Drawing The Derivative Of A Graph
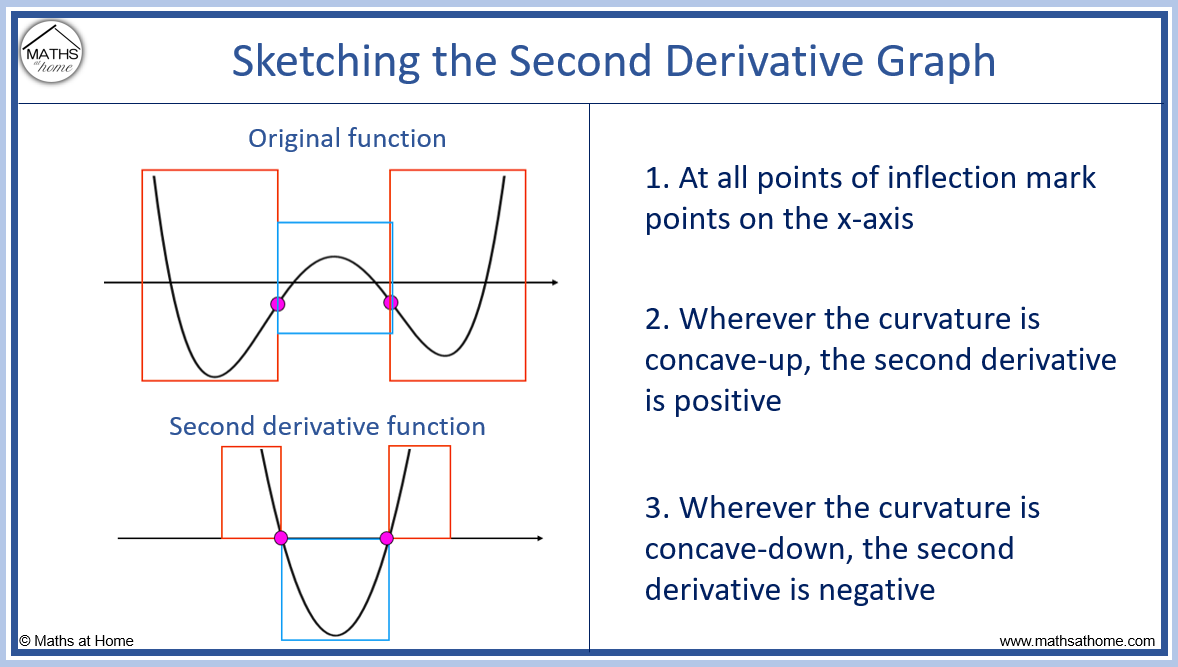
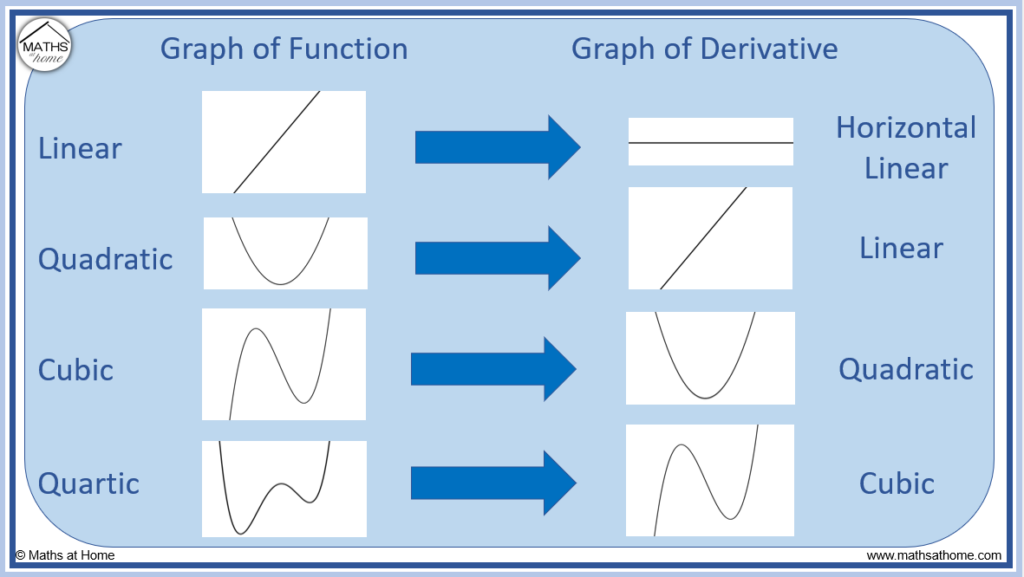
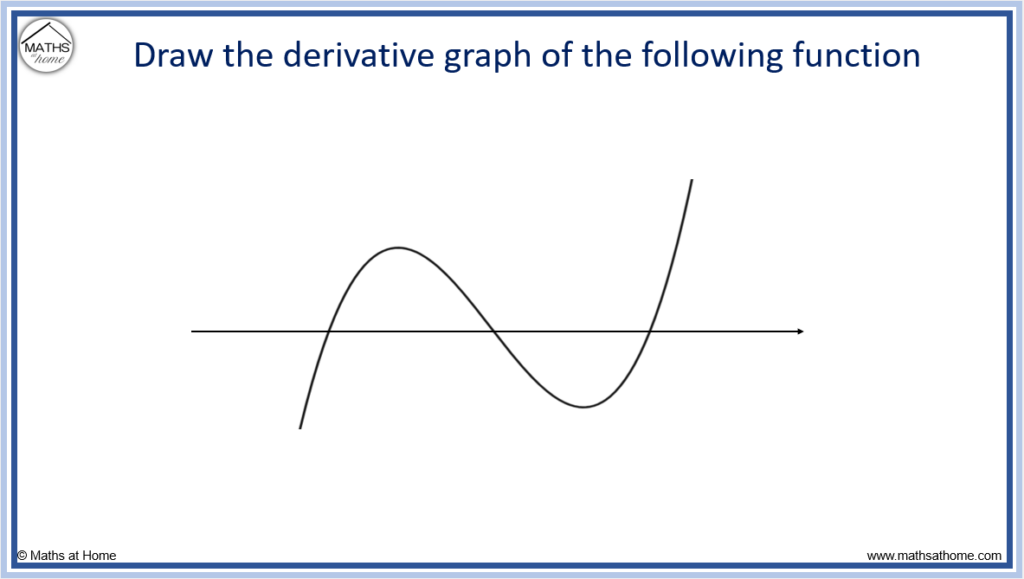
Drawing The Derivative Of A Graph - Web if the original graph is of a parabola, rather than a circle, then the graph of the derivative is a straight line, since d/dx [ax² + bx + c] = 2ax + b. Mark zeros at the locations of any turning points or stationary inflection points. Exercise \ (\pageindex {5}\) exercise \. Below is the graph of the derivative of a function. When you think you have a good representation of f ′ (x), click the show results!. Web 4.5.1 explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. This is the graph of function g. Explain the concavity test for a function over an open. This is the graph of the function y = x. Web the derivative of a function f (x) is the function whose value at x is f′ (x). Web first, we learn how to sketch the derivative graph of a continuous, differentiable function f (x), either given the original function or its graph y=f (x). From this graph determine the intervals in which the function increases and decreases. Obtain a writing utensil and blank paper. Let’s start with an easy one: Web 4.5.1 explain how the sign of. Learn for free about math, art,. Web use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the second derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. Where (f (x) has a tangent. 4.5.3 use concavity and inflection. From this graph determine the intervals in which the function increases and decreases. When you think you have a good representation of f ′ (x), click the show results!. Exercise \ (\pageindex {5}\) exercise \. A derivative is positive when the original function is increasing, and negative when the original function is decreasing. This is the graph of function g. Web thanks to all of you who support me on patreon. But it’s best to learn how through exploration. 4.5.3 use concavity and inflection. Describe three conditions for when a. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Web the derivative of a function f (x) is the function whose value at x is f′ (x). Remember, this graph represents the derivative. This relies on a solid. Web well, the secret to understanding a graph lies in properly labelling it and learning how to read it. Web 4.5.1 explain how the sign of the first derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. The graph of a derivative of a function f (x) is related to. Web use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the second derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. If the original graph is a circle, then. So you look at where the original. Replace dx in the equation with 0. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. This calculus video tutorial explains how to sketch the derivatives of the parent function using. Web the derivative of a function f (x) is the function whose value at x is f′ (x). Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Below is the graph of the derivative. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. 4.5.2 state the first derivative test for critical points. What is the graph of its derivative, g ′ ? Replace dx in the equation with 0. Web drag the blue points up and down so that together they follow the shape of the graph of f ′. Replace dx in the equation with 0. What is the graph of its derivative, g ′ ? 4.5.3 use concavity and inflection. This calculus video tutorial explains how to sketch the derivatives of the parent function using. Here we have the graph of the derivative f' (x) = x. Find space on a flat surface for you to work on. From this graph determine the intervals in which the function increases and decreases. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Web use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the second derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph. Web if the original. Where (f (x) has a tangent. Examine an original graph that is on a coordinate plane of. Remember, this graph represents the derivative. This is the graph of the function y = x. Graph a derivative function from the graph of a given function. So you look at where the original. Web thanks to all of you who support me on patreon. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. The graph of a derivative of a function f (x) is related to the graph of f (x). But it’s best to learn how through exploration. Exercise \ (\pageindex {1}\) exercise \ (\pageindex {2}\) exercise \ (\pageindex {3}\) exercise \ (\pageindex {4}\) stage 2. Replace dx in the equation with 0. Describe three conditions for when a. This relies on a solid. Web use concavity and inflection points to explain how the sign of the second derivative affects the shape of a function’s graph.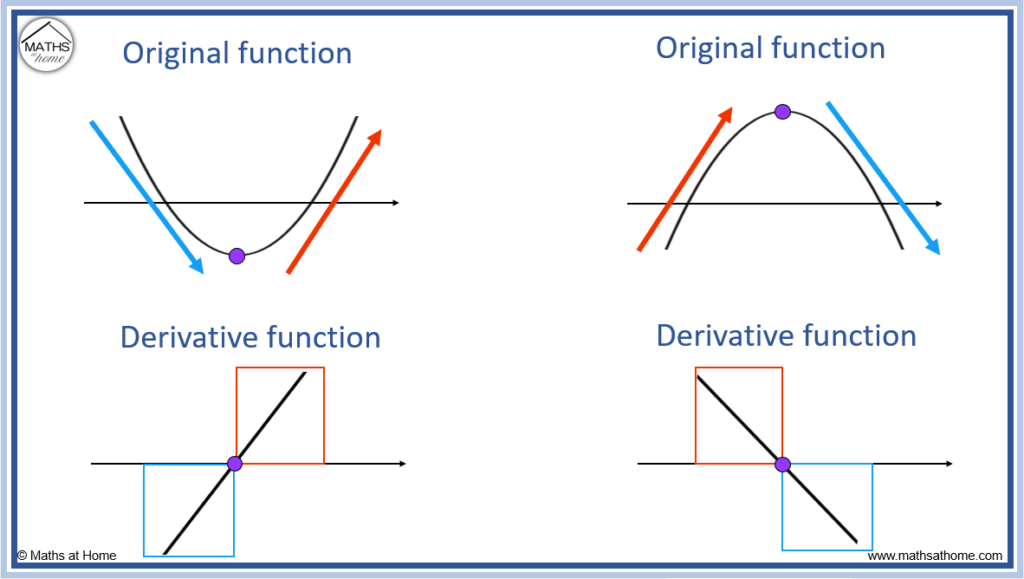
How to Sketch the Graph of the Derivative
How to Sketch the Graph of the Derivative
How to Sketch the Graph of the Derivative

Steps to Sketch Graph of Function From Derivative YouTube
How to Sketch the Graph of the Derivative

Drawing the Graph of a Derivative YouTube
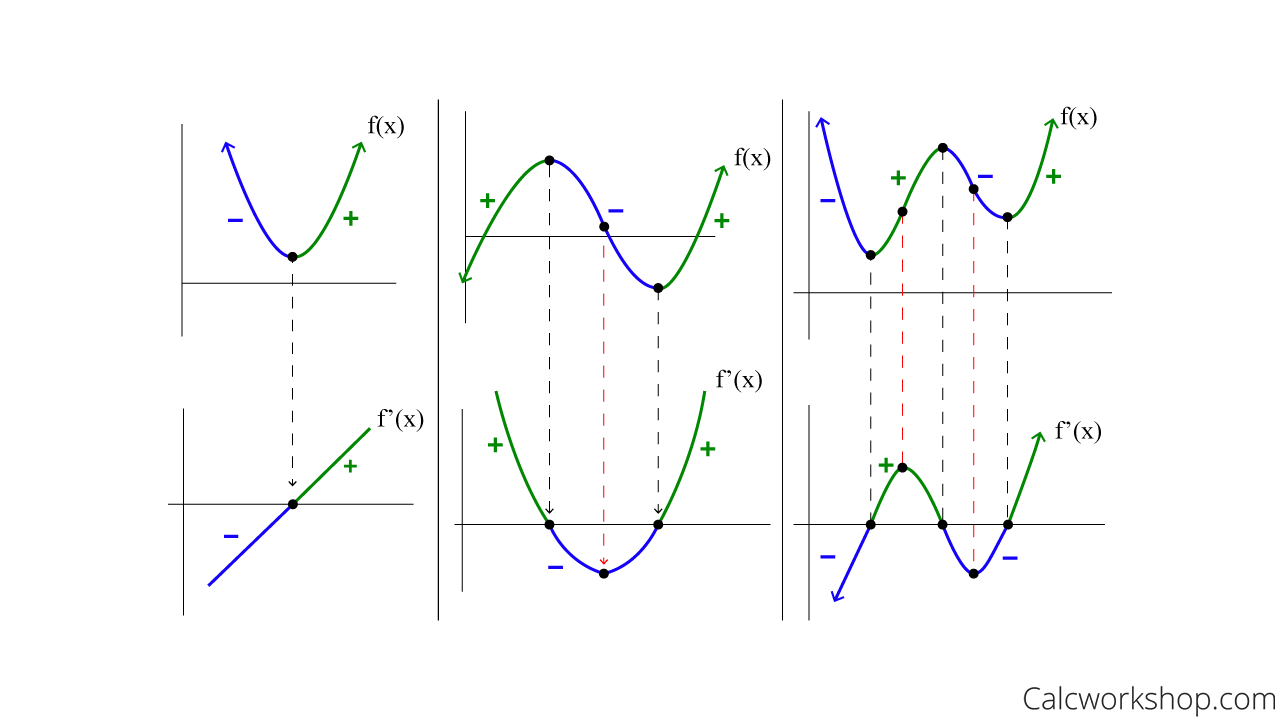
Derivative Graph Vs Original Function (w/ 15+ Examples!)
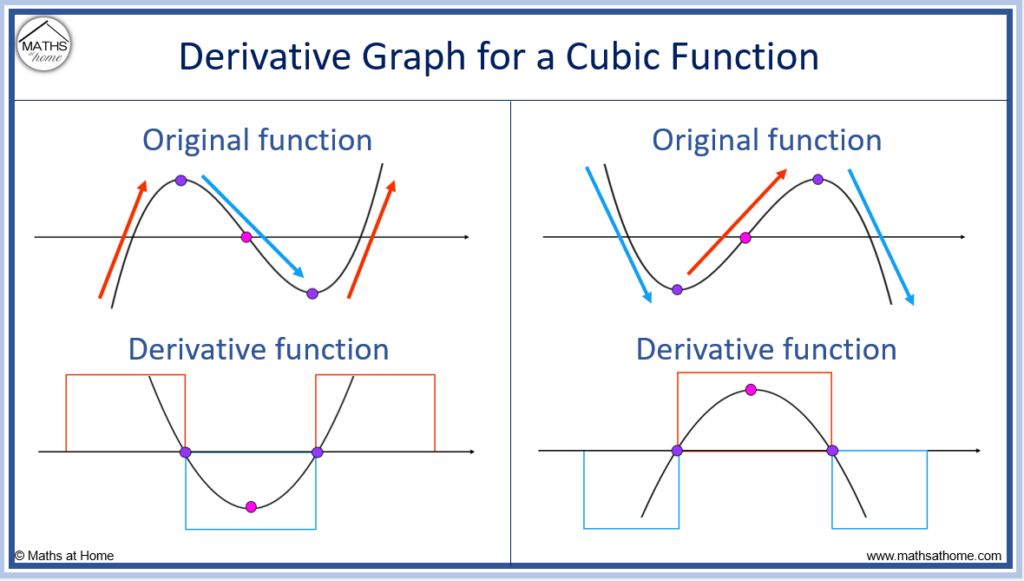
How to Sketch the Graph of the Derivative

How to sketch first derivative and Function from graph of second

Draw the Function given Graph of Derivative YouTube
Explain The Concavity Test For A Function Over An Open.
Graph Functions, Plot Points, Visualize Algebraic Equations, Add Sliders, Animate Graphs, And More.
Web Explore Math With Our Beautiful, Free Online Graphing Calculator.
From This Graph Determine The Intervals In Which The Function Increases And Decreases.
Related Post: