Longitudinal Wave Drawing
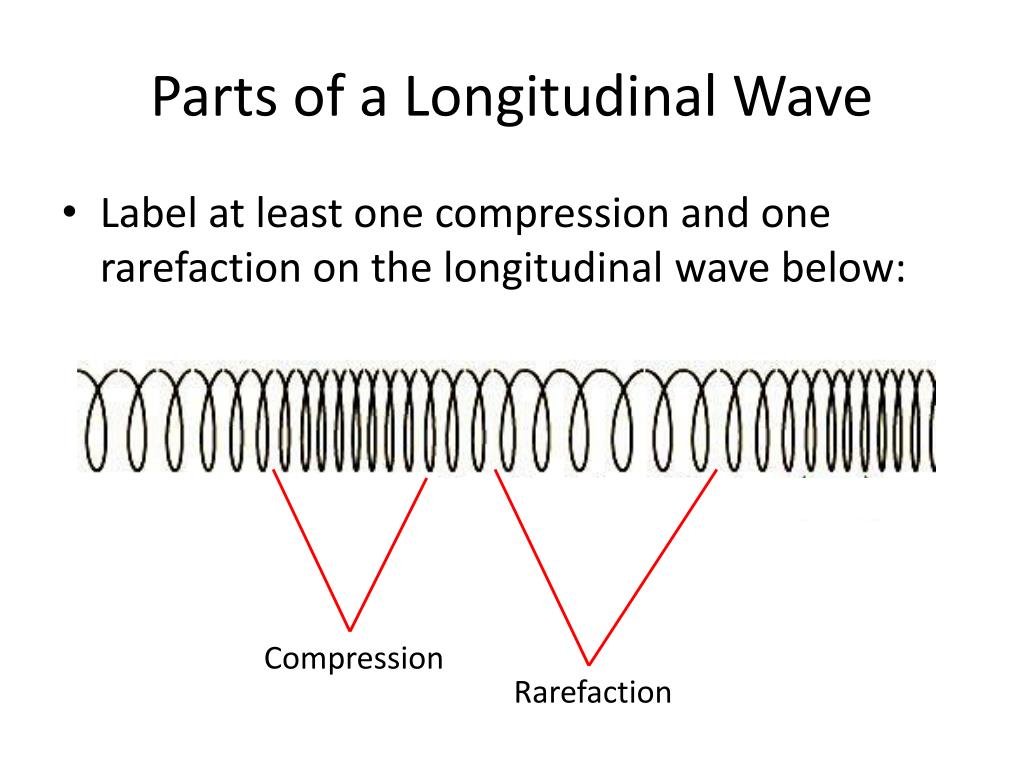
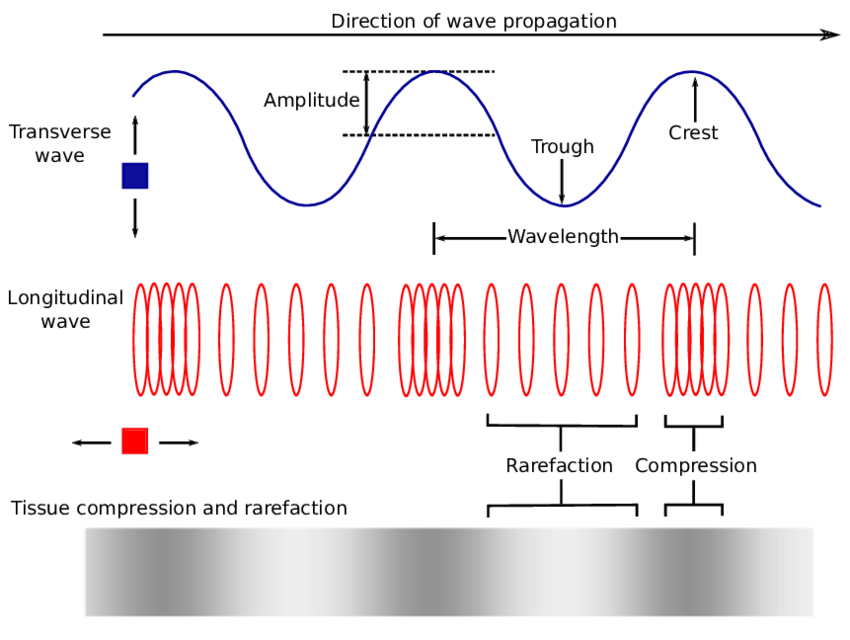
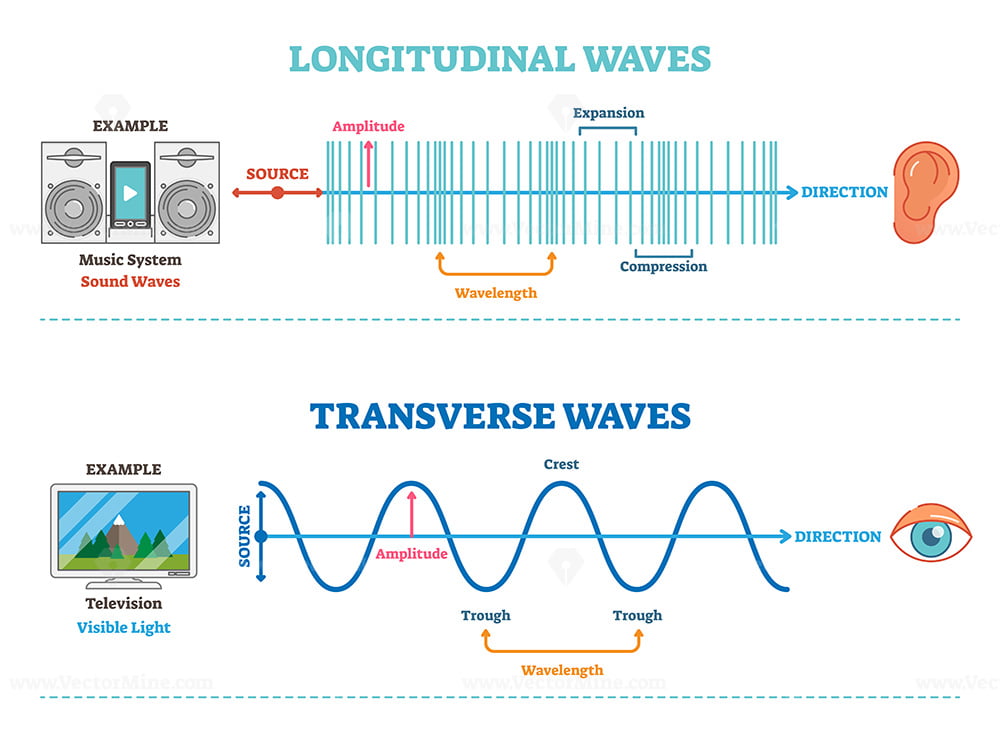
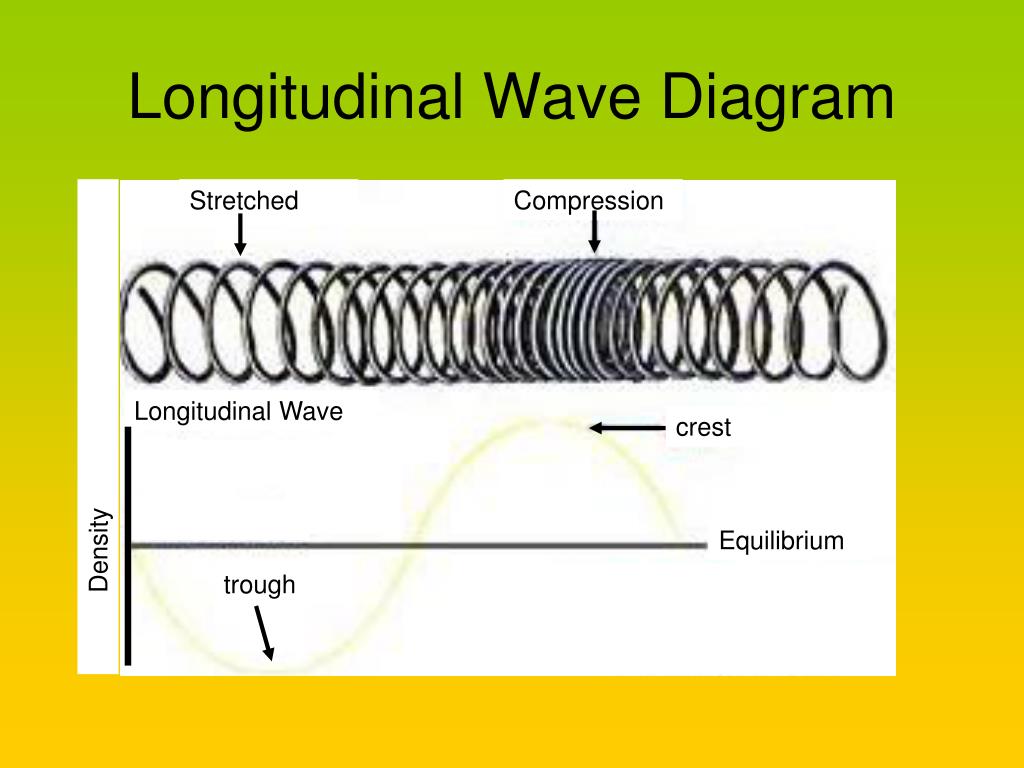
Longitudinal Wave Drawing - Web what is longitudinal wave? Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. In transverse waves, the displacement of the particle is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave. In this section we will familiarize ourselves with waves by focusing on material waves. Web longitudinal wave model | desmos. You could therefore draw the wave by. Frequency measured like normal, but wavelength. Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. The graphics show a collection of random points under each type of wave motion. Web 10k views 3 years ago physics of light & waves. Did this video help you? Waves are repeated vibrations that transfer energy. By plotting the displacements of individual particles through which a wave is passing, students can develop their ideas of the underlying process of a wave. In this wave, each particle of matter vibrates in its normal position. Small waves may cause lag f: Web 10k views 3 years ago physics of light & waves. Animated longitudinal travelling and standing waves. By plotting the displacements of individual particles through which a wave is passing, students can develop their ideas of the underlying process of a wave. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in. In this wave, each particle of matter vibrates in its normal position along the axis of propagation, causing alternative regions of compression and rarefaction in the medium. A smooth curve drawn through the ends of the vertical lines gives a transverse curve. Waves are repeated vibrations that transfer energy. Web the simple wave simulator interactive provides the learner with a. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Energy is transferred by parts of the wave knocking nearby parts. Click here to donate to ophysics.com to help keep the site going. Longitudinal waves (like sound) move in the direction of propagation while transverse waves (like light) move perpendicular to this direction. These represent the peaks and troughs. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. There are primarily two types of mechanical waves,. The red points move around their equilibrium positions.;; This is similar to the effect of people knocking into one another in a crowd, or a mexican wave at football matches. Web lines are drawn upward from the axis when displacement is to the left and downward when to the right. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. These represent the peaks and troughs. Animated longitudinal travelling and standing waves. Web longitudinal waves are waves in which the vibration of the medium is parallel to the direction the wave travels and displacement of the medium is in the same (or opposite) direction of the wave propagation.. Web there are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves: Drawing the lines further apart represents the rarefactions. Web what is longitudinal wave? Energy is transferred by parts of the wave knocking nearby parts. These represent the peaks and troughs. These represent the peaks and troughs. Web we begin our study of waves in this first unit of physics 7c with an introduction to waves and then a thorough development of the harmonic plane wave model, which we will use extensively to model and understand a wide variety of wave phenomena. What changes is the density along the line. Web. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Web 10k views 3 years ago physics of light & waves. The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. Web the curves are drawn so that they are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer. Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different. This is a limit from how desmos works. Longitudinal waves and transverse waves. Longitudinal waves are defined as: Longitudinal waves are usually drawn as several lines to show that the wave is moving parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Click here to donate to ophysics.com to help keep the site going. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport. Web we begin our study of waves in this first unit of physics 7c with an introduction to waves and then a thorough development of the harmonic plane wave model, which we will use extensively to model and understand a wide variety of wave phenomena. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. The animations below demonstrate both types of wave and illustrate the difference between the motion of the wave and the motion of the particles in the medium through which the wave is travelling. There is no transverse motion, so the system simply lies along a straight line. Wave height self explanatory, cannot go above 1. The distance between the centres of two consecutive regions of compression or the rarefaction is defined by wavelength, λ. These represent the peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred by parts of the wave knocking nearby parts. The graphics show a collection of random points under each type of wave motion.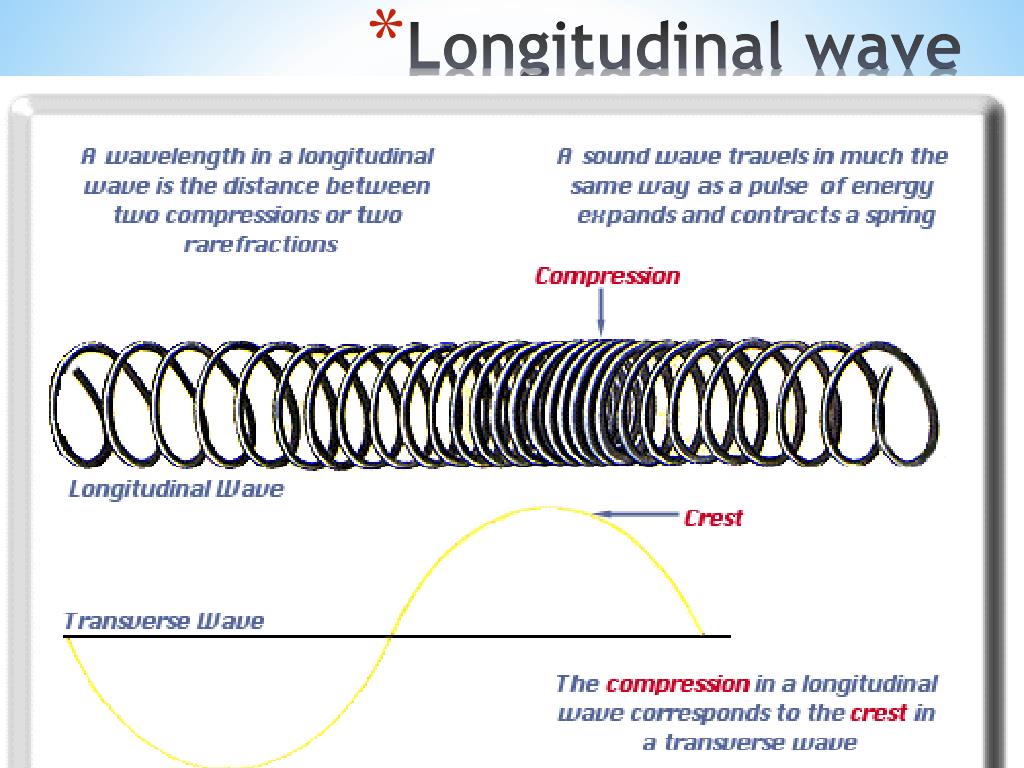
Diagram Templates
PPT Chapter 17 Mechanical Waves & Sound PowerPoint Presentation ID
Wave, its types and characteristics Online Science Notes
Types of longitudinal, transverse and surface waves examples outline

Longitudinal and Transverse wave type, vector illustration scientific

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and

Longitudinal Wave Diagram Physics Stock Vector (Royalty Free

Lesson Video Transverse and Longitudinal Waves Nagwa
PPT Properties of Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

Examples Of Longitudinal Waves page2 / Generally, waves moving
The Wave Can Be Visualized As Compressions And Expansions Travelling Along The Medium.
Amount Of Displayed Particles Particles Will Scale In Size At 20/P^ (5/16) Particle Count Cannot Exceed 10000.
Use The Buttons To Select A Travelling Wave Or A Standing Wave.
Transverse Waves Are Represented As A Continuous Solid Line.
Related Post: