Positive Posterior Drawer Test
Positive Posterior Drawer Test - Web the posterior drawer test is a common orthopedic test to assess for posterior cruciate ligament tears. Web the examiner grasps the proximal lower leg, approximately at the tibial plateau or joint line with the thumbs placed on the tibial tuberosity. Then the examiner attempts to translate the lower leg posteriorly. 7.8k views 6 years ago pcl assessment. Web the anterior drawer test is a physical examination doctors use to test the stability of the knee’s anterior cruciate ligament (acl). Don't be confused by the resting position and the leg. Excessive displacement of the tibia anteriorly suggests that the anterior cruciate ligament is injured, whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior cruciate ligament. Web the test is considered positive if there is excessive anterior or posterior translational movement of the tibia compared to the contralateral side. Theoretically, the anterior translation if less than 6mm. The examiner sits on the subject’s foot, with fingers behind the proximal tibia and thumbs on the tibial plateau. The posterior drawer test assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee. Web after a positive anterior drawer test. Doctors may use this test, along with images and other. Web the anterior drawer test is a set of knee and lower leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose acl tears. Web the posterior drawer test is. Web the test is considered positive if there is excessive anterior or posterior translational movement of the tibia compared to the contralateral side. Web after a positive anterior drawer test. Web this review analyses the most commonly used tests and signs for knee examination, outlining the correct way to perform the test, the correct interpretation of a positive test and. A positive test occurs when the tibia excessively translates posteriorly beyond the resting position or if the movement lacks a solid end feel. Excessive posterior translation of the talus. The posterior drawer test assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee. This video demonstrates how to perform the posterior drawer. Be sure to check out the. Web after a positive anterior drawer test. Web posterior drawer test. 6.7k views 1 year ago. A positive test occurs when the tibia excessively translates posteriorly beyond the resting position or if the movement lacks a solid end feel. Excessive posterior translation of the talus. In particular, it prevents the tibia (shinbone) from moving too far backwards relative to the femur (thighbone). A positive test occurs when the tibia excessively translates posteriorly beyond the resting position or if the movement lacks a solid end feel. Web a positive lachman test or pivot test is strong evidence of an existing anterior cruciate ligament (acl) tear, and. Web if the tibia pulls forward or backward more than normal, the test is considered positive. If it is more than 6mm, the test is considered positive. Isolated pcl tears are less common and usually result from a direct blow to the proximal tibia. The posterior drawer test assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee.. Web the posterior drawer test is considered positive if a posterior displacement of the proximal tibia, relative to the distal femur, more than 5 mm, or a “soft” end point, indicates posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. Ligamentous laxity or rupture with presence of sulcus and pain, and/ or. Subscribe to amboss youtube for the latest. This test is performed with the. The acl connects two of the. Web the test is considered positive if there is a lack of end feel or excessive anterior translation relative to the contralateral side. Doctors may use this test, along with images and other. The examiner sits on the subject’s foot, with fingers behind the proximal tibia and thumbs on the tibial plateau. This video. Web the posterior drawer test is considered positive if a posterior displacement of the proximal tibia, relative to the distal femur, more than 5 mm, or a “soft” end point, indicates posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. You’ll lie on your back and your provider will move your lower leg to check how far your knee moves. .1 (the accuracy of the. Your doctor or therapist uses the anterior drawer test to check your anterior cruciate ligament, or acl, for an injury. If your healthcare provider suspects a pcl tear, the posterior drawer test is. Web the test is considered positive if there is excessive anterior or posterior translational movement of the tibia compared to the contralateral side. Web special test:posterior drawer. Web the anterior drawer test is a set of knee and lower leg movements healthcare providers use to diagnose acl tears. Excessive displacement of the tibia anteriorly suggests that the anterior cruciate ligament is injured, whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior cruciate ligament. .1 (the accuracy of the clinical examination in the setting of posterior cruciate ligament injuries). Excessive posterior translation of the talus. A positive test occurs when the tibia excessively translates posteriorly beyond the resting position or if the movement lacks a solid end feel. Web the examiner grasps the proximal lower leg, approximately at the tibial plateau or joint line with the thumbs placed on the tibial tuberosity. Don't be confused by the resting position and the leg. Web if the tibia pulls forward or backward more than normal, the test is considered positive. Web after a positive anterior drawer test. Your doctor or therapist uses the anterior drawer test to check your anterior cruciate ligament, or acl, for an injury. Web the test is considered positive if there is a lack of end feel or excessive anterior translation relative to the contralateral side. Web posterior drawer test. Web the posterior drawer test is a common orthopedic test to assess for posterior cruciate ligament tears. Web this review analyses the most commonly used tests and signs for knee examination, outlining the correct way to perform the test, the correct interpretation of a positive test and the best management for evaluating an injured knee both in the acute and delayed timing. According to rubinstein et al. If your healthcare provider suspects a pcl tear, the posterior drawer test is.
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear

Posterior Drawer Test for PCL Tears YouTube
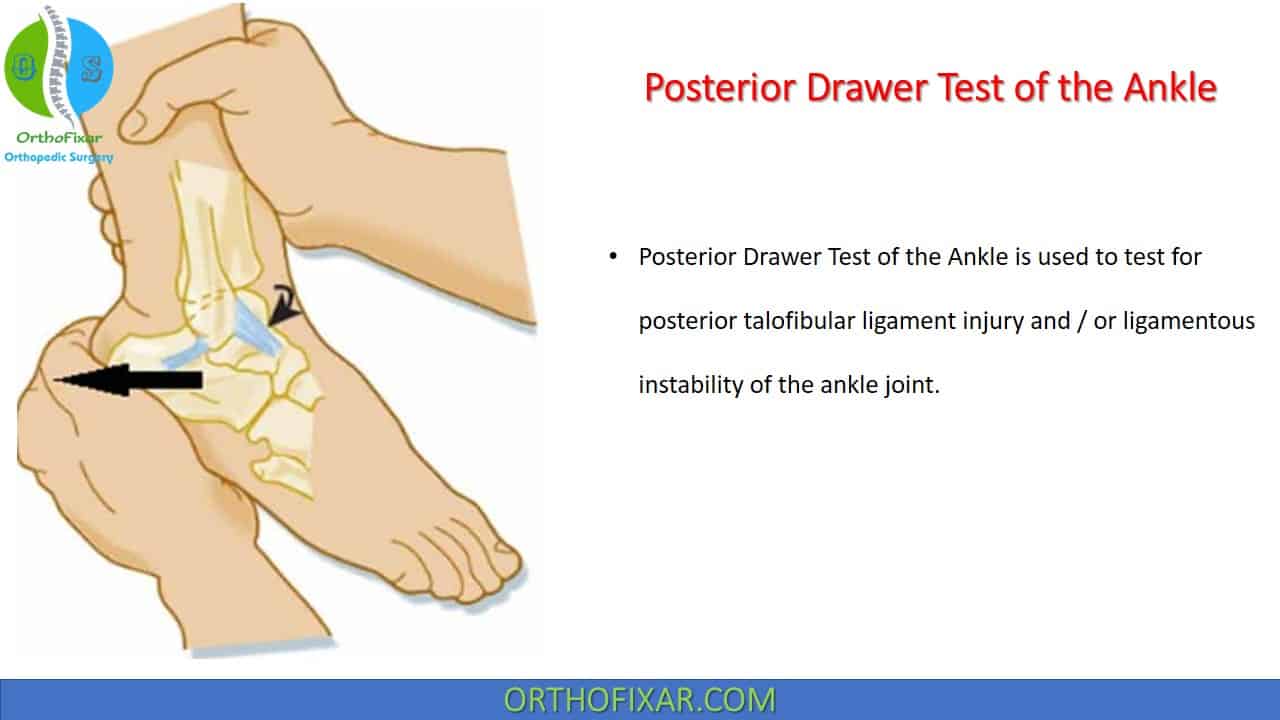
Special Test Category Ankle & Foot Examination OrthoFixar

Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament YouTube

Posterolateral Drawer Test YouTube

Posterior drawer test for the ankle YouTube

Posterior Drawer Test YouTube
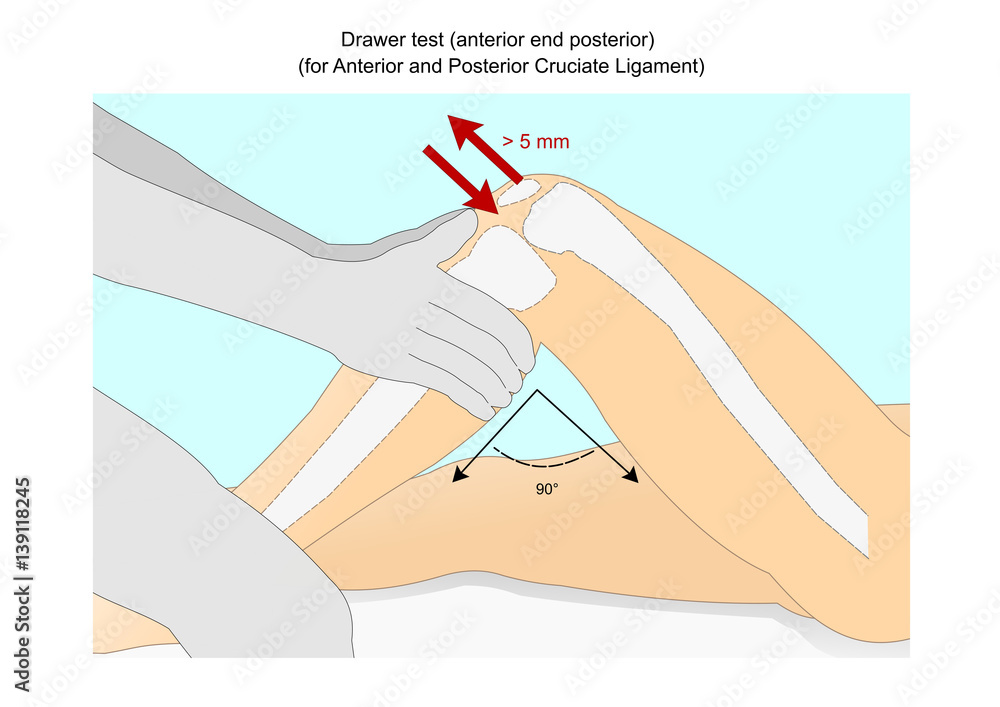
Drawer test to check the integrity of the anterior and posterior

Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury Knee

Knee Tests The Knee Resource
Positive Posterior Drawer Test Of The Knee.
Web Kai Demonstrates The Posterior Drawer Test To Assess For Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tears.
Isolated Pcl Tears Are Less Common And Usually Result From A Direct Blow To The Proximal Tibia.
The Examiner Sits On The Subject’s Foot, With Fingers Behind The Proximal Tibia And Thumbs On The Tibial Plateau.
Related Post: