How To Draw A Cos
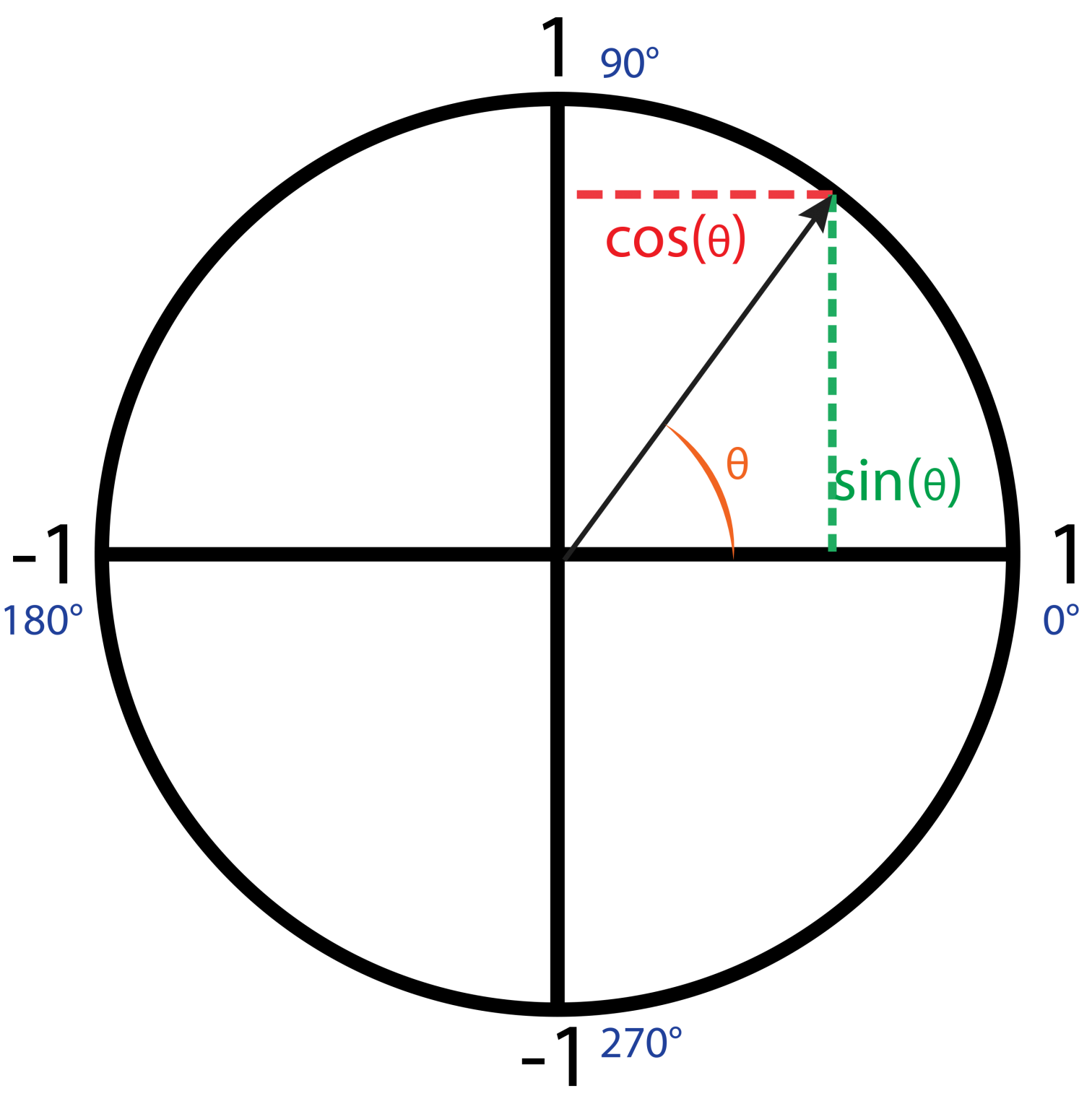
How To Draw A Cos - And just to remind ourselves what the a, b's, and c's are, c is the side that's opposite the angle theta. This is similar to the equation x^2+y^2=1, which is the graph of a circle with a radius of 1 centered around the origin. Web the organic chemistry tutor. Try playing around with the variable z, amplitude, and frequency. Using the table of standard curves, we can plot all of these on the same axes. 2ab cos (c), and put them together: Web graphs of trigonometric functions. A2 + b2 = c2, then a 2 nd abc : Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Web graphs of trigonometric functions. Web learn how to find the sine, cosine, and tangent of angles in right triangles. These graphs are used in many areas of engineering and science. (for all triangles) a2 + b2 − 2ab cos (c) = c2. Web sketching a cosine function. All four angles have a reference angle of π 4 radians or 45 ∘. Using the table of standard curves, we can plot all of these on the same axes. Sketch the graph of y = 2 cos x for 0˚ ≤ x ≤ 360˚. Sines, cosines, and tangents, oh my! So, θ = 90˚ we know that for a. Web sketching a cosine function. Where the cosine curve has a maximum, the secant curve will have an upward u. Web graphs of trigonometric functions. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side.. Where the cosine curve has a maximum, the secant curve will have an upward u. Plot of sine and cosine. Since b = 1 , the graph has a period of 2 π. Period = 2 π | b |. The trigonometric functions sin, cos and tan all have special periodic graphs that you need to be able to sketch. They follow each other, exactly π /2. You can go through a similar procedure to find the values of cosθ and sinθ for θ = π 4, 3π 4, 5π 4, and 7π 4. This is similar to the equation x^2+y^2=1, which is the graph of a circle with a radius of 1 centered around the origin. Determine the midline,. Determine the midline, amplitude, period, and phase shift. Draw a straight line from the axis of the known value to the cosine curve. Web [cos(θ)]^2+[sin(θ)]^2=1 where θ has the same definition of 0 above. Graph the polar curves on the same axes. (for all triangles) a2 + b2 − 2ab cos (c) = c2. Using the table of standard curves, we can plot all of these on the same axes. All four angles have a reference angle of π 4 radians or 45 ∘. Sketch the graph of y = 2 cos x for 0˚ ≤ x ≤ 360˚. Cosine is just like sine, but it starts at 1 and heads down until π. (for all triangles) a2 + b2 − 2ab cos (c) = c2. Graph sine and cosine functions, adjust the amplitude and frequency, and see the effects. Period = 2 π | b |. And just to remind ourselves what the a, b's, and c's are, c is the side that's opposite the angle theta. So, r = 360˚ example: Graph the polar curves on the same axes. Using the table of standard curves, we can plot all of these on the same axes. We know that for a cosine graph, cos θ = 0 for θ = 90˚ and 270˚. The ratios of the sides of a right triangle are called trigonometric ratios. Web sketching a cosine function. Plot of sine and cosine. Determine the midline, amplitude, period, and phase shift. Web the organic chemistry tutor. Using the table of standard curves, we can plot all of these on the same axes. They follow each other, exactly π /2. A2 + b2 = c2, then a 2 nd abc : So, r = 360˚ example: Web [cos(θ)]^2+[sin(θ)]^2=1 where θ has the same definition of 0 above. Cosine is just like sine, but it starts at 1 and heads down until π radians (180°) and then heads up again. This trigonometry video tutorial explains how to graph sine and cosine functions using. Web draw the graph of \(f(x)=a\cos(bx−c)+d\) sketch the vertical asymptotes, which occur where the cosine curve passes through its midline at \(y=d\) fill in the secant curve in between the asymptotes. Use desmos to easily graph inverse trig relations and functions, or to build interactive unit circles and sine wave tracers. Few of the examples are the growth of animals and plants,. Web sin, cos, and tan are trigonometric ratios that relate the angles and sides of right triangles. Where the cosine curve has a maximum, the secant curve will have an upward u. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. This is an illustration on how sine and cosine creates a circle. Graph is set to radians. Set up a table of values for the equation y = 2cos x A2 + b2 − 2ab cos (c) = c2. Three common trigonometric ratios are the sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan).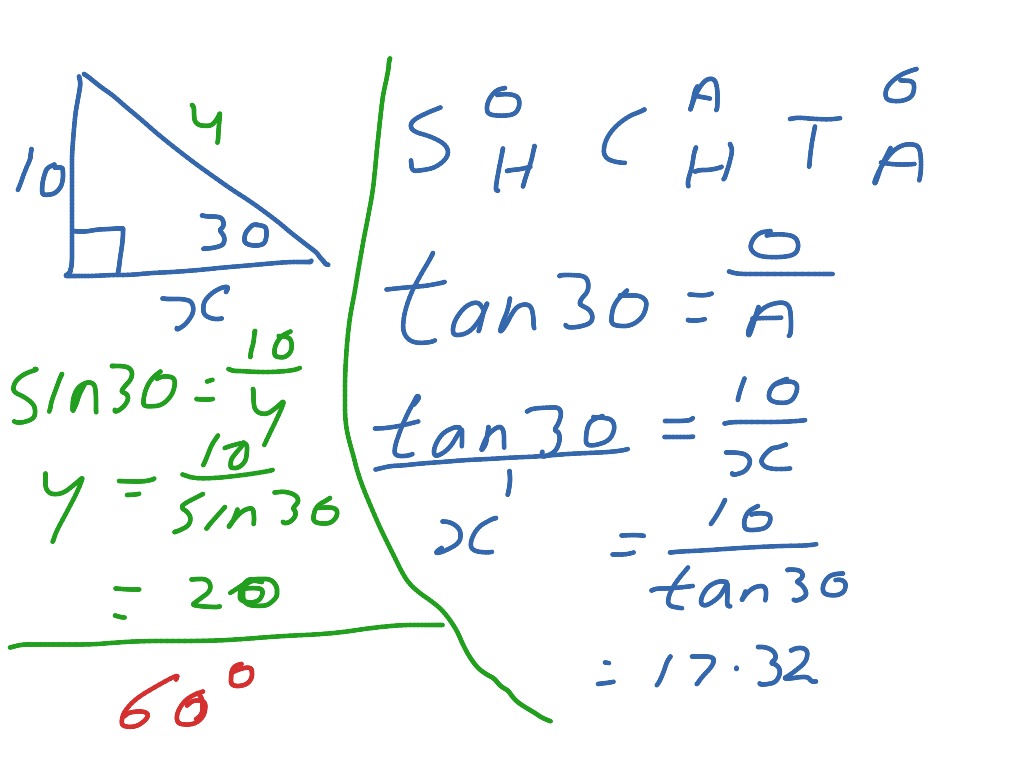
How To Calculate Cos Draw a picture so you can see a familiar shape

Easy Ways to Draw a Good Cross Richards Gicarearse

Grade 10 Trigonometry How to draw a Cos Graph YouTube

Trigonometry Find the exact value of cos ( a b ) YouTube

Graphing Cosine Functions YouTube

Sine, Cosine and Tangent graphs explained + how to sketch Math Hacks

Trigonometric Graph How to draw y = 2 cos (3x)1 YouTube
How to Draw a Cross Step by Step YouTube

How to Draw a Cross, Cross, Step by Step, Stuff, Pop Culture, FREE
p5 Trigonometric functions and oscillation (sin, cos) EMS Interactivity
Sines, Cosines, And Tangents, Oh My!
Web Draw A Circle With Sine And Cosine.
For The Function Y = 2 Cos ( X ) , The Graph Has An Amplitude 2.
The Ratios Of The Sides Of A Right Triangle Are Called Trigonometric Ratios.
Related Post: