Hyaline Cartilage Drawing
Hyaline Cartilage Drawing - Where is hyaline cartilage found? Web in part i , there are four slides to examine, showing hyaline cartilage (webslide 26), elastic cartilage (webslide 12 and umich 44h), and fibrocartilage (webslides 45 and 74). We will examine those tissues in greater detail in lab 5 the appendicular skeleton & lab 6 the axial skeleton. Web hyaline cartilage, the most common type of cartilage, is composed of type ii collagen and chondromucoprotein and often has a glassy appearance. Supporting connective tissue comprises bone and cartilage. Web the illustrative book of cartilage repair. Use the image slider below to learn how to use a microscope to identify and study hyaline cartilage on a microscope slide of the trachea. Web micrograph showing fibrocartilage (centre) surrounded by areas of hyaline cartilage (upper left and right) that are being converted to bone. [digitalscope] note the general organization of hyaline cartilage. Web hyaline cartilage is the most common of the three types of cartilage. Step by step drawing of histology of hyaline cartilage Star star star star star. These cells have relatively small nuclei and often demonstrate lipid. This article will focus on important features of hyaline cartilage, namely its matrix, chondrocytes, and perichondrium. Use the image slider below to learn more about the characteristics of hyaline cartilage. We will examine those tissues in greater detail in lab 5 the appendicular skeleton & lab 6 the axial skeleton. This post will describe the basic histology of hyaline cartilage with slide images and labeled diagram. Web the hyaline cartilage in the trachea is in the middle of the tracheal wall. Web hyaline cartilage tissue (also referred to as hyaline. [digitalscope] note the general organization of hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most prevalent type, forming articular cartilages and the framework for parts of the nose, larynx, and trachea. Web lab 3 exercise 3.3.1 3.3. When a chondroblast has surrounded itself with cartilage, it is then called a chondrocyte. Supporting connective tissue comprises bone and cartilage. It is the most common type of cartilage characterized by a glossy and smooth appearance. This article will focus on important features of hyaline cartilage, namely its matrix, chondrocytes, and perichondrium. Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and appendicular skeleton. (more) three main. This post will describe the basic histology of hyaline cartilage with slide images and labeled diagram. Step by step drawing of histology of hyaline cartilage Multipotential cells in the fibrous layer of the perichondrium differentiate into chondroblasts in the chondrogenic layer. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread and is the type that makes up the embryonic skeleton. Web lab 3. Web articular cartilage is a remnant of the hyaline cartilage that formed the template for the developing bone. This image shows a cross section of a cartilage ring that supports the trachea and maintains the. Tamás oláh, tunku kamarul, henning madry & malliga raman murali. Articular cartilage contains no blood vessels or nerves. New articular cartilage is limited to interstitial. Cells that form and maintain the cartilage. Web hyaline cartilage is the most common of the three types of cartilage. New articular cartilage is limited to interstitial growth because of the absence of a perichondrium. Web micrograph showing fibrocartilage (centre) surrounded by areas of hyaline cartilage (upper left and right) that are being converted to bone. Web during embryonic development,. Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in areas such as the nose, ears, and trachea of the human body. Web hyaline cartilage is the most common of the three types of cartilage. Cartilage is flexible connective tissue found throughout the whole body. This image shows a cross section of a cartilage ring that supports the trachea and. The bar shows the position of the hyaline cartilage. A joint of the jaw that connects it to the temporal bones of the skull. Supporting connective tissue comprises bone and cartilage. [digitalscope] note the general organization of hyaline cartilage. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Use the hotspot image below to learn more about the characteristics of hyaline cartilage. Where is hyaline cartilage found? We will examine those tissues in greater detail in lab 5 the appendicular skeleton & lab 6 the axial skeleton. A joint of the jaw that connects it to the temporal bones of the skull. Step by step drawing of histology. A type of cartilage found on many joint surfaces; Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and appendicular skeleton. A joint of the jaw that connects it to the temporal bones of the skull. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread and is the type that makes up the embryonic skeleton. Web articular cartilage is a remnant of the hyaline cartilage that formed the template for the developing bone. New articular cartilage is limited to interstitial growth because of the absence of a perichondrium. It is the most common type of cartilage characterized by a glossy and smooth appearance. It contains no nerves or blood vessels, and its structure is relatively simple. Web hyaline cartilage tissue (also referred to as hyaline connective tissue or hyaline tissue) is a type of a cartilage tissue. Web the hyaline cartilage in the trachea is in the middle of the tracheal wall. Web the illustrative book of cartilage repair. When a chondroblast has surrounded itself with cartilage, it is then called a chondrocyte. Use the image slider below to learn more about the characteristics of hyaline cartilage. This image shows a cross section of a cartilage ring that supports the trachea and maintains the. These cells have relatively small nuclei and often demonstrate lipid. Cells that form and maintain the cartilage.
Illustrations Hyaline Cartilage General Histology
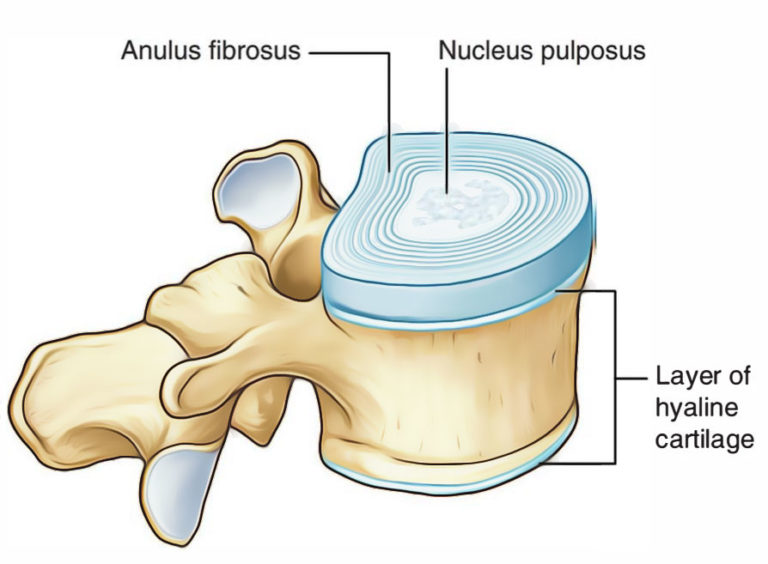
Hyaline Cartilage Earth's Lab

Hyaline Cartilage Labeled Diagram

Hyaline Cartilage Drawing YouTube
Hyaline cartilage hires stock photography and images Alamy

Histology Image Cartilage
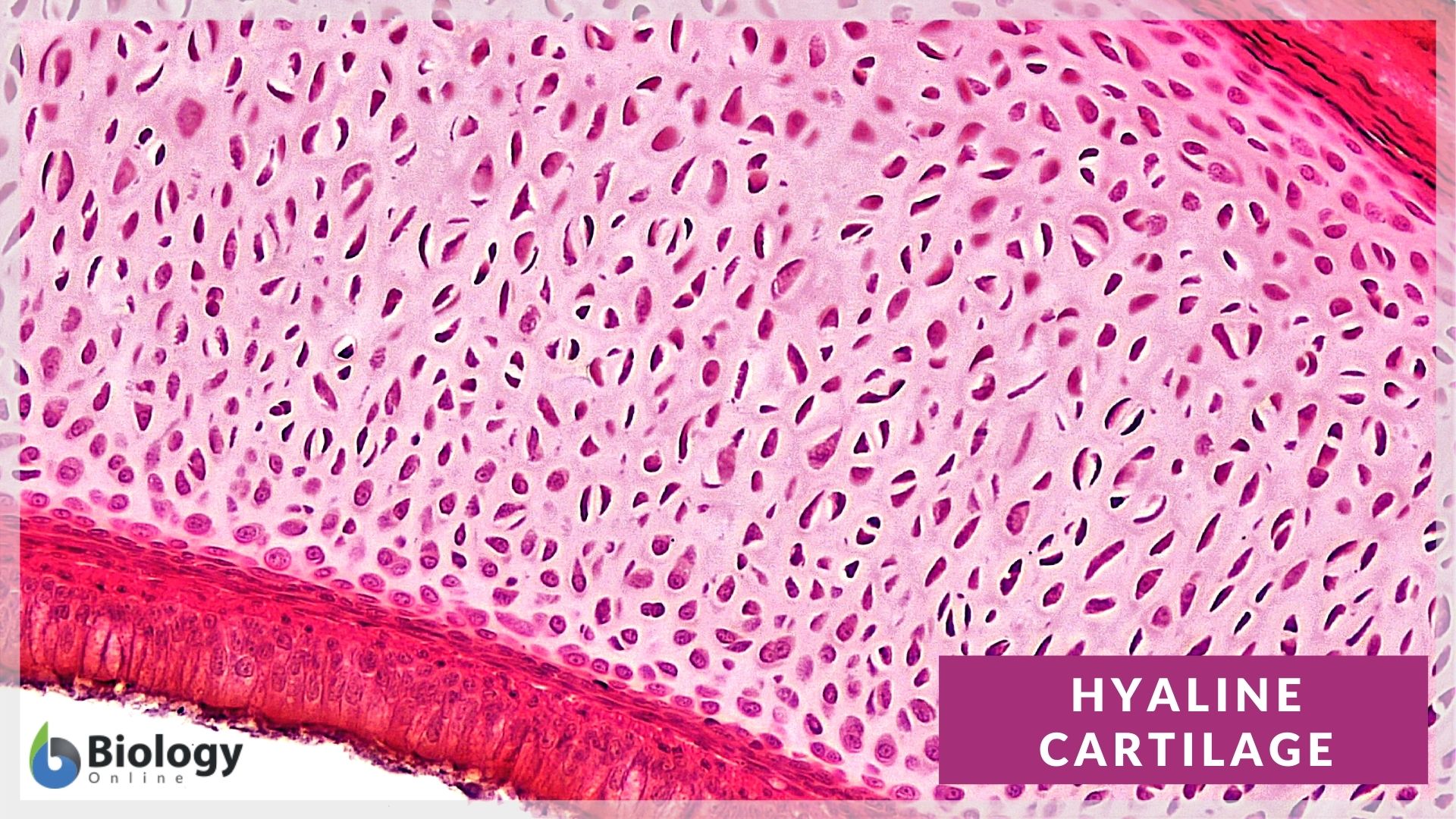
Hyaline cartilage Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

How to Draw Hyaline Cartilage Simple and easy steps Biology Exam

Schematic drawing of articular (hyaline) cartilage containing abundant
Hyaline Cartilage Cells ClipArt ETC
Multipotential Cells In The Fibrous Layer Of The Perichondrium Differentiate Into Chondroblasts In The Chondrogenic Layer.
Hyaline Cartilage Is A Type Of Connective Tissue Found In Areas Such As The Nose, Ears, And Trachea Of The Human Body.
Use The Image Slider Below To Learn How To Use A Microscope To Identify And Study Hyaline Cartilage On A Microscope Slide Of The Trachea.
This Post Will Describe The Basic Histology Of Hyaline Cartilage With Slide Images And Labeled Diagram.
Related Post: