How To Draw A Longitudinal Wave
How To Draw A Longitudinal Wave - Parts of a longitudinal wave. List the different types of waves. 36k views 2 years ago. Exactly 6 crests are observed to move past a given point in 9.1 s. We learn how to graph longitudinal waves with a displacement vs time graph as well as a pressure vs time graph. Properties of transverse & longitudinal waves. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Learn how to quickly label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting. An example of longitudinal waves is compressions moving along a slinky. A material wave is longitudinal if the medium displacement from equilibrium is in the same direction that the wave is traveling. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Tutorial video on longitudinal waves, examples of these waves and how to label distinguishing features on three different types of wave. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction. Edited jan 17 at 19:55. The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. Parts of a longitudinal wave. X is the distance the point travelled from the wave’s source. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. Adjacent crests are 2.4 m apart. The direction of oscillations with regards to the direction of wave travel determine what type of wave it is. Web longitudinal waves are waves where the motion of the material in the wave is back and forth in the same direction that the wave moves. Determine the wavelength, frequency, and speed of this wave.. What changes is the density along the line. 36k views 2 years ago. Many people simply lump all of these together, and use the terms ‘sound waves’ and ‘longitudinal waves’ as synonyms. The animation below (from ) visualizes this for a longitudinal and for a transverse wave. List the different types of waves. Keep your eye on the moving spots marked in red. Web a longitudinal wave is observed to be moving along a slinky. This time the displacement of a single point in the medium is parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave, the defining characteristic of a longitudinally polarized wave. Other examples include (some forms of) seismic waves. Adjacent crests are 2.4 m apart. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. We learn how to graph longitudinal waves with a displacement vs time graph as well as a pressure vs time graph. Web however, for a longitudinal wave, ˆ is the longitudinal displacement, so although fig. List the different types of waves. 36k views 2 years ago. Determine the wavelength, frequency, and speed of this wave. Web in a longitudinal wave the particles are displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels. Adjacent crests are 2.4 m apart. Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. Parts of a longitudinal wave. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Web a longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction parallel to the direction of energy transport. Web light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. List the different types. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Keep your eye on the moving spots marked in red. Explain the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves, and give examples of each type. Parts of a longitudinal wave. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. Web at the end of this lesson, you will be able to:define a longitudinal wave.draw a diagram to represent a longitudinal wave in a spring, showing the direction. Web a longitudinal wave is observed to be moving along a slinky. Web in a longitudinal wave, the medium moves back and forth in the direction of the wave, which is represented. The advantages of both are discussed. Describe the basic characteristics of wave motion. Other examples include (some forms of) seismic waves and ultrasound. The distance between adjacent compressions is the wavelength. T is the time elapsed. 36k views 2 years ago. 1 is a perfectly valid plot of ˆ, it does not indicate what the wave actually looks like. Explain the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves, and give examples of each type. In most examples of longitudinal waves that we explore, this displacement occurs as periodic compressions (region of more dense medium) and rarefactions (regions of less dense. The wave can be visualized as compressions and expansions travelling along the medium. Define the terms wavelength, amplitude, period, frequency, and wave speed. Properties of transverse & longitudinal waves. Web longitudinal waves form when the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction of the traveling wave. This time the displacement of a single point in the medium is parallel to the direction of the motion of the wave, the defining characteristic of a longitudinally polarized wave. For a longitudinal wave the amplitude is again the maximum deviation of a single particle from its equilibrium position. Web at the end of this lesson, you will be able to:define a longitudinal wave.draw a diagram to represent a longitudinal wave in a spring, showing the direction.
How to Draw a Wave HelloArtsy
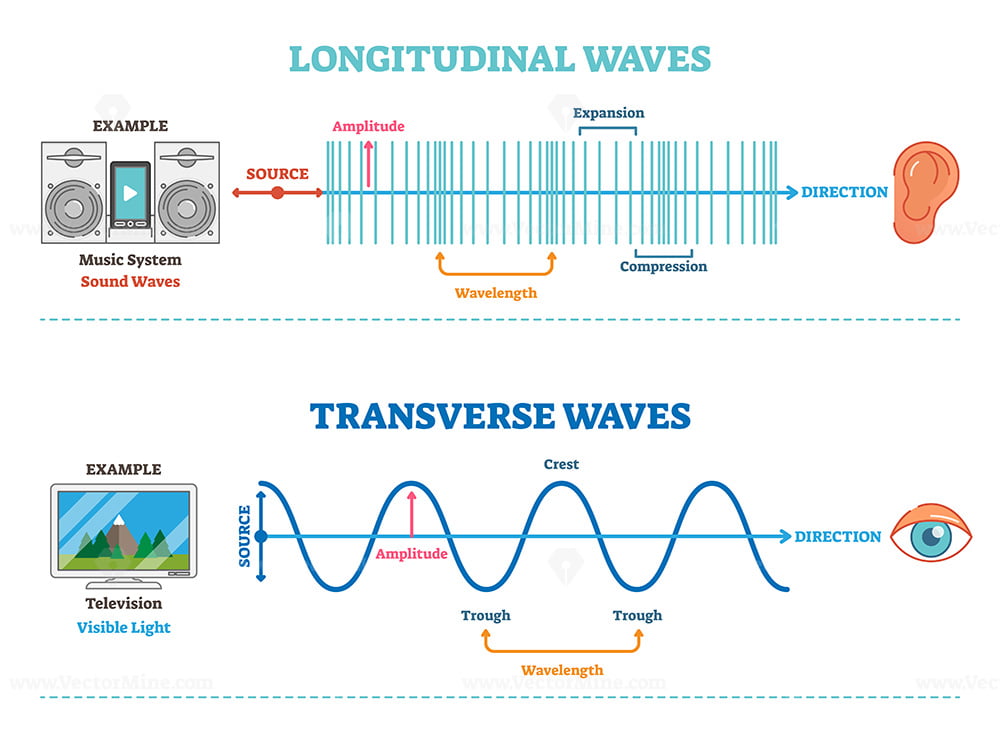
Types of longitudinal, transverse and surface waves examples outline

Drawing & Labeling Transverse and Longitudinal Waves YouTube
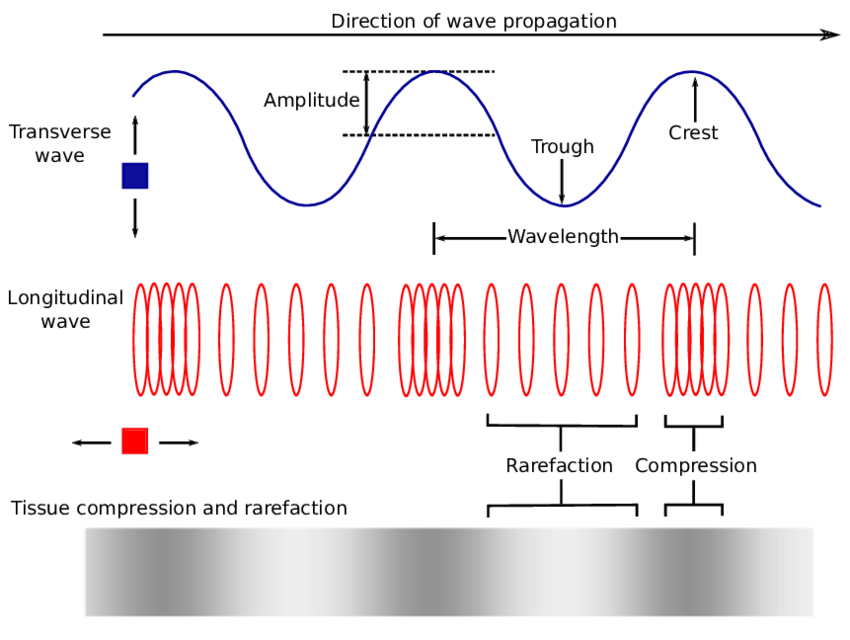
Wave, its types and characteristics Online Science Notes

How to Draw Waves Easy Drawing Tutorial For Kids

The Amplitude of a Wave

Examples Of Longitudinal Waves page2 / Generally, waves moving
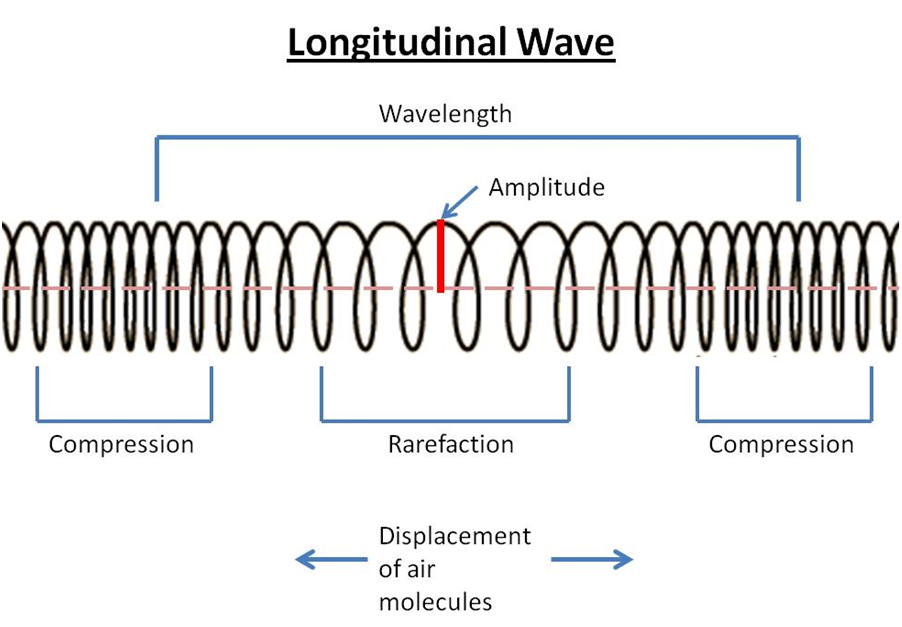
Waves at emaze Presentation
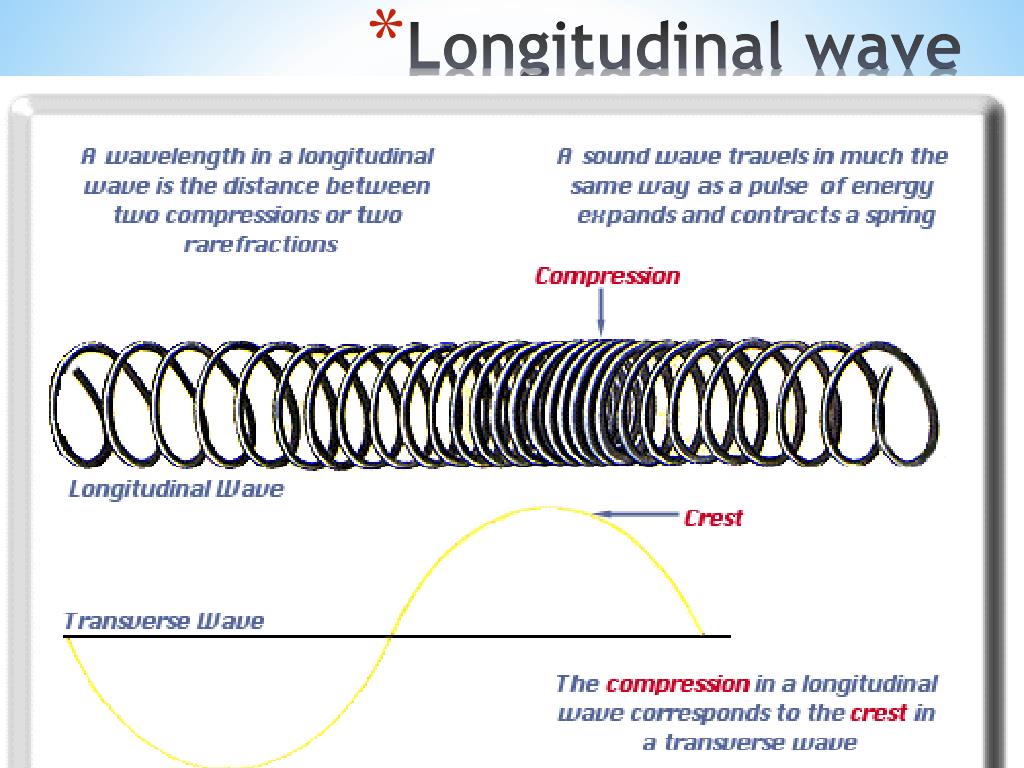
PPT Chapter 11 Waves PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1901329

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and
An Example Of Longitudinal Waves Is Compressions Moving Along A Slinky.
Web Longitudinal Waves Are Waves Where The Motion Of The Material In The Wave Is Back And Forth In The Same Direction That The Wave Moves.
Web In A Longitudinal Wave, The Medium Moves Back And Forth In The Direction Of The Wave, Which Is Represented By An Arrow.
Exactly 6 Crests Are Observed To Move Past A Given Point In 9.1 S.
Related Post: