Fainting During Blood Draw
Fainting During Blood Draw - Consciousness is usually regained quickly. Start by finding a comfortable position on the chair or bed so that you can relax. In this article, you will find out why people pass out, how to avoid passing out and what to do if you feel like passing out when getting blood. Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Vasovagal syncope is usually what causes people to faint when they have blood drawn or. Being prepared for this situation and knowing how to handle it is essential. When we are anxious, our heart rate and blood pressure actually go up. However, if you stand up too soon after fainting — within about 15 to 30 minutes — you're at risk of fainting again. The chapter includes background information (section 2.1), practical guidance (section 2.2) and illustrations (section 2.3) relevant to best practices in phlebotomy. Web patients with a history of fainting during a blood draw should be drawn while they are in a recumbent position; Some causes of syncope are fairly benign, such as from dehydration, or during a frightening or uncomfortable event, such as a blood draw. Also known as a vasovagal response or vasovagal syncope, this cause of fainting is common in children and young adults. This is why it is so rare to faint when you are feeling anxious. Do not get. Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain. Start by finding a comfortable position on the chair or bed so that you can relax. Web some people faint in response to the sight of blood or to an emotional upset. 1 passing out is common when getting. How to handle patients fainting during blood draw. Some common signs that people may present before fainting include: Vasovagal syncope happens more often in people donating blood for the first time. It happens to healthy patients, young, old, and even those accustomed to blood draws. Other common causes of fainting include standing for a long period of time and exposure. For some, it may be scary enough to cause them to pass out. The most common reason for fainting, especially with children and young adults, is neurally mediated syncope. Web this chapter covers all the steps recommended for safe phlebotomy and reiterates the accepted principles for blood drawing and blood collection (31). Keep reading to learn more about. Web vasovagal. Some people faint in association with anxiety attacks, strenuous coughing, or even urinating. Some people have a severe reaction to blood draws including fainting. It happens to healthy patients, young, old, and even those accustomed to blood draws. Being prepared for this situation and knowing how to handle it is essential. For some, it may be scary enough to cause. Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain. When we are anxious, our heart rate and blood pressure actually go up. Start by finding a comfortable position on the chair or bed so that you can relax. Web fainting occurs when the brain doesn't receive enough blood. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including low blood pressure, low blood sugar, or a heart condition. While not everyone experiences it, it’s considered a normal physiological response. You may want to sit upright with your back against a firm surface. Some patients give no warning before passing out. Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary. The chapter includes background information (section 2.1), practical guidance (section 2.2) and illustrations (section 2.3) relevant to best practices in phlebotomy. This can help if you have needle phobias or faint before an injection. Consciousness is usually regained quickly. Web the most common cause of fainting (especially among children and young adults) is neurally mediated syncope, which is also commonly. Web fainting is when you lose consciousness or “pass out” for a short time, usually about 20 seconds to a minute. Fainting, also known as syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain. In a vasovagal response, your blood pressure drops and the heart does not pump a normal amount of. Some causes of syncope are fairly benign, such as from dehydration, or during a frightening or uncomfortable event, such as a blood draw. Web fainting, or passing out — a temporary loss of consciousness also known as syncope — is caused by insufficient blood flow to the brain. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including low blood. Web most people who faint during blood draws are likely to present some signs and symptoms before they lose consciousness. In medical terms, fainting is known as syncope. Web it’s hard to identify which patients will faint during a blood draw and which will not. While not everyone experiences it, it’s considered a normal physiological response. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including low blood pressure, low blood sugar, or a heart condition. Web fainting occurs when the brain doesn't receive enough blood for a brief time. The most common reason for fainting, especially with children and young adults, is neurally mediated syncope. This can help if you have needle phobias or faint before an injection. Web the most common cause for fainting during blood draw is neurally mediated syncope. Other common causes of fainting include standing for a long period of time and exposure to heat or crowds or both. But how does vasovagal syncope affect people giving blood samples through needles? Some causes of syncope are fairly benign, such as from dehydration, or during a frightening or uncomfortable event, such as a blood draw. Some common signs that people may present before fainting include: It happens to healthy patients, young, old, and even those accustomed to blood draws. Web the most common cause of fainting (especially among children and young adults) is neurally mediated syncope, which is also commonly referred to as vasovagal syncope or a vasovagal response. Do not get more than one step away from a seated patient while he/she is in your care.
Fear of Needles Top Tips to Avoid Fainting During Your Next Blood Draw
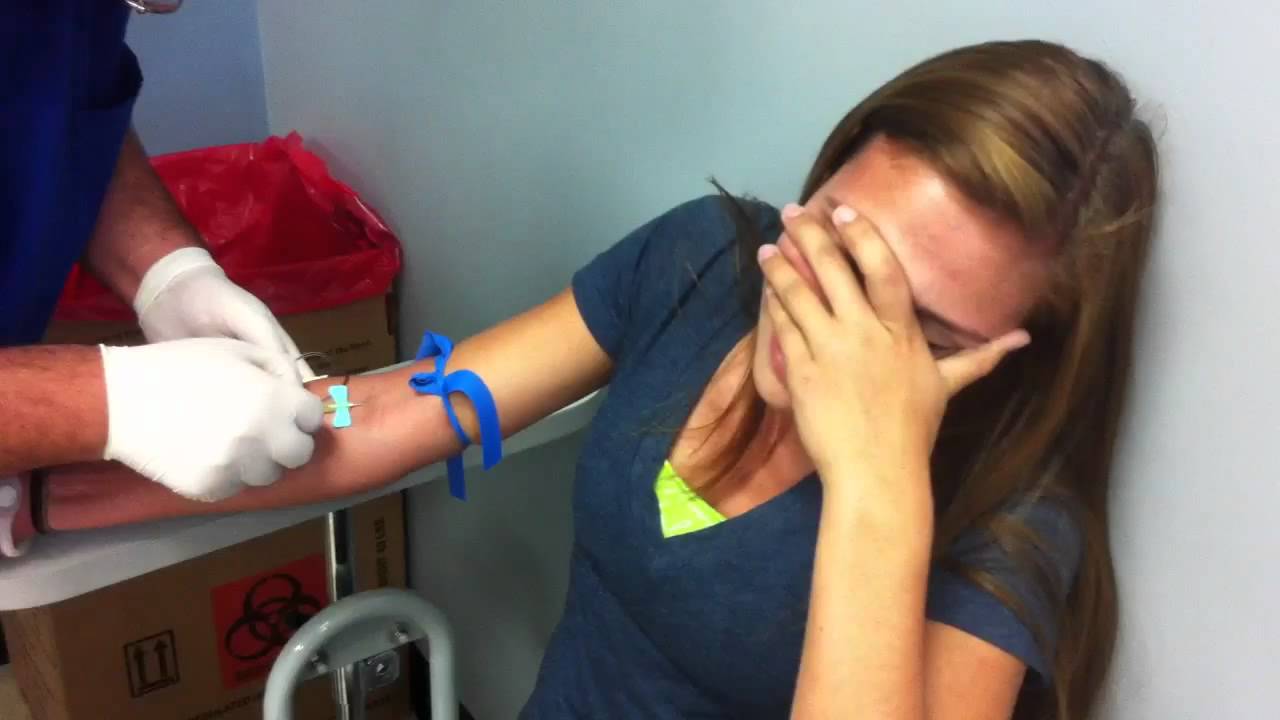
Miranda's blood test! YouTube

Why did you pass out during the blood draw?

Phlebotomy and Patient Fainting Be Prepared
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-cardioneurogenic-syncope-1746389-color3-ce8587834a804fb994d99352d0d7329b.jpg)
Medical Causes of Syncope or Fainting
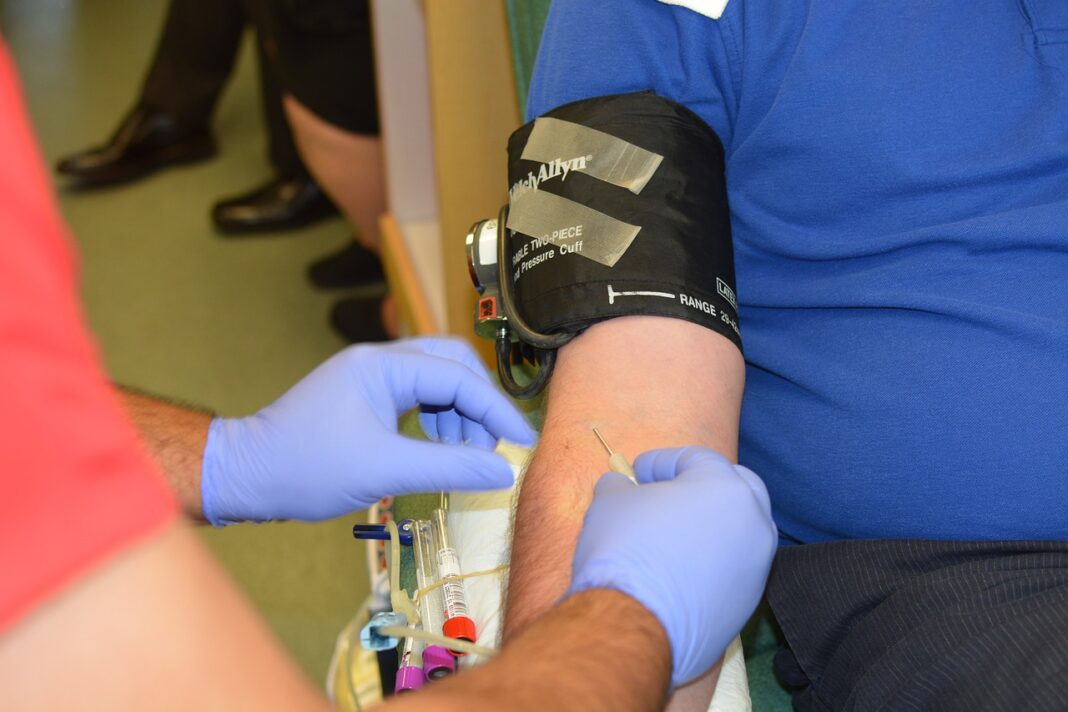
What to do if Faint after Blood Draw Healths Digest

Fainting After Giving Blood Causes and Coping Methods New Health Advisor

Phlebotomy Tips How to Help a Fainting Patient During a Blood Draw

Phlebotomy Tips How to Help a Fainting Patient During a Blood Draw

PHLEBOTOMIST MADE ME CRY, FAINTING // My Terrible Blood Draw
Fainting, Also Known As Syncope, Is A Temporary Loss Of Consciousness Caused By A Decrease In Blood Flow To The Brain.
What Does It Mean When Blood Stops Flowing During Blood Draw?
1 Passing Out Is Common When Getting Blood Drawn.
Being Prepared For This Situation And Knowing How To Handle It Is Essential.
Related Post: