Draw The Ray Diagram
Draw The Ray Diagram - Web once the method of drawing ray diagrams is practiced a couple of times, it becomes as natural as breathing. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. The two diagrams below show how to determine image location, size, orientation and type for situations in which the object is located at the center of curvature and when the object. Relation between radius of curvature and focal length. Draw reflected rays to the image. The method of drawing ray diagrams for convex mirrors is described below. And it is on the other side of the mirror. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. With an arrowhead pointing in the direction that the light travels. For a convex lens, object can be kept at different positions. Web draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass prism. Hence, we take different cases. Web join teachoo black. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Web concave mirror ray diagrams. Draw the mirror and the object. Each diagram yields specific information about the image. Last updated at april 16, 2024 by teachoo. This physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. To draw a ray diagram, you will need the following materials: With an arrowhead pointing in the direction that the light travels. Web so, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. For a convex lens, object can be kept at different positions. Draw a ray parallel to the principal axis starting at the top of the object. Draw ray diagrams each showing (i) myopic eye and (ii) hypermetropic eye. To draw a ray diagram, you will need the following materials: 250k views 6 years ago new physics video playlist. The method of drawing ray diagrams for convex mirrors is described below. Web ray diagrams are employed to comprehend the behaviour of light and better understand image formation. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: To draw a ray diagram, you will need the following materials: Ray diagrams are used to. These diagrams use lines with arrows to represent incident and reflected rays, allowing us to trace their paths and interactions with the mirror. Web the location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Once through the. These diagrams use lines with arrows to represent incident and reflected rays, allowing us to trace their paths and interactions with the mirror. There are a few important things to note: Draw the mirror and the object. Ray diagrams are used to explain a variety of optical phenomena, such as reflection, refraction, and diffraction. The method of drawing ray diagrams. For a convex lens, object can be kept at different positions. Yes, you can draw different rays of light when creating the ray diagram. Remember to use a ruler and a sharp pencil. Web concave mirror ray diagrams. In this case, object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance) so, we draw rays parallel to principal axis. A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. To draw a ray diagram, you will need the following materials: These diagrams use lines with arrows to represent incident and reflected rays, allowing us to trace their. Draw the image as an arrow and give a description of the image. Linear magnification (m) concave mirror solved questions. For example, you can draw a ray of light parallel to the principal axis which reflects off the mirror and passes through the principal focus (like in this video). Web ray diagrams — isaac physics. C f description of image: A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. Web ray diagrams are employed to comprehend the behaviour of light and better understand image formation. Web the location (and nature) of the image can be found by drawing a ray diagram: Draw the mirror and the object. The rays bend according to the refractive indices provided in table 16.4. Hence, we take different cases. Last updated at april 16, 2024 by teachoo. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. Web ray diagrams — isaac physics. On the diagram, rays (lines with arrows) are drawn for the incident ray and the reflected ray. Web draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass prism. Each diagram yields specific information about the image. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. On the diagram mark a) incident angle b) emergent ray c) angle of deviation. A concave mirror will curve inward, looking like a closing parenthesis, or this:
How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10
Ray diagrams for convex mirrors
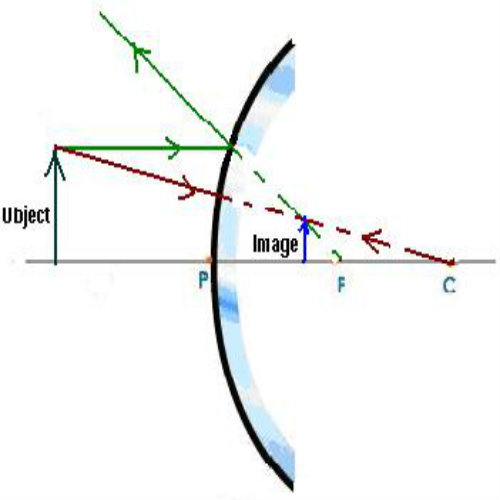
How to Draw a Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
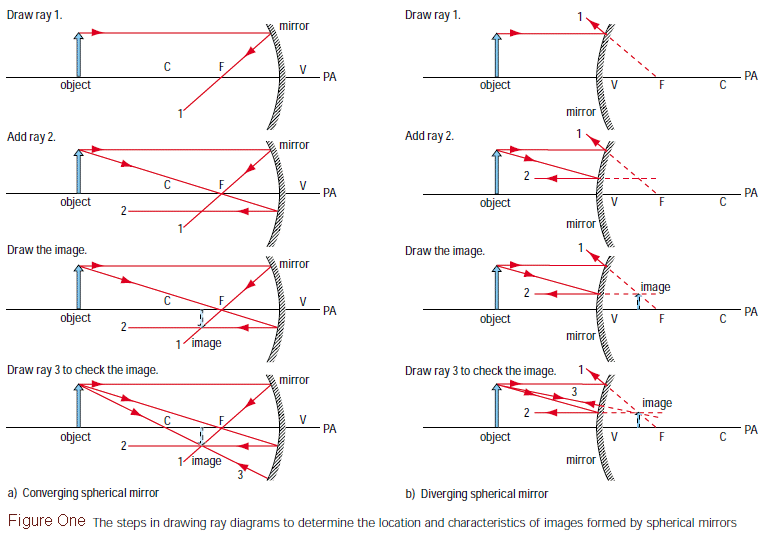
My Physics Webschool Ray Diagram
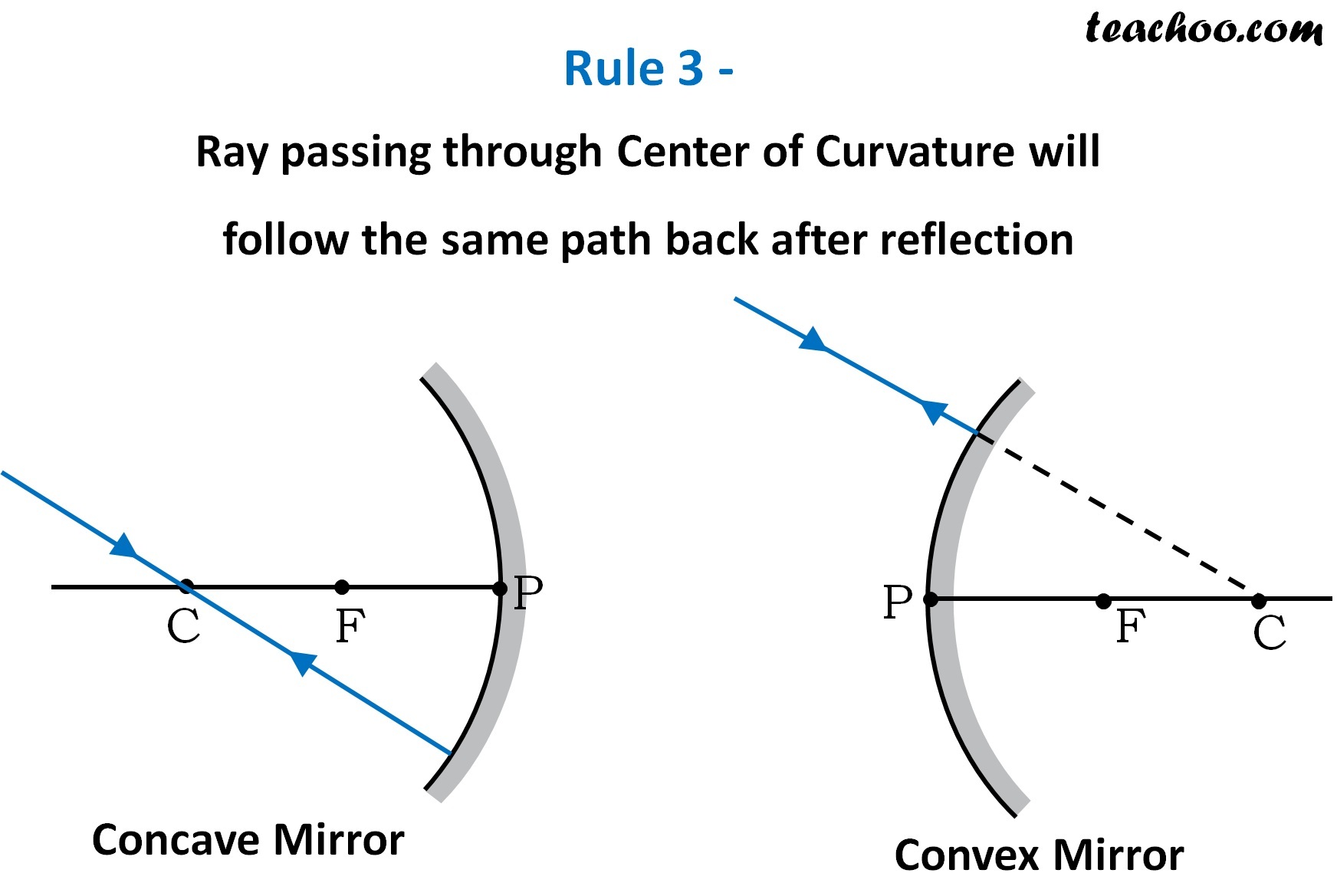
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
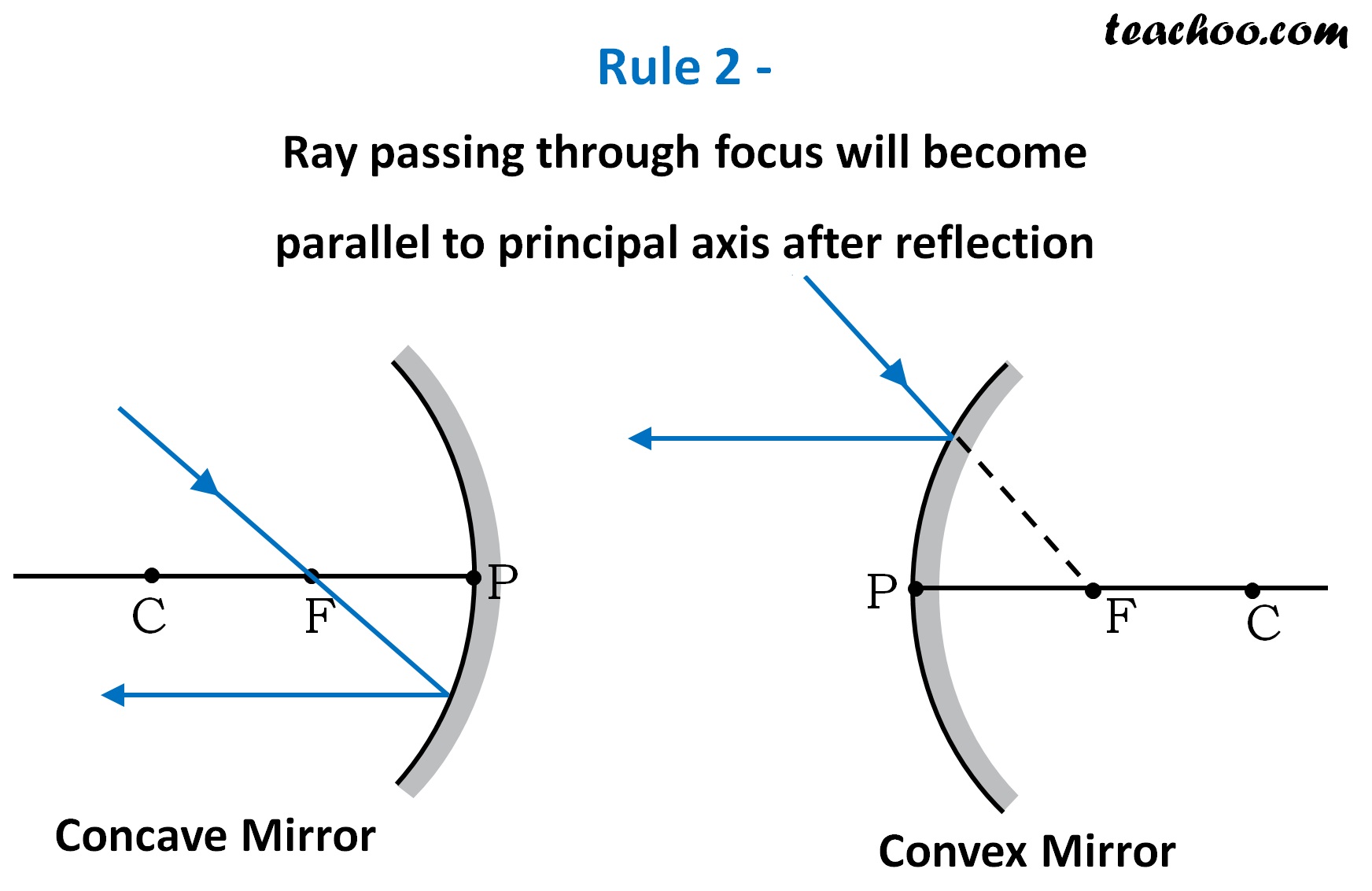
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
How to Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT)
Using A Straight Edge, Accurately Draw One Ray So That It Passes Exactly Through The Focal Point On The Way To The Lens.
Hence, Image Is Formed At Focus.
Since Ray Parallel To Principal Axis Appear To Pass Through The Focus.
Web Join Teachoo Black.
Related Post:
.PNG)
