Hypertonic Drawing
Hypertonic Drawing - Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. Therefore, a hypertonic solution has more solutes than the intracellular environment, so water will leave the cell to try to achieve equilibrium. This biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic. Hyper is a latin prefix meaning over or above. This video covers a recap of the foundation of passive tran. 929k views 8 years ago membranes and transport | biology | khan academy. In a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cell, which can lead to cell shrinkage or crenation. This means that the concentration of water is relatively higher inside. Hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions (tonicity). Web hypertonic saline solutions (hts) are used to treat a variety of neurologic conditions in the icu. Web simplenursing editorial team jan 8, 2018. This means that the concentration of water is relatively higher inside. A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute than. Hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions (tonicity). In an isotonic environment, there is the same amount of water on each side, so there is no change in the size of the cell. Web in a situation in which solutions of two different osmolarities are separated by a membrane permeable to water, though not to the solute, water will move from the side of the membrane with lower osmolarity (and more water) to the side with higher osmolarity (and less water). A solution outside of a cell is called hypertonic if it has. In an isotonic environment, there is no net water movement, so there is no change in the size of the cell. Hyper is a latin prefix meaning over or above. Clinicians use hypertonic fluids to increase intravascular fluid volume. This means that the concentration of water is relatively higher inside. Web this activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse. This means that the concentration of water is relatively higher inside. Web hypertonic refers to a solution with higher osmotic pressure than another solution. Intravenous (iv) solutions are burdensome and sometimes confusing to remember. Web in the human body, hypertonic solutions can draw excess water out of cells and tissues. This movement can be due to mechanical blockage by larger. Web in this video we discuss the three types of osmotic solutions: The words hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic are most often used when comparing chemical solutions while discussing osmosis. 94k views 4 years ago biology. Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. Web this activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse events, and contraindications of hypertonic fluids. A solution outside of a cell is called hypertonic if it has a greater concentration of solutes than the cytosol inside the cell. This means that the concentration of water is relatively higher inside. However, due to the cell walls of plants, the visible effects differ. Web in biology, the tonicity of a solution usually refers to its solute concentration. 94k views 4 years ago biology. Web simplenursing editorial team jan 8, 2018. 10% dextrose in water (d10w) And it gets even more complicated if iv solutions (hypertonic, hypotonic, & isotonic) show up on your exams. Web this activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse events, and contraindications of hypertonic fluids in the management of hyponatremia and increased intracranial. The word “hyper” refers to something that is “more or above”, so we can infer that hypertonic fluids are those that have a higher concentration of solutes when compared to blood. The words hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic are most often used when comparing chemical solutions while discussing osmosis. Web hypertonic fluids are the opposite of hypotonic, meaning they have a. Web hypertonic fluids are the opposite of hypotonic, meaning they have a higher sodium content, which draws water out of the cells rather than brings it in. Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. Web in the human body, hypertonic solutions can draw excess water out of cells and tissues. Finally, we have hypertonic fluids. In a hypertonic. Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. For example, the renal medulla in the kidneys uses hypertonic interstitial fluid to concentrate urine by pulling water out of the collecting ducts. The word “hyper” refers to something that is “more or above”, so we can infer that hypertonic fluids are those that have a higher concentration of solutes when. Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. 10% dextrose in water (d10w) On the other hand, a doctor might administer a hypotonic iv solution to increase the total volume of fluid in your body. Web in a hypotonic solution, water moves into the cell, potentially causing it to swell and burst. Web as the water moves between the two solutions. Hyper is a latin prefix meaning over or above. If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will leave the cell, and the cell will shrink. Hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions (tonicity). Web hypertonic saline solutions (hts) are used to treat a variety of neurologic conditions in the icu. Web tonicity in living systems. For example, plant cells use a hypertonic solution within their central vacuole to help draw water into the vacuole. The cell has an excessive amount of solute extracellularly and osmosis is causing water to rush out of the cell intracellularly to the extracellular area which will cause the cell to shrink. Osmosis is a fascinating process where water molecules move from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration through a semipermeable membrane. This makes hypertonic iv fluids ideal for replacing electrolytes but not as. Web if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will be attracted to the environment and leave the cell, and the cell will shrink. Web in the human body, hypertonic solutions can draw excess water out of cells and tissues.
Illustration showing the effect of hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic

Definition Of Hypertonic In Biology definitionjulb
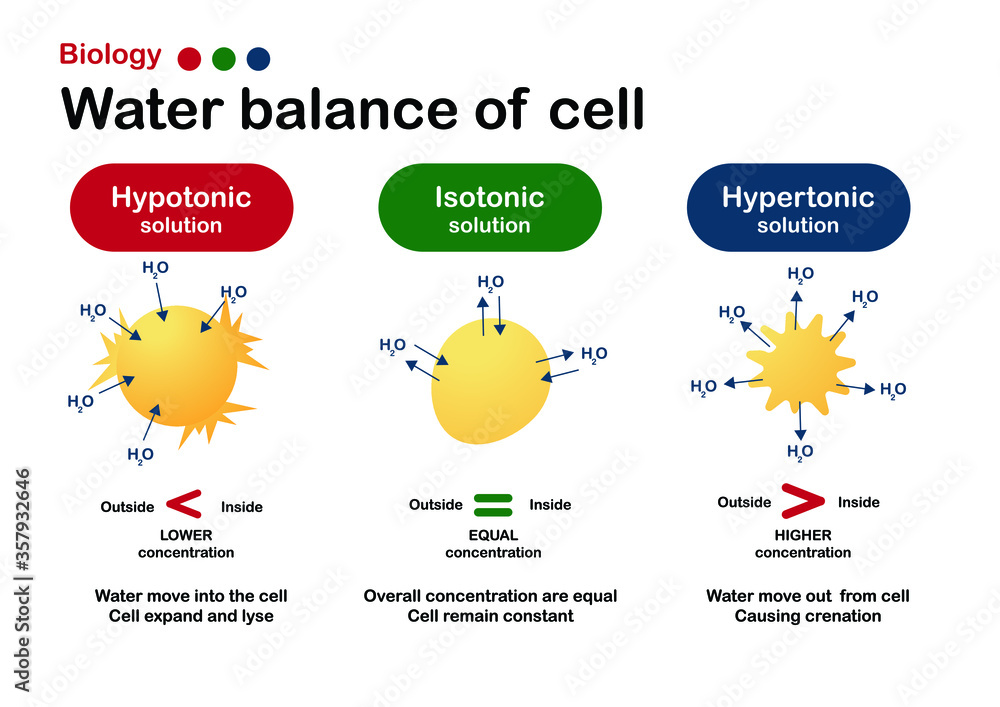
Biology diagram show effect of isotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic
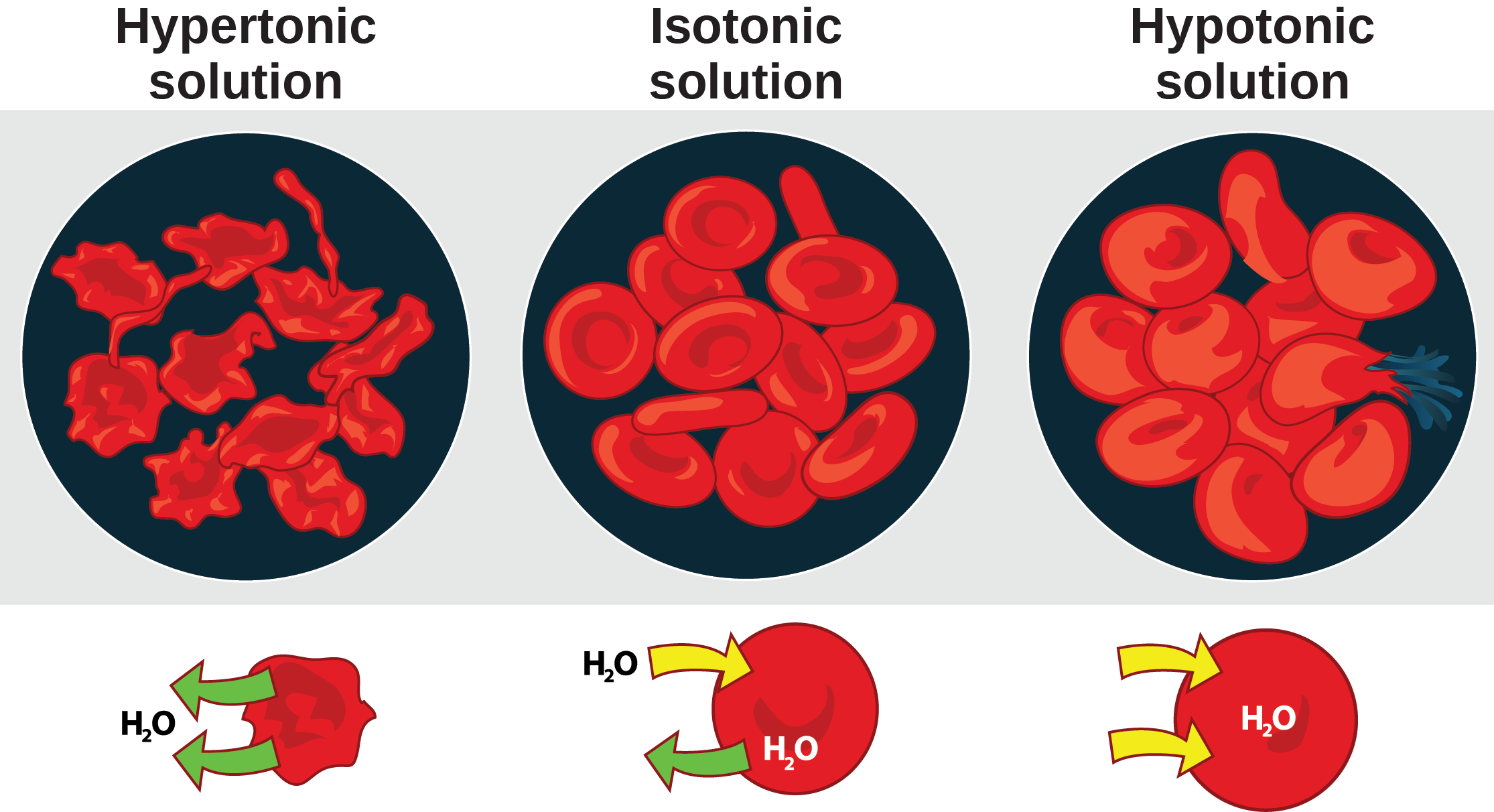
Osmoregulation and Osmotic Balance OpenStax Biology 2e

Hypertonic, Hypotonic and Isotonic Solutions! YouTube

effets de hypertonique, hypotonique et istonique solutions à rouge du

What Is Hypertonic Solution slide share

Types of solutionshypertonic hypotonic and isotonic explained YouTube

Plant Cell in Hypertonic Solution
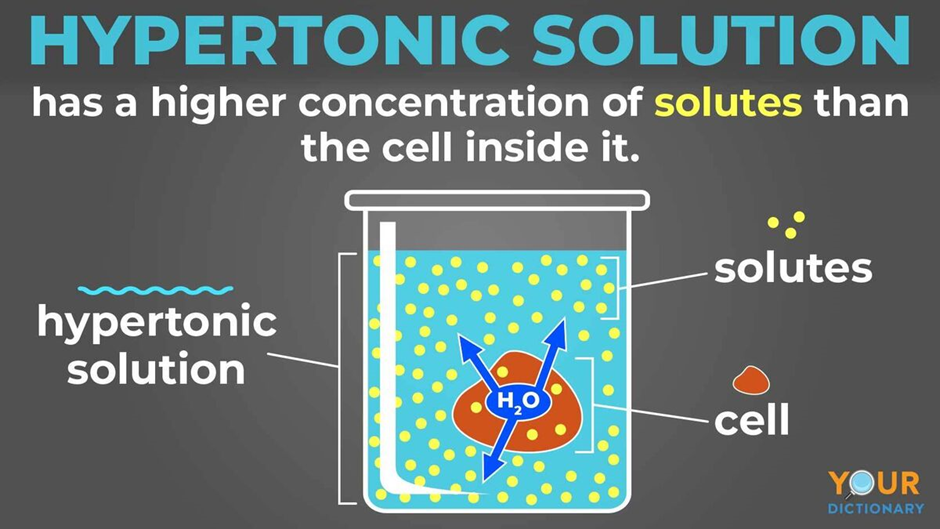
Hypertonic solution Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Web Hypertonic Refers To A Solution With Higher Osmotic Pressure Than Another Solution.
In An Isotonic Environment, There Is No Net Water Movement, So There Is No Change In The Size Of The Cell.
The Word “Hyper” Refers To Something That Is “More Or Above”, So We Can Infer That Hypertonic Fluids Are Those That Have A Higher Concentration Of Solutes When Compared To Blood.
In A Hypertonic Solution, Water Moves Out Of The Cell, Which Can Lead To Cell Shrinkage Or Crenation.
Related Post: