
[Solved] The drawing shows two situations in which charges
[Solved] The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed
Solved The drawing shows two situations in which charges are
Solved The drawing shows two situations in which charges are

Your T The drawing shows two situations in which charges are placed on
Solved The drawing shows two situations in which charges are
Solved The drawing shows two situations in which charges are
SOLVED The drawing shows the situation in which charges are placed on
In This Situation, Charges Are Placed In A Uniform Electric Field, Which Means That The Electric Field Has The Same Magnitude.
Web The Drawing Shows Three Point Charges Fixed In Place.
They Are All Located At The Same Distance Of 6.1 \Mathrm {~Cm} 6.1 Cm From The Origin.
Calculate The Total Force (Magnitude And Direction) Exerted On A Test Charge From.
Related Post:
![[Solved] The drawing shows two situations in which charges](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/cd1/cd1176b0-7ad2-485f-9f81-e384bb2bbbfe/image)