Hemolysis From Blood Draw
Hemolysis From Blood Draw - Web hemolysis is the destruction of red blood cells (rbcs). Web haemolysis refers to the breakdown of erythrocytes, commonly referred to as red blood cells, resulting in the release of haemoglobin into the surrounding fluid. The real art of hemolysis is in avoiding it in the first place. Hemolysis rates in blood drawn using iv cannula vary greatly from 1 to 77% with an average of 23% [ 12 ]. A cbc offers valuable information about all of your blood cells, including your red blood cells. Hemolysis often occurs in the preanalytical phase due to factors like improper specimen handling, incorrect needle size, and extended tourniquet time. The availability of an intravenous line already placed pushes many nurses to use this route for blood drawing, even if it is known that this technique is associated with an increased rate of hemolysis compared to blood sampling with a needle. Mild hemolysis can cause gradually progressive fatigue, dizziness, pale skin, and feeling cold. Using venipuncture for blood draws reduces medical errors and improves the patient experience. In this study, the blood draw collection factors with the highest hemolysis rates included blood samples drawn between 12:00 am to 5:59 am; Web a healthcare provider will perform a blood draw to check for problems related to hemolysis. Web rates of hemolysis decrease with the implementation of proper blood draw procedures. Web hemolysis occurs when the red cells are damaged during sample collection. Hemolysis often occurs in the preanalytical phase due to factors like improper specimen handling, incorrect needle size, and extended. In this study, the blood draw collection factors with the highest hemolysis rates included blood samples drawn between 12:00 am to 5:59 am; Web hemolysis, the breakdown of red blood cells, can compromise sample quality, leading to inaccurate test results, potential misdiagnosis, and delayed treatment. Hemolysis rates in blood drawn using iv cannula vary greatly from 1 to 77% with. Web rates of hemolysis decrease with the implementation of proper blood draw procedures. In the emergency department (ed), pseudohyperkalemia from hemolysis may indirectly harm patients by exposing them to increased length of stay, cost, and repeat blood draws. Each of these studies reported “substantial” reductions in hemolysis when drawn from an antecubital site relative to a more distal site. Web. Preanalytical hemolysis of blood samples is a common problem in medical practice, especially in emergency departments. Hemolysis often occurs in the preanalytical phase due to factors like improper specimen handling, incorrect needle size, and extended tourniquet time. When red blood cells rupture, they spill their contents (namely, hemoglobin) into the liquid portion of the blood. Hemolysis is one of the. Typically, rbcs can live for up to 120 days before the body naturally destroys them. Derived from the word “hemo”, meaning blood, and “lysis”, meaning destruction of cells, hemolysis is the most common reason for a rejected blood sample. Mild hemolysis can cause gradually progressive fatigue, dizziness, pale skin, and feeling cold. 2 tries for intravenous placement; Web hemolysis is. Hemolysis rates in blood drawn using iv cannula vary greatly from 1 to 77% with an average of 23% [ 12 ]. Rapid hemolysis can cause hematuria (blood in the urine), a significant drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness. Web hemolysis is conventionally defined as the release of hemoglobin and other intracellular components of erythrocytes into the extracellular. Typically, rbcs can live for up to 120 days before the body naturally destroys them. Hemolysis rates in blood drawn using iv cannula vary greatly from 1 to 77% with an average of 23% [ 12 ]. Severe hemolysis can have intravascular and extravascular features. Each of these studies reported “substantial” reductions in hemolysis when drawn from an antecubital site. Web hemolysis or haemolysis ( / hiːˈmɒlɪsɪs / ), [1] also known by several other names, is the rupturing ( lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents ( cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. Web hemolysis occurs when the red cells are damaged during sample collection. Web hemolysis is the destruction of red blood cells (rbcs).. 1 improper specimen collection during the blood drawing process is a major cause of hemolysis, potentially rendering a blood sample unusable or the results inaccurate. Web since accurate results begin with the collector, those who draw blood specimens are in the best position to make sure patients are treated according to results that are not delayed or altered because of. However, certain conditions and medications. 2 factors that may contribute to hemolysis of blood samples can. Intravascular hemolysis often starts acutely and can be a medical emergency associated with dic, aki, and hypotension. They may perform any of the following tests to determine if your blood cell count is low because of hemolysis. Reducing hemolysis rates improves time for results. Web hemolysis or haemolysis ( / hiːˈmɒlɪsɪs / ), [1] also known by several other names, is the rupturing ( lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents ( cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. Samples drawn by patient care technicians; Derived from the word “hemo”, meaning blood, and “lysis”, meaning destruction of cells, hemolysis is the most common reason for a rejected blood sample. When red blood cells rupture, they spill their contents (namely, hemoglobin) into the liquid portion of the blood. Hemolyzed serum or plasma is pale pink to red in color rather than the normal clear straw or pale yellow color. Web hemolysis occurs when the red cells are damaged during sample collection. Hemolysis is one of the main factors that can damage a blood sample. Hemolysis often occurs in the preanalytical phase due to factors like improper specimen handling, incorrect needle size, and extended tourniquet time. Typically, rbcs can live for up to 120 days before the body naturally destroys them. 1, 2 hemolysis may occur in vivo and in vitro. A cbc offers valuable information about all of your blood cells, including your red blood cells. The availability of an intravenous line already placed pushes many nurses to use this route for blood drawing, even if it is known that this technique is associated with an increased rate of hemolysis compared to blood sampling with a needle. Intravascular hemolysis often starts acutely and can be a medical emergency associated with dic, aki, and hypotension. Web hemolysis, the breakdown of red blood cells, can compromise sample quality, leading to inaccurate test results, potential misdiagnosis, and delayed treatment. Web four studies, three rated “good” and one rated “fair” examined the effectiveness of drawing blood from an iv start placed at the antecubital site rather than a more distal site. Each of these studies reported “substantial” reductions in hemolysis when drawn from an antecubital site relative to a more distal site.
(a) Blood resistivity (left axis) and hemolysis percentage (right axis
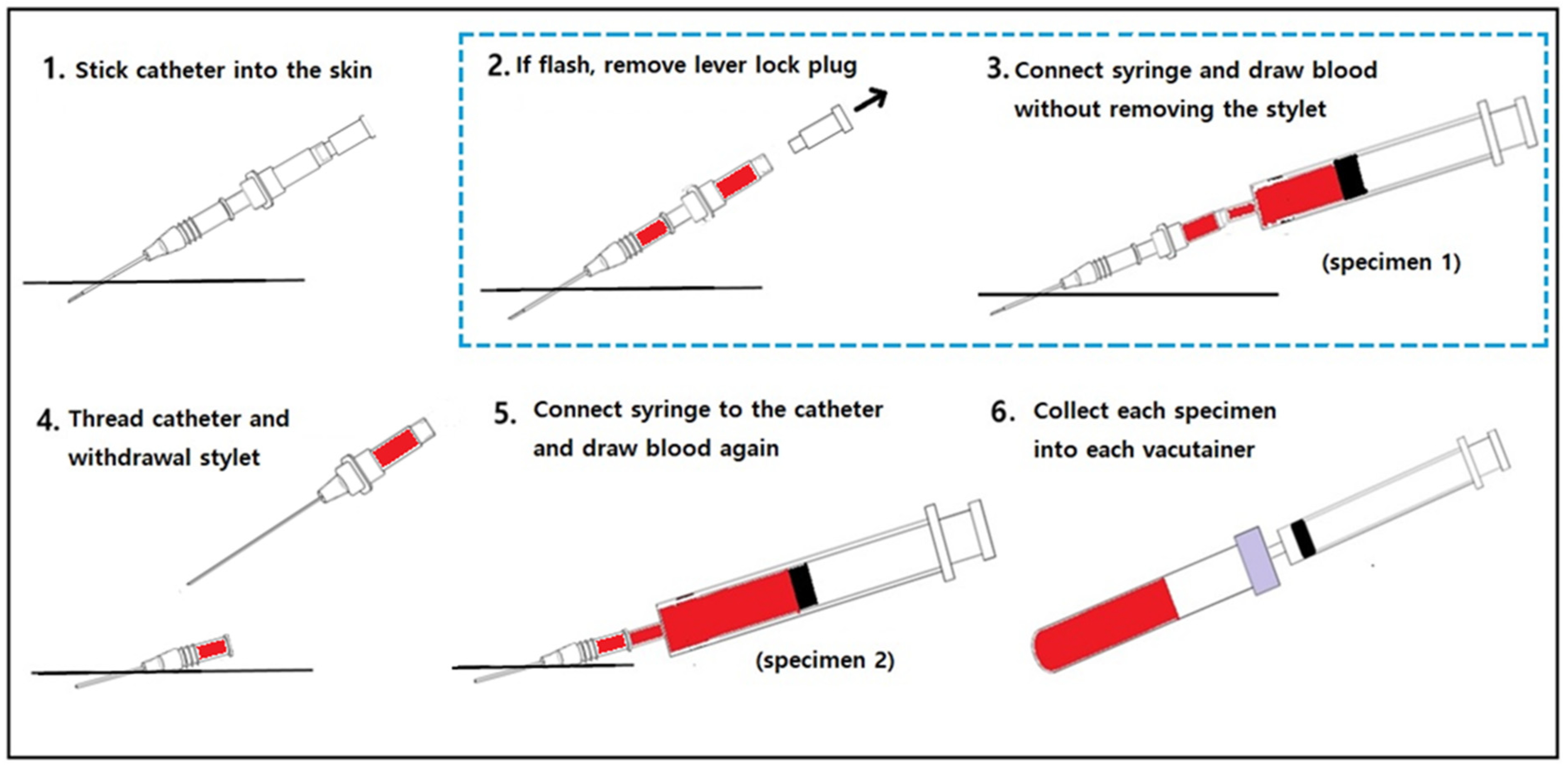
JPM Free FullText Hemolysis Control in the Emergency Department by

Clinical Chemistry
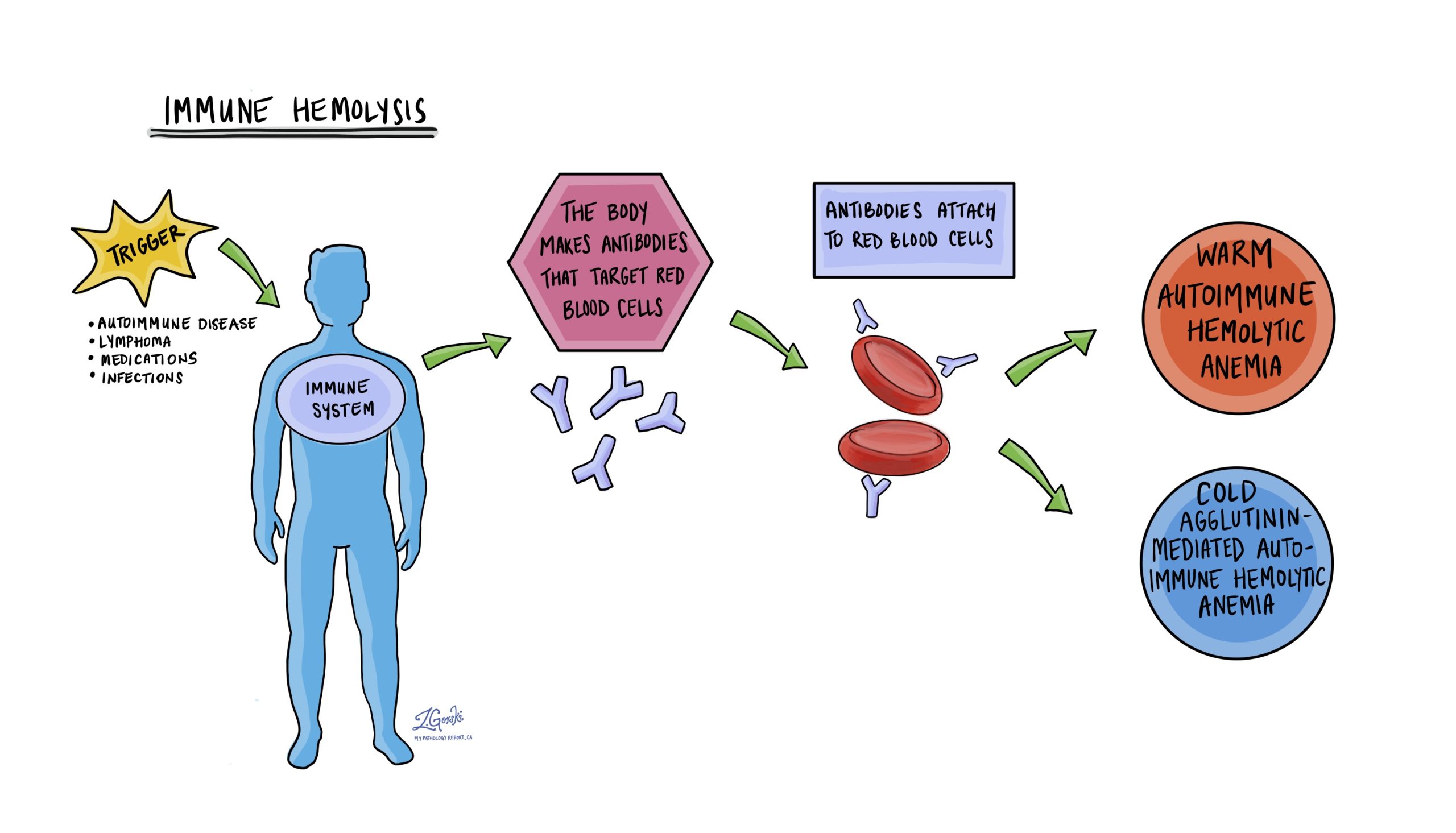
Hemolytic anemia MyPathologyReport.ca
Hemolysis Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

What Causes Hemolysis During A Blood Draw Warehouse of Ideas
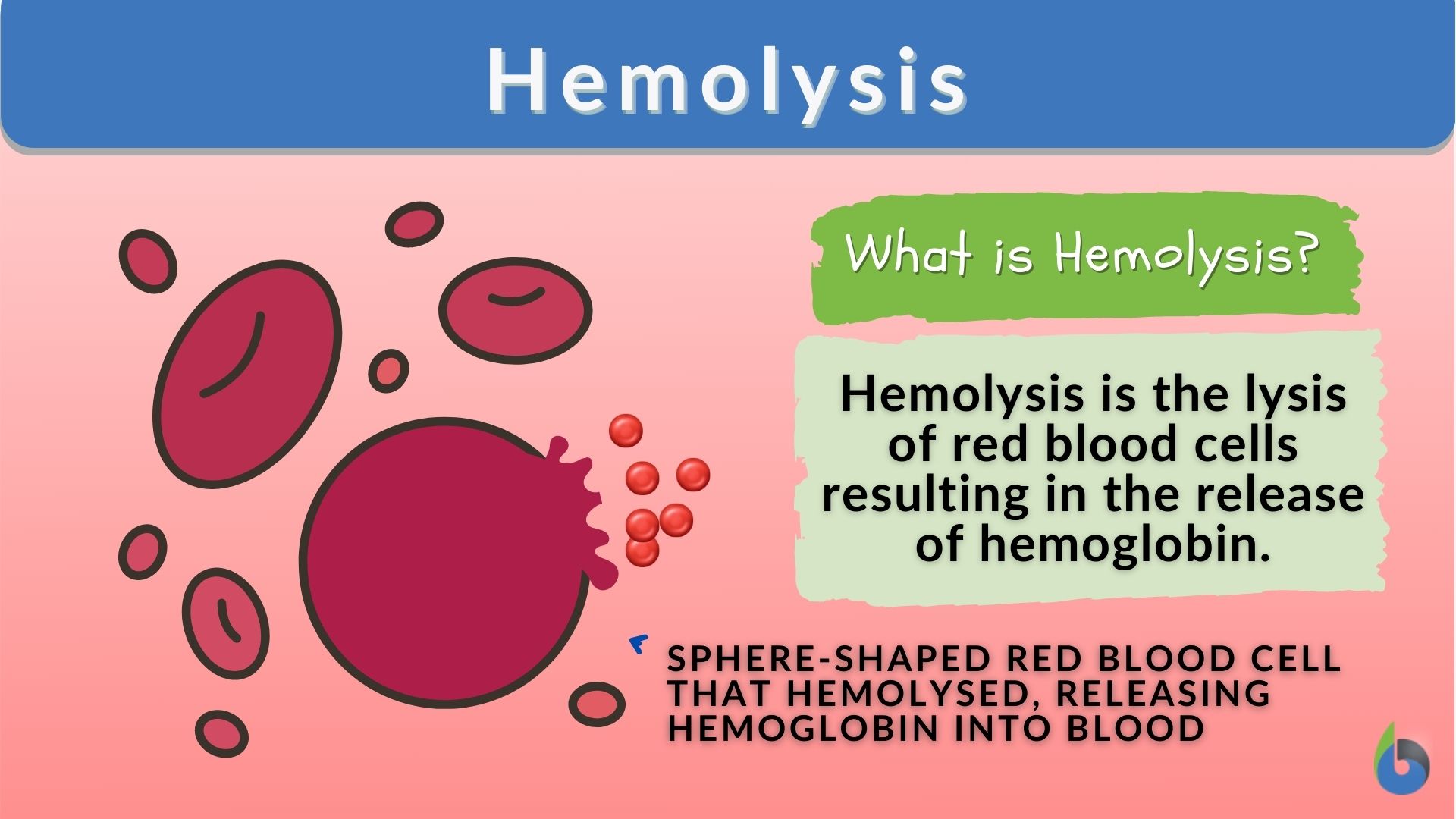
Hemolysis Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

Factors Affecting Hemolysis Rates in Blood Samples Drawn From Newly
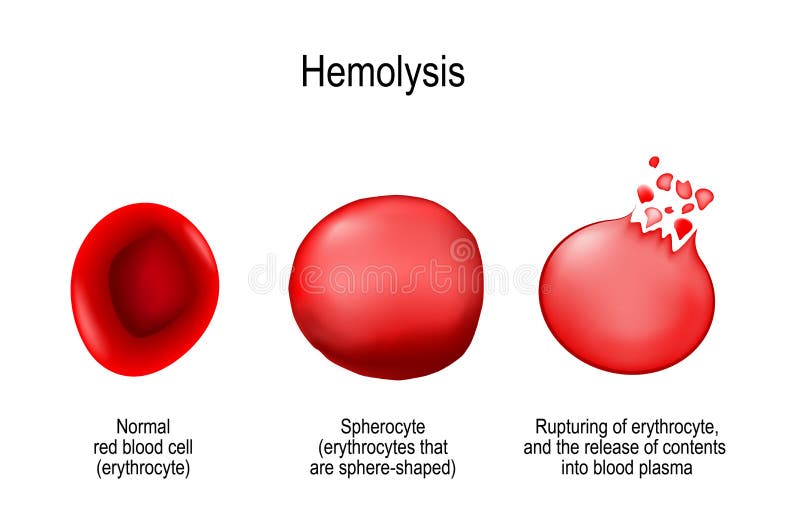
Hemolysis. Normal Red Blood Cell, Spherocyte, and Rupturing of E Stock
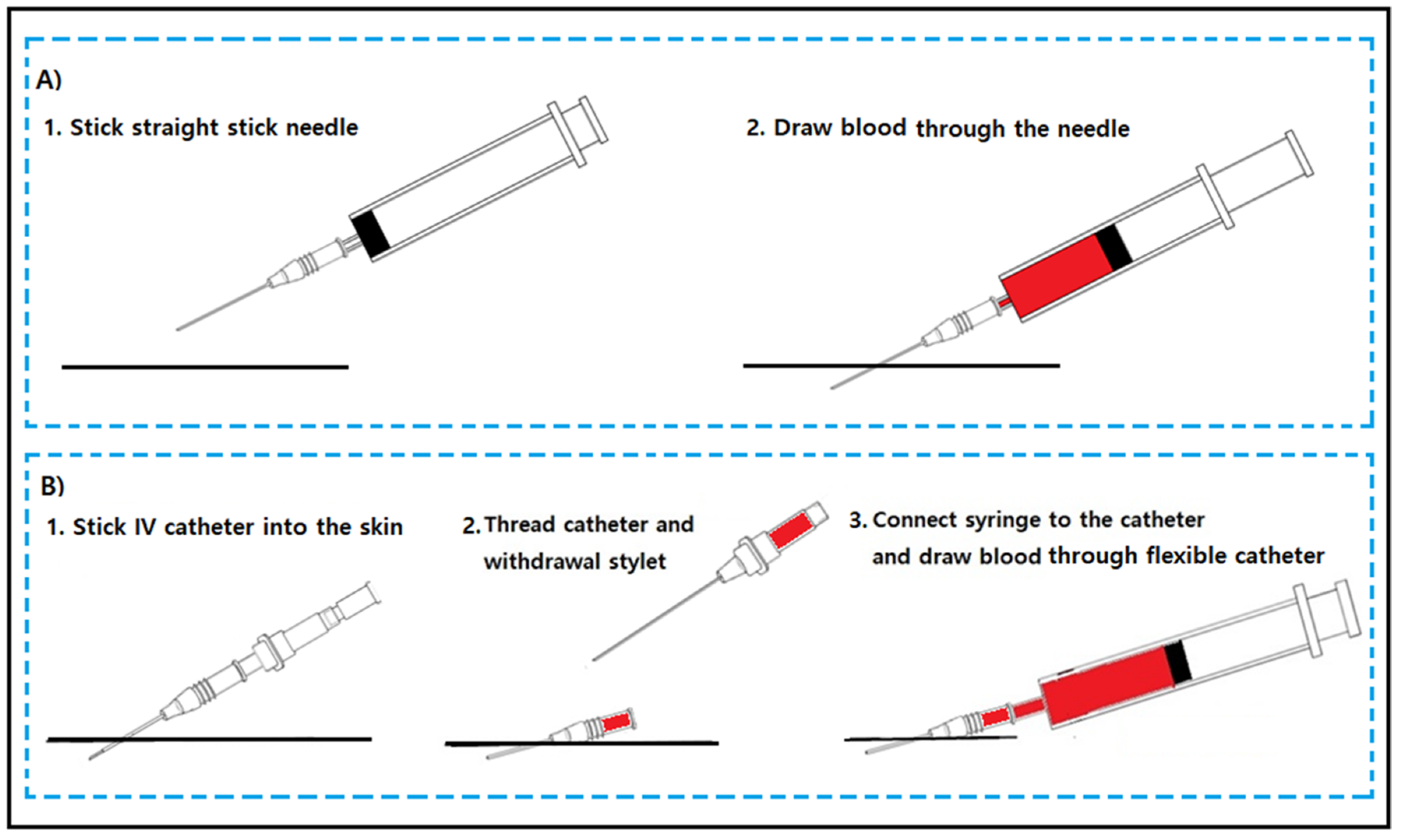
JPM Free FullText Hemolysis Control in the Emergency Department by
Web Hemolysis Is The Breaking Down Of Red Blood Cells Due To The Mishandling Of Blood Samples During Routine Blood Collection And Transport.
They May Perform Any Of The Following Tests To Determine If Your Blood Cell Count Is Low Because Of Hemolysis.
Web A Healthcare Provider Will Perform A Blood Draw To Check For Problems Related To Hemolysis.
2 Tries For Intravenous Placement;
Related Post: