The Drawing Shows A Square Each Side Of Which
The Drawing Shows A Square Each Side Of Which - Two different positive charges q 1 and q 2 are fixed at the corners of the square. On two corners of the square are fixed. Together, we'll explore a video introducing area by comparing two figures' space on a surface. Two different positive charges q 1 and q 2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.25 m. The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l=0.250 m. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. All four sides are equal. Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.25 m. Two different positive charges, q1 and q2, are fixed at the corners of the square. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.25 m. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. All four sides of a square are equal and parallel to each other. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. A square is a quadrilateral in which: Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Two different. The drawing shows that each side has a length of at least two meters. Two different positive charges, q1 and q2, are fixed at the corners of the square. Web intro to area and unit squares. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.25 m. Two different positive charges q1 and. The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. Using unit squares, we'll measure their areas, emphasizing the importance of a unit square for measuring various shapes. On two corners of the square are fixed different positive charges a_ (1), and a_ (2).\\n=\\\\sqrt (. The opposite sides are parallel. Find the electric. Two positive charges are fixed at the corners of a square. It starts with a given line segment ab. Find the electric potential energy of a third charge q3 = 5.00x10^9 c placed at corner a and then at corner b. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. Web. Web this page shows how to construct (or draw) a square given the length of a side. Web intro to area and unit squares. The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. At the corners of the square there are two different positive. Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. At the corners of the square there are two different positive. Using unit squares, we'll measure their areas, emphasizing the importance of a unit square for measuring various shapes. All four sides of a square are equal and parallel to each other.. Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Two different positive charges 91 and 92 are fixed at the corners of the square. A square is a quadrilateral in which: Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.25 m. The basic figure of a. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.250 m. The drawing shows that each side has a length of at least two meters. Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Two different positive charges q 1 and q 2 are fixed at the corners of the square. Web the drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l = 0.25 m. The compass is then set to the length of the given side, and the other three sides are marked off. All four sides are equal. Using unit squares, we'll measure their areas, emphasizing the importance of a unit square for measuring various shapes. On two corners of the square are fixed. So, find the electric potential energy. Two positive charges are fixed at the corners of a square. There is a problem in this. On two corners of the square are fixed different positive charges, q1 andq2. Two different positive charges q1 and q2 are fixed at the corners of the square. At the corners of the square there are two different positive. The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a length of l=0.25 \mathrm {~m} l = 0.25 m.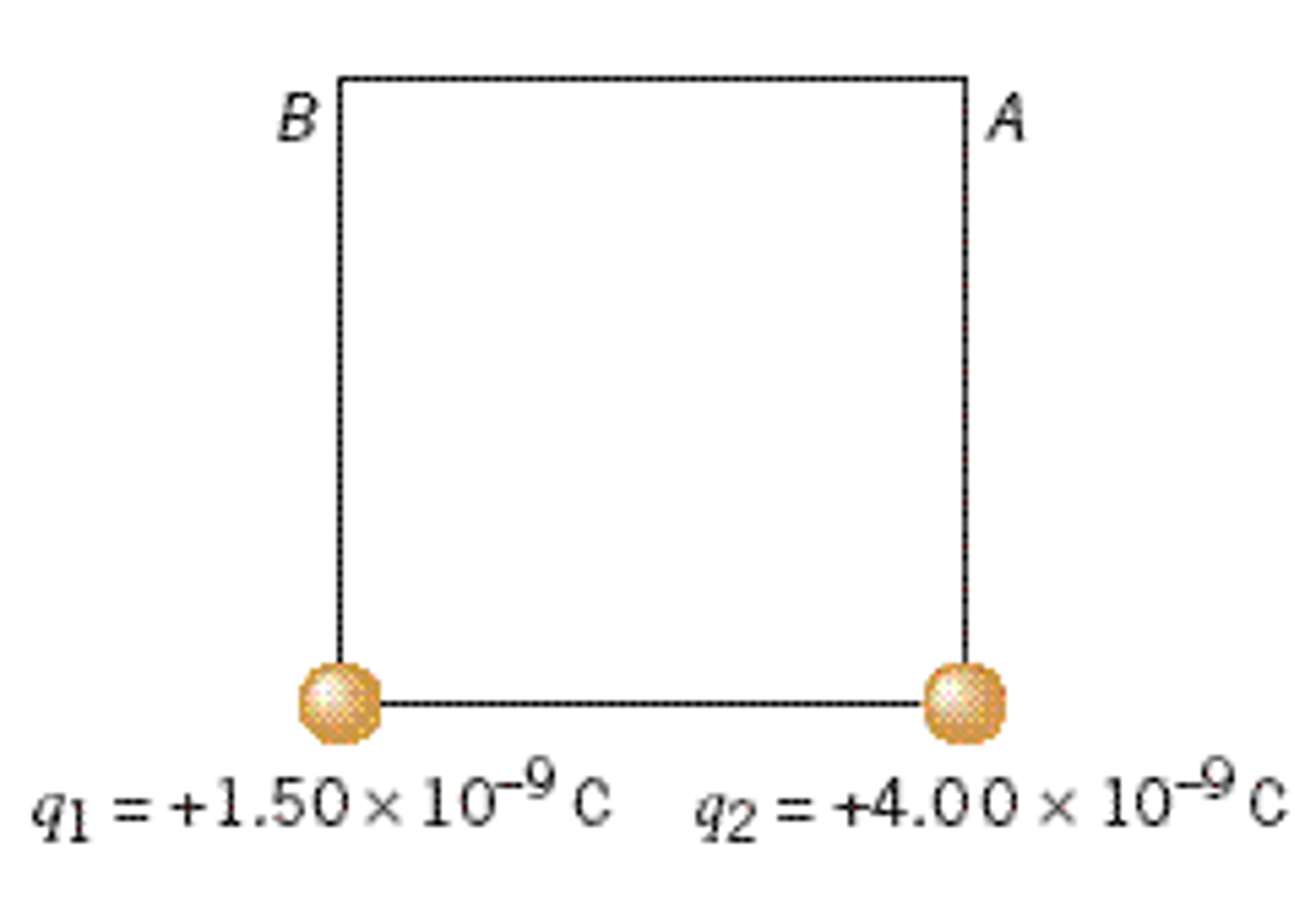
Solved The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a
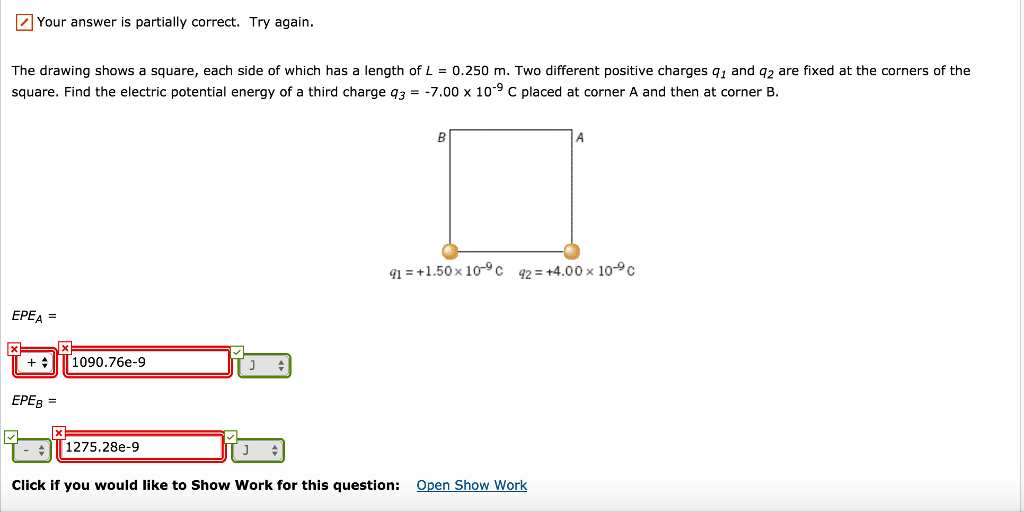
Solved The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a
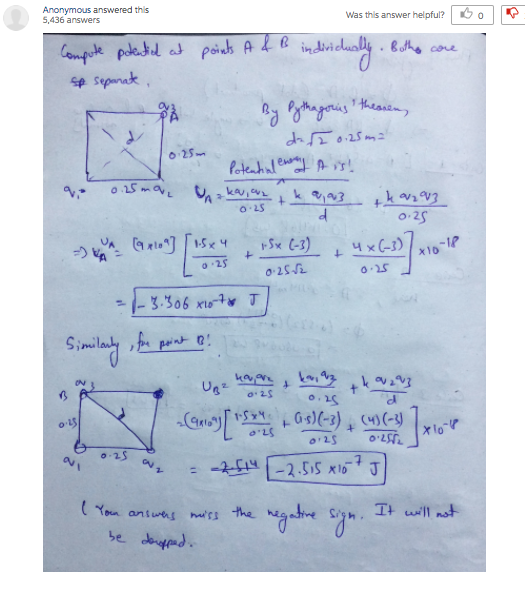
Solved The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a

How to Draw a Square wikiHow

Solved The drawing shows a square, each side of which has a
How to draw a square Using ruler and set square (Step by Step) Easy
Solved 16. The drawing shows a square, each side of which

How To Draw A Geometric Square Design (Easy Drawing Tutorial) YouTube

How to Draw a Square 9 Steps (with Pictures) wikiHow

how to draw a perfect square geometrically YouTube
It Then Erects A Perpendicular At One End Of The Line, Which Will Become The Second Side Of The Square.
Web The Drawing Shows A Square, Each Side Of Which Has A Length Of L = 0.250 M.
Web The Drawing Shows A Square, Each Side Of Which Has A Length Of L = 0.250 M.
Two Different Positive Charges, Q1 And Q2, Are Fixed At The Corners Of The Square.
Related Post:
