How To Draw Indifference Curves From Utility Function
How To Draw Indifference Curves From Utility Function - Web if you are given a utility function u(x,y), it is easy to derive a given indifference curve from it: Explain how to derive an indifference curve from a utility function. Web u ( x 1, x 2) = x 1 α x 2 1 − α where 0 < α < 1. 1) plot an indiffrencre curve, 2) draw an. Identify utility functions based on the typical preferences they represent. 5.9k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory 2: 2.4k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory 2: To visualize this function, we’ll need a 3d plot. Web given an indifference curve, how do you go about finding a utility function? Web and then, adding the budget constraint will let you visualize the utility maximization problem. Web the marginal rate of substitution is the amount of of a good that has to be given up to obtain an additional unit of another good while keeping the satisfaction the same. Indifference curves and marginal rate of substitution. The mrs is basically a way of mathematically representing the. Explain how to derive an indifference curve from a utility. The principle of diminishing marginal utility implies that ∂u/∂x , the marginal utility of x, falls as the quantity of x consumed increases and that ∂u/∂y , the marginal utility of y, rises as the quantity of y consumed decreases. Utility maximization with indifference curves. Suppose u(x, y) = x1/2 ⋅y1/2 u ( x, y) = x 1 / 2. Economics > microeconomics > consumer theory > For example, given z = k1 δ xα δy β δ z = k 1 δ x α δ y β δ (defined by u(⋅) = k u ( ⋅) = k ), find a utility function. This is a good idea. Would i calculate the utility for (a,b) , then set u(x,y). In this episode we draw indifference curves of utility functions with the form u=min {ax+by,cx+dy}. The principle of diminishing marginal utility implies that ∂u/∂x , the marginal utility of x, falls as the quantity of x consumed increases and that ∂u/∂y , the marginal utility of y, rises as the quantity of y consumed decreases. ) = m u 2. Explain how one indifference curve differs from another. 106k views 9 years ago consumer theory i: The principle of diminishing marginal utility implies that ∂u/∂x , the marginal utility of x, falls as the quantity of x consumed increases and that ∂u/∂y , the marginal utility of y, rises as the quantity of y consumed decreases. To visualize this function,. For example, given z = k1 δ xα δy β δ z = k 1 δ x α δ y β δ (defined by u(⋅) = k u ( ⋅) = k ), find a utility function. That is, the set of all bundles which “produce” the same “quantity” of utility, just like an isoquant for a production function. Decisions. The utility function and indifference curve have distinct features. Where dy/dx is the slope of the indifference curve. Thus u(36, 100) = 6 ⋅ 10 = 60 u ( 36, 100) = 6 ⋅ 10 = 60. Identify utility functions based on the typical preferences they represent. For example, given z = k1 δ xα δy β δ z =. Suppose u(x, y) = x1/2 ⋅y1/2 u ( x, y) = x 1 / 2 ⋅ y 1 / 2 and (a, b) = (36, 100) ( a, b) = ( 36, 100). Web utility function meaning refers to a mathematical function in economics that ranks baskets of consumption goods based on consumers’ preferences by allotting a number to every. Web and then, adding the budget constraint will let you visualize the utility maximization problem. In this episode we draw indifference curves of utility functions with the form u=min {ax+by,cx+dy}. Simply plot all points (x,y) such that u(x,y) equals a constant. Dy/dx = − ∂u/∂x / ∂u/∂y. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Web if you are given a utility function u(x,y), it is easy to derive a given indifference curve from it: That is, the set of all bundles which “produce” the same “quantity” of utility, just like an isoquant for a production function. Web learn to graph indifference curves from a quasilinear utility function: 5.9k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory. An indifference curve is a contour line where utility remains constant across all points on the line. Optimal point on budget line. 2.4k views 3 years ago microeconomic theory 2: Explain how one indifference curve differs from another. What is an indifference curve? In this episode we draw indifference curves of utility functions with the form u=min {ax+by,cx+dy}. Where dy/dx is the slope of the indifference curve. Identify utility functions based on the typical preferences they represent. The principle of diminishing marginal utility implies that ∂u/∂x , the marginal utility of x, falls as the quantity of x consumed increases and that ∂u/∂y , the marginal utility of y, rises as the quantity of y consumed decreases. Web u ( x 1, x 2) = x 1 α x 2 1 − α where 0 < α < 1. 106k views 9 years ago consumer theory i: To visualize this function, we’ll need a 3d plot. In this video, you will learn how to: Web learn to graph indifference curves from a quasilinear utility function: Web you can calculate the slope of the indifference curve at a given point by dividing the marginal utility of x by the marginal utility of y (=taking the derivative of the utility function by x and by y, and divide them). Economics > microeconomics > consumer theory >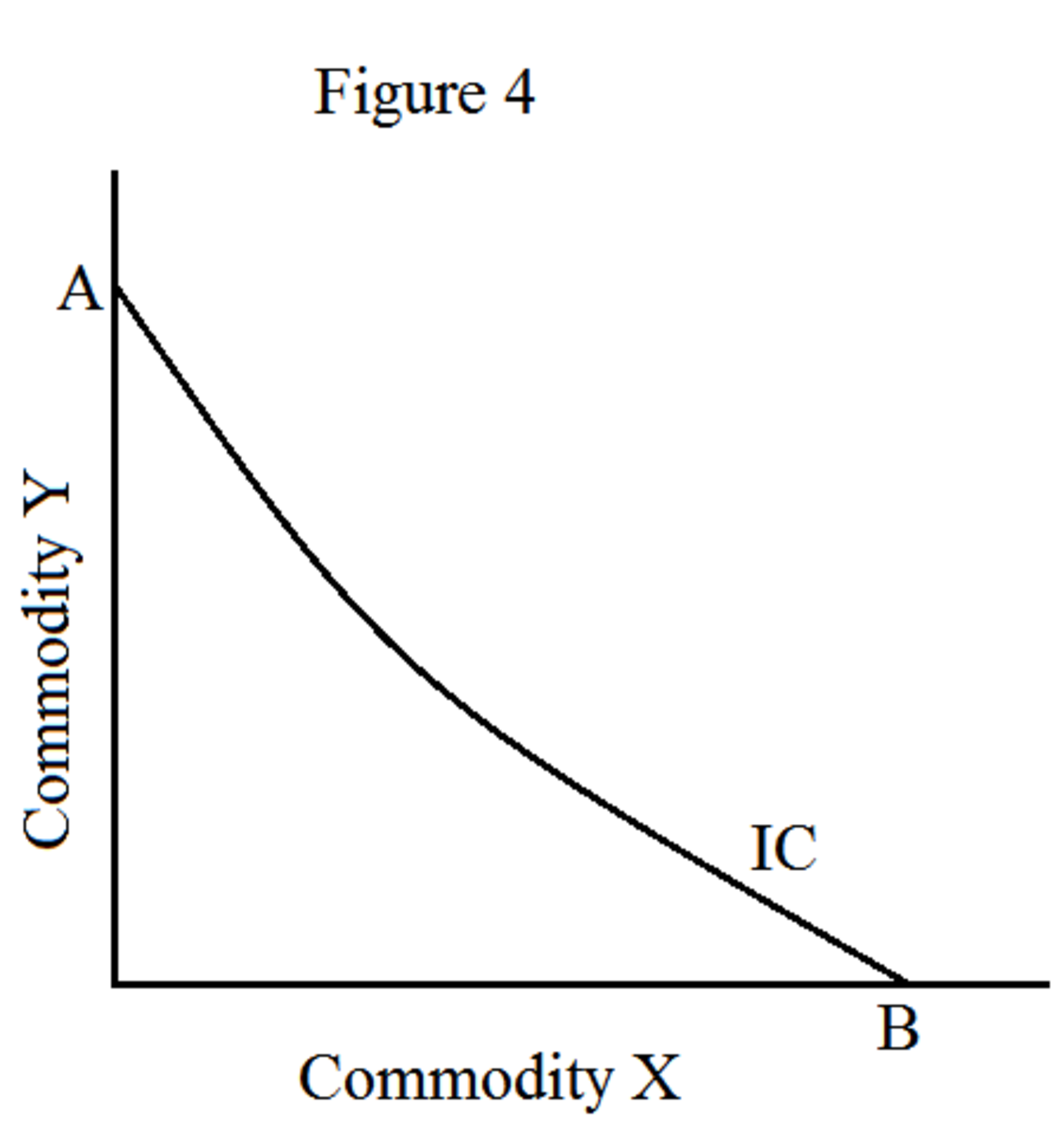
🏷️ An indifference curve is always. Features Of Indifference Curve

Optimal Bundle (Utility Maximization) Wize University Microeconomics
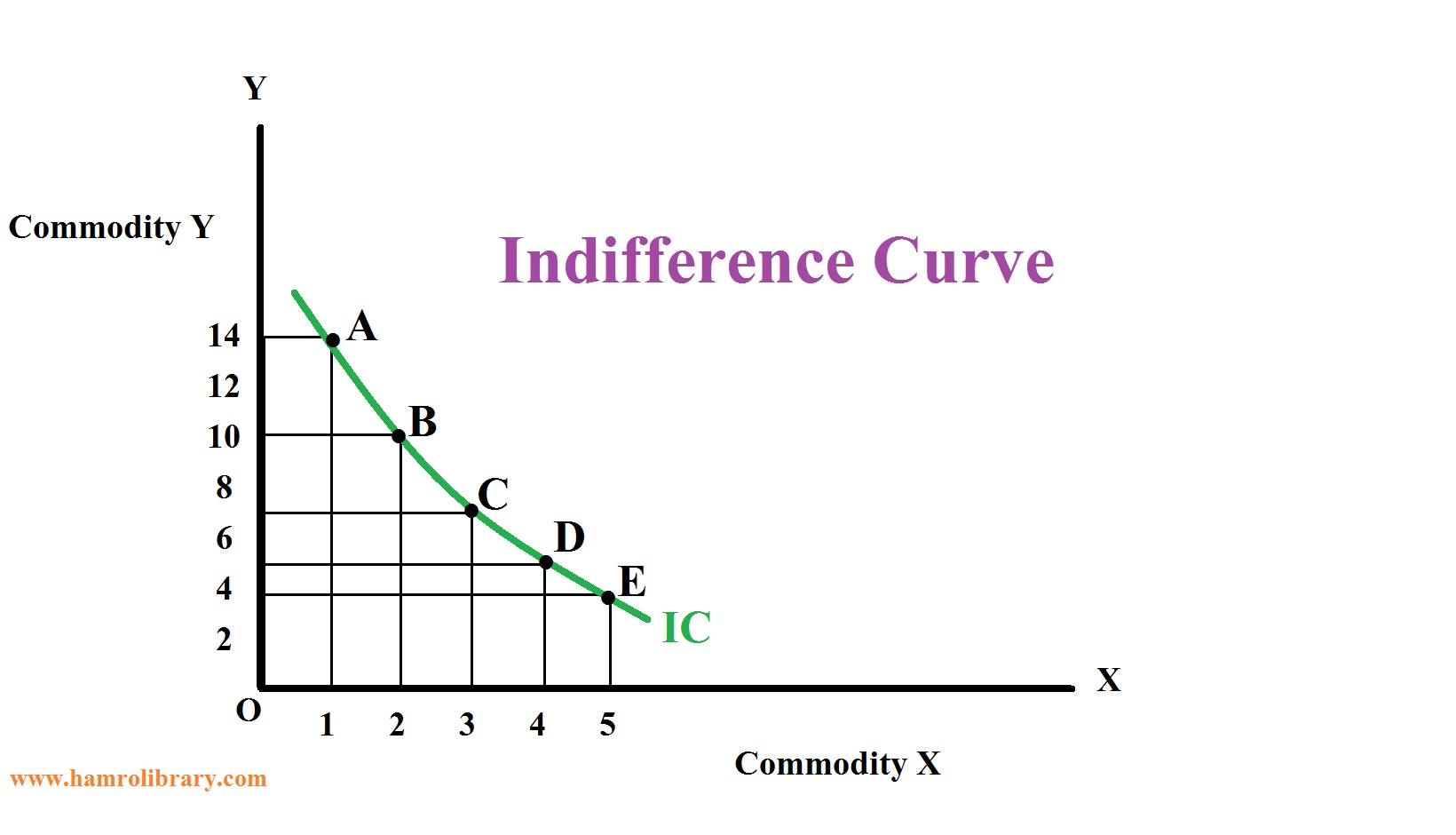
How To Plot Indifference Curve

1 A representative indifference curve for a utility function Source
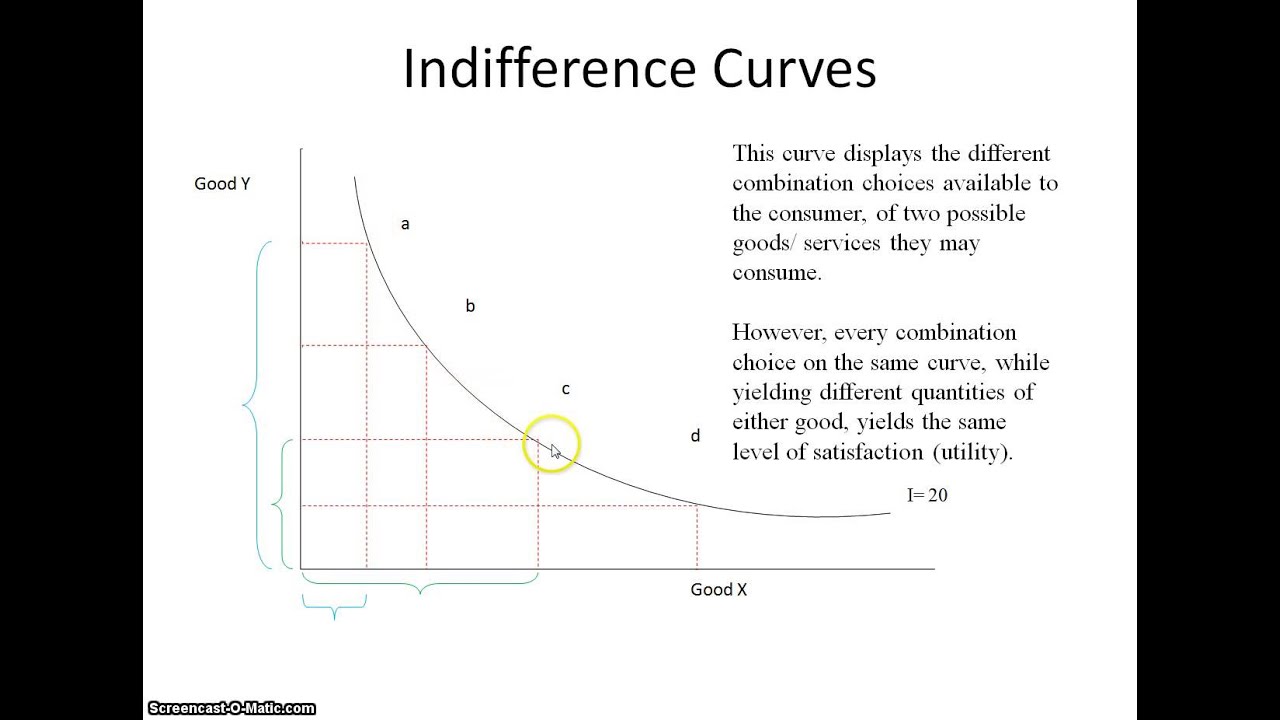
Ordinal Utility Theory Indifference Curves YouTube
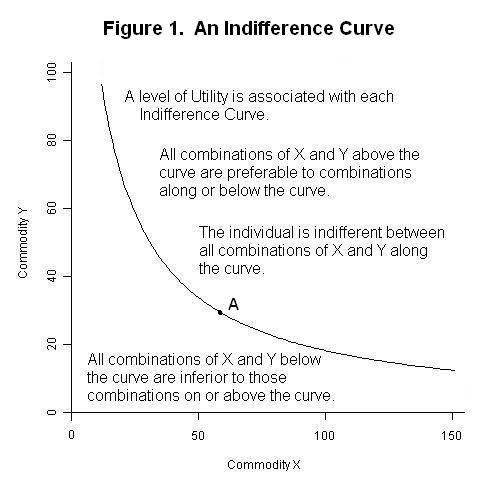
Indifference Curves

1 A representative indifference curve for a utility function Source

Quasilinear Utility Function Graphing Indifference Curves YouTube
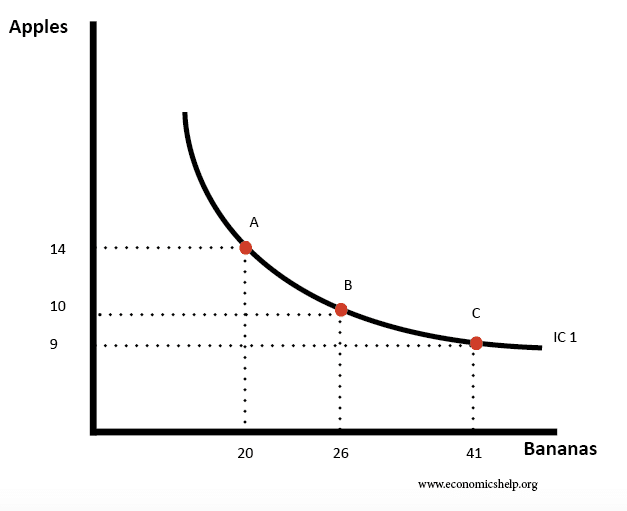
INDIFFERENCE CURVES AND BUDGET LINES
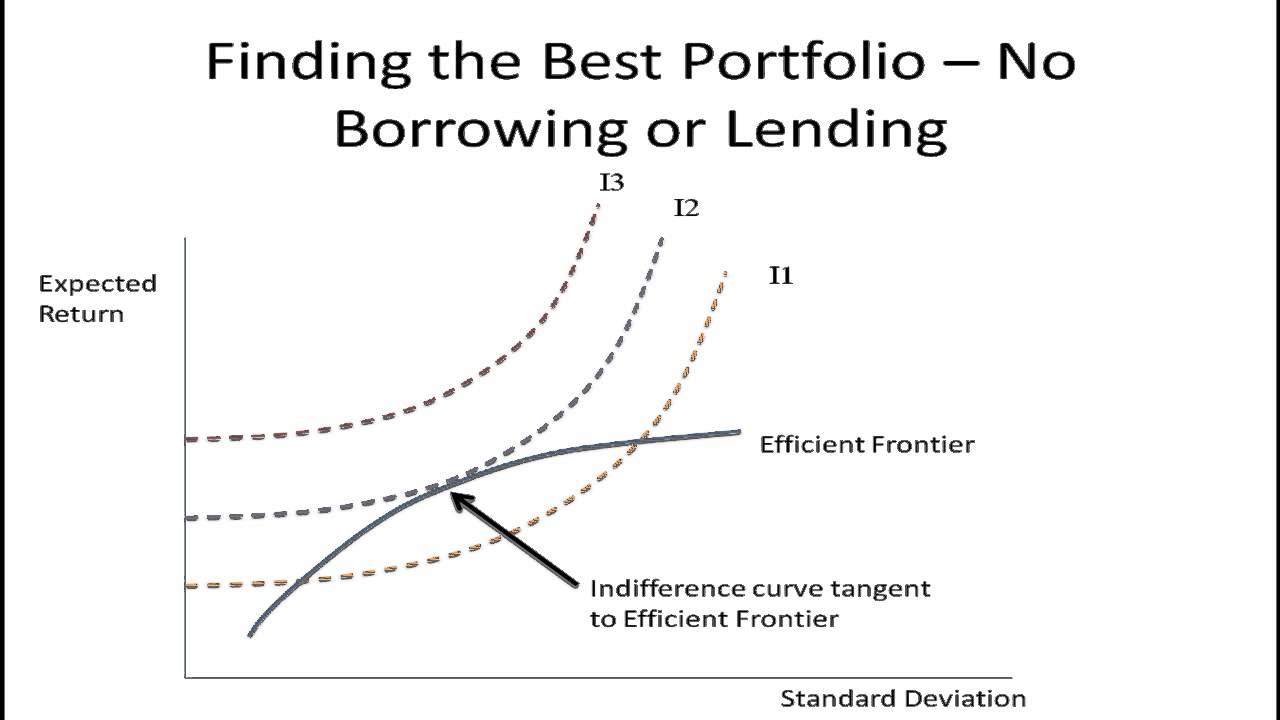
Utility and Risk Preferences Part 2 Indifference Curves YouTube
The Utility Function And Indifference Curve Have Distinct Features.
That Is, The Set Of All Bundles Which “Produce” The Same “Quantity” Of Utility, Just Like An Isoquant For A Production Function.
Suppose U(X, Y) = X1/2 ⋅Y1/2 U ( X, Y) = X 1 / 2 ⋅ Y 1 / 2 And (A, B) = (36, 100) ( A, B) = ( 36, 100).
Web The Marginal Rate Of Substitution Is The Amount Of Of A Good That Has To Be Given Up To Obtain An Additional Unit Of Another Good While Keeping The Satisfaction The Same.
Related Post: