Drawing Orbital Diagrams
Drawing Orbital Diagrams - Write out the electron configuration to determine which orbitals are filled. Discover the three rules for creating electron orbital charts, and study examples of filling electron orbital in a diagram. Below are dot density diagrams, boundary surface diagrams, and a rotating image. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: This is a way of showing the electron configuration of the atom. This article will explore the basics of how to draw each type of diagram, and important rules to follow in their construction. Each box represents one orbital, and each arrow indicates one electron. Web commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals. Web how to draw orbital diagrams. Web a p orbital which extends along the x axis is labeled a p x orbital. Web orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Write out the electron configuration to determine which orbitals are filled. The orbital box diagrams are listed for the first 20 elements in the figure below. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Web how to draw orbital diagrams. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2p subshell. Below are dot density diagrams, boundary surface diagrams, and a rotating image. Draw a long vertical arrow that points upward. Web steps for drawing an orbital diagram. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Web an orbital box diagram can be written as well. Web how to do orbital diagrams. Want to join the conversation? An orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. We classified the different orbital into shells and sub shells to distinguish them more easily. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. The remaining two electrons occupy the 2p. None of the approaches we have described so far can adequately explain why some compounds are colored and others are not, why some substances with unpaired electrons are stable, and why others are effective semiconductors. This article will. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. Four of them fill the 1s and 2s orbitals. None of the approaches we have described so far can adequately explain why some compounds are colored and others are not, why some substances with unpaired electrons are stable, and why others are effective semiconductors. Want. Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. A p orbital along the y axis is labeled p y and one along the z axis is a p z orbital. Four of them fill the 1s and 2s orbitals. Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes. Four of them fill the 1s and 2s orbitals. Web commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals. Web. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. You will also learn how to use hund'. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. Web the bohr model shows the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with the electrons in circular electron shells at specific distances from the nucleus, similar to. Get a pencil (preferably a mechanical pencil for precision), a good eraser, a ruler, and a sheet of drawing paper. Web a p orbital which extends along the x axis is labeled a p x orbital. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Web in orbitals diagrams, the orbitals are shown as boxes, and the electrons in them as arrows. You will also learn how to use hund'. This will represent the nucleus of the atom. Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. Typically, they only show the outermost electrons. Web when drawing orbital diagrams, we include empty boxes to depict any empty orbitals in the same. Write out the electron configuration to determine which orbitals are filled. This article will explore the basics of how to draw each type of diagram, and important rules to follow in their construction. This is a way of showing the electron configuration of the atom. We classified the different orbital into shells and sub shells to distinguish them more easily. Web commonly, the electron configuration is used to describe the orbitals of an atom in its ground state, but it can also be used to represent an atom that has ionized into a cation or anion by compensating with the loss of or gain of electrons in their subsequent orbitals. Remember, we can use the periodic table to help us. Web learn how to draw orbital diagrams. Draw a long vertical arrow that points upward. The arrow shows a qualitative representation of increasing orbital energy. Web learn how to draw orbital diagrams. Web steps for drawing an orbital diagram. Web a p orbital which extends along the x axis is labeled a p x orbital. This is also due to the history when they were discovered. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons. Atoms & elements 4h 15m. Carbon (atomic number 6) has six electrons.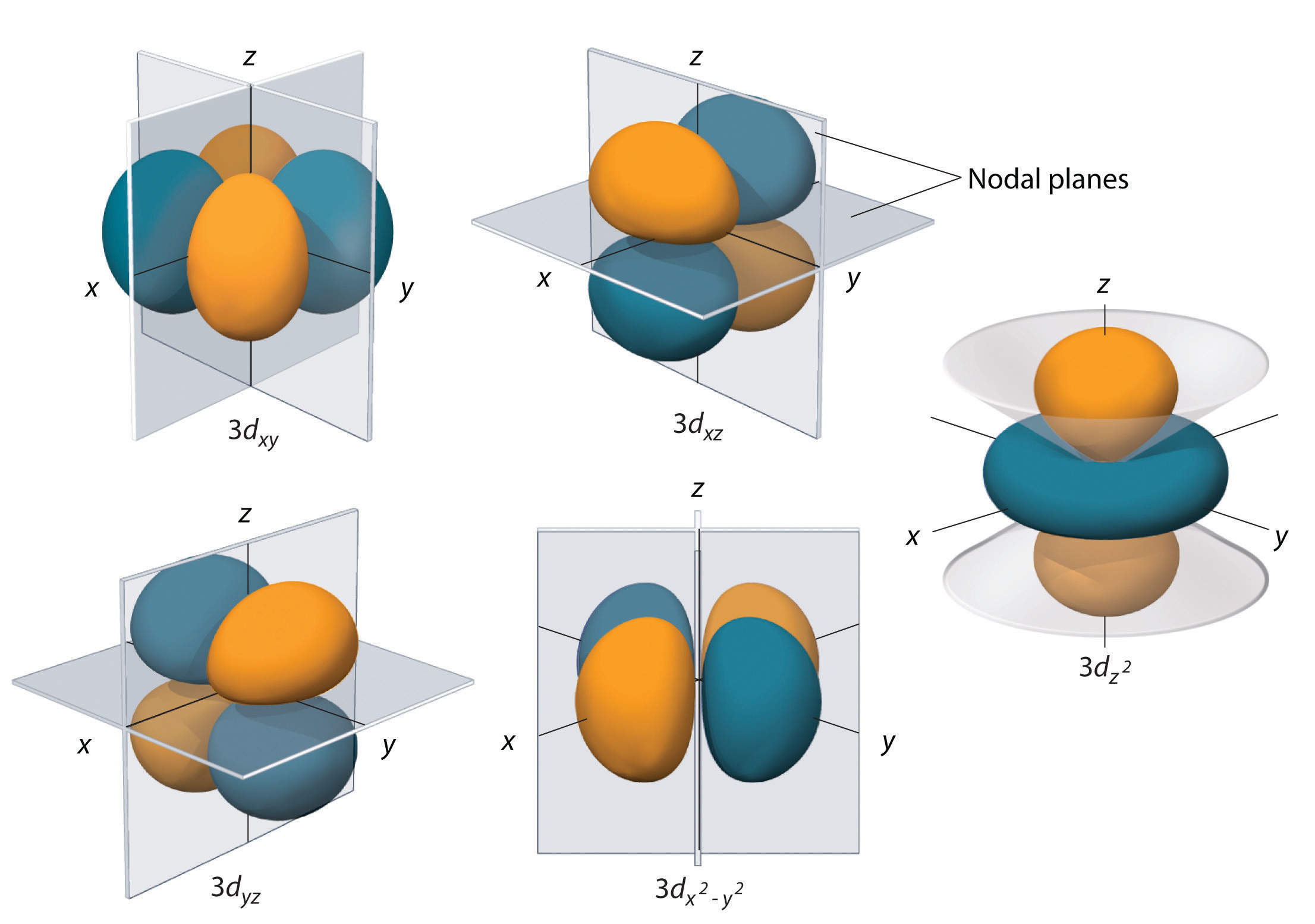
6.6 3D Representation of Orbitals Chemistry LibreTexts

Molecular Orbital Diagrams 101 Diagrams
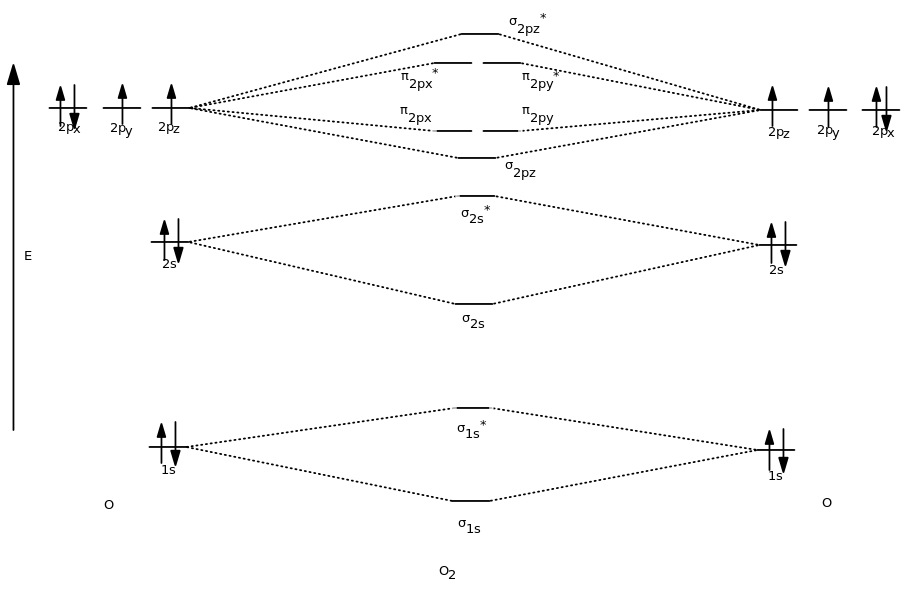
Drawing Atomic and Molecular Orbitals Diagrams for Molecules Organic

Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge

how to draw molecular orbital diagram for heteronuclear molecules

Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified by Megan Lim Medium
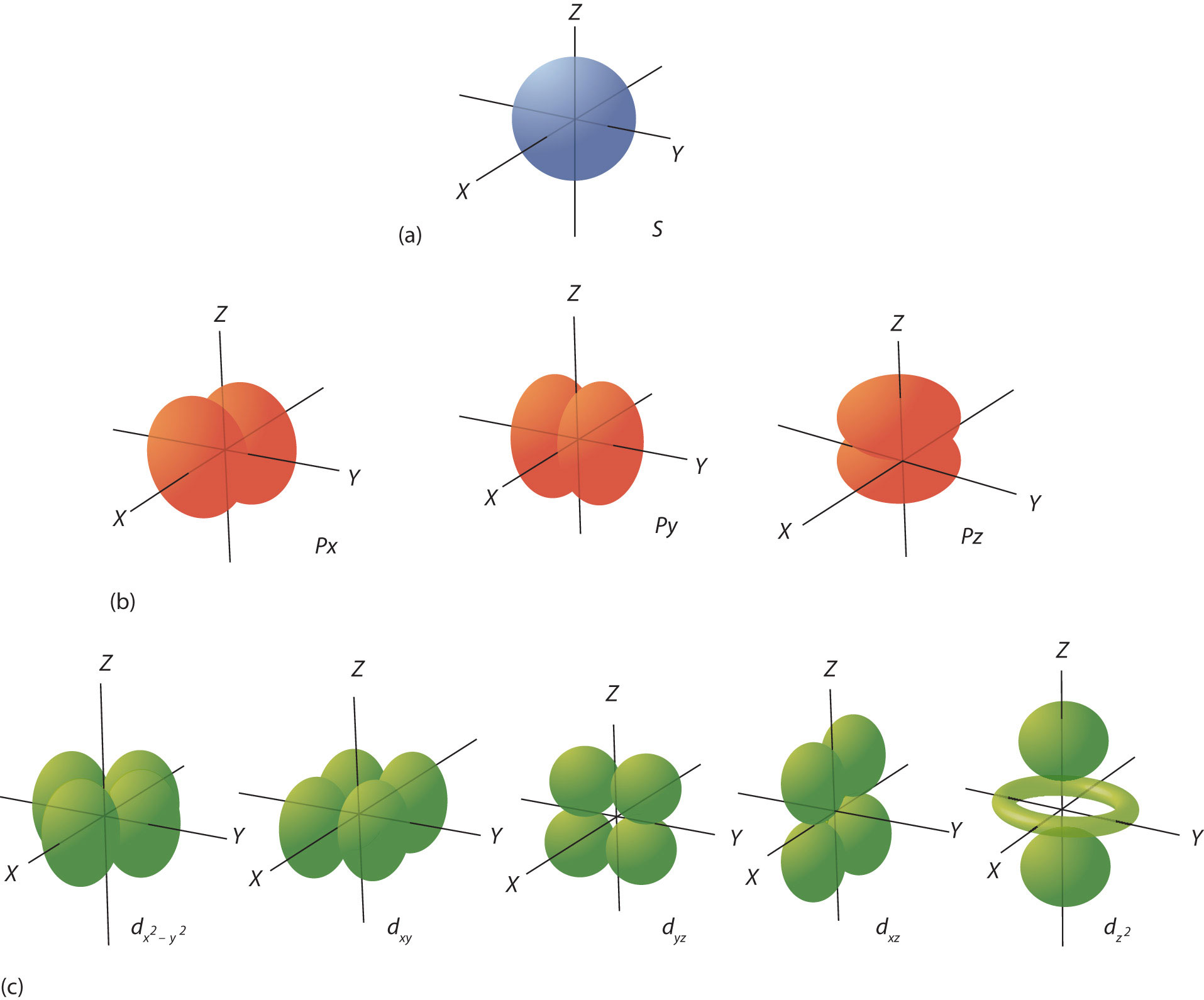
3.7 Electron Arrangement The Quantum Model Chemistry LibreTexts
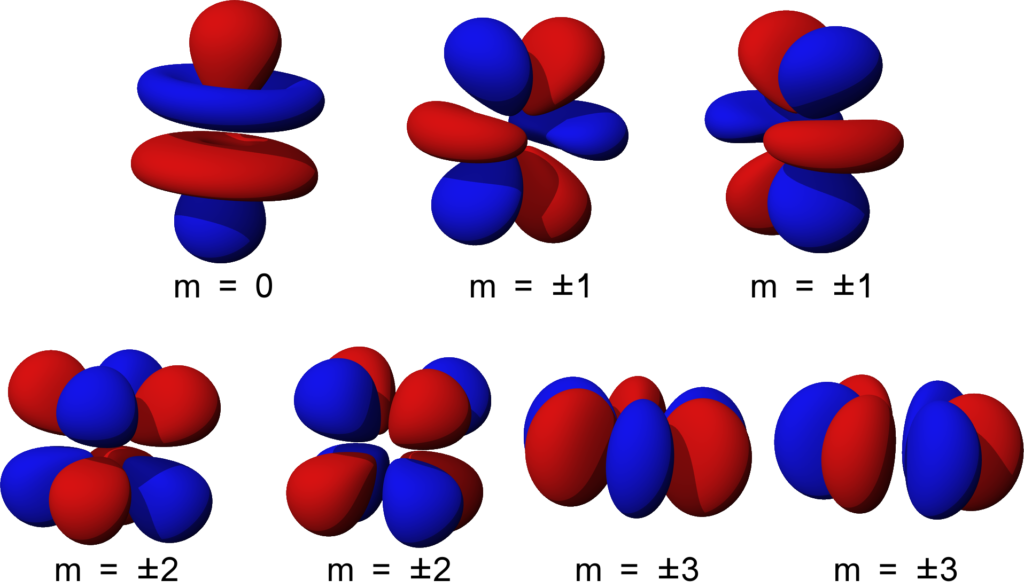
Shapes of Orbitals and their Types Chemistry Skills

Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii
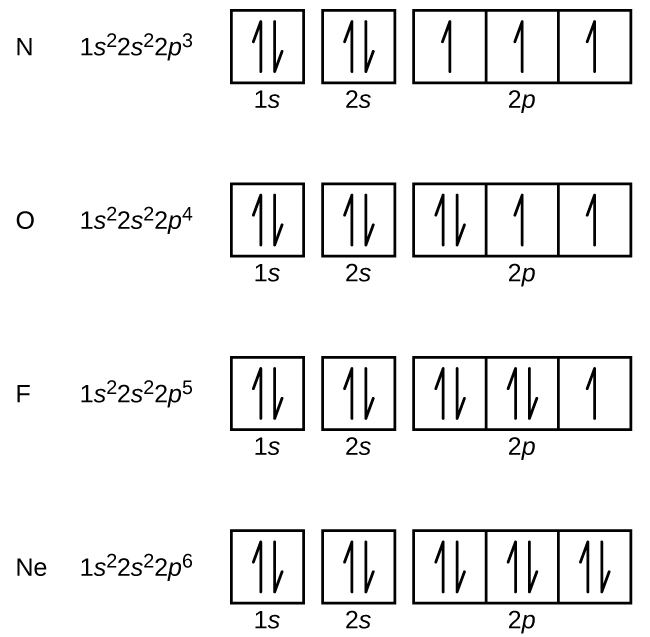
Electron Configurations, Orbital Box Notation (M7Q7) UWMadison
Discover The Three Rules For Creating Electron Orbital Charts, And Study Examples Of Filling Electron Orbital In A Diagram.
Web This Chemistry Video Tutorial Provides A Basic Introduction Into Orbital Diagrams And Electron Configuration.
Start By Drawing A Large Circle In The Center Of Your Paper.
For Example, The Electron Configuration Of Lithium, 1S²2S¹, Tells Us That Lithium Has Two Electrons In The 1S Subshell And One Electron In The 2S Subshell.
Related Post: