Draw Phospholipid
Draw Phospholipid - Overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Structure and function of the cell membrane. 1k views 2 years ago a level biology. Please support the channel my. Web in contrast, the interior of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and will not interact with water. The head and the two tails. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. The phospholipids are very important structural components of all cell membranes including those of the cell organelles. Web describe the structure of a phospholipid. Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key terms below. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. Click the card to flip 👆. The phospholipids are very important structural components of all cell membranes including those of the cell organelles. 1k views 2 years ago a level biology. When you go to the dentist to get a tooth pulled, you really do not want to feel any. Web the parts of a phospholipid molecule. Please support the channel my. Web draw the general structure of a phosphoglyceride. The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in the single phospholipid molecule. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. Web phospholipids are lipids containing phosphorus. It has that polar phosphate head group, and it has two fatty acid chains. The head and the two tails. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Image modified from openstax biology. Web the parts of a phospholipid molecule. Web phospholipids are a very important class of lipids containing phosphorous bound in a diester linkage. Infant respiratory distress syndrome (irds) The two tails are made up of fatty acids (chains of carbon atoms) that aren’t compatible with, or repel, water ( hydrophobic ). Label the three major parts. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. Web in contrast, the interior of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and will not interact with water. Infant respiratory distress syndrome (irds) Properties of the phospholipid bilayer. Image modified from openstax biology. All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes, and this characteristic best portrayed by the fluid mosaic model. Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Label the three major parts. Identify the polar (hydrophilic) and nonpolar (hydrophobic) regions of a phospholipid. Each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. One of the proteins is shown with a channel in it. Image modified from openstax biology. Some phospholipids like lecithin’s may also play an important role in transport of ions across the membranes. Click the card to flip 👆. Click the card to flip 👆. This phospholipid molecule is composed of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. The two tails are made up of fatty acids (chains of carbon atoms) that aren’t compatible with, or repel, water ( hydrophobic ). There are two important parts of a phospholipid: There are two important parts of a phospholipid: It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Web phospholipids are a very important class of lipids containing phosphorous bound in a diester linkage. Web the parts of a phospholipid molecule. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ). A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Web in contrast, the interior of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and will not interact with water. The head and the two tails. This phospholipid molecule is composed of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. All cells are surrounded by the cell. Web draw the general structure of a phosphoglyceride. All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes, and this characteristic best portrayed by the fluid mosaic model. It has that polar phosphate head group, and it has two fatty acid chains. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. Web a diagram of a plasma membrane shows a phospholipid bilayer with 3 proteins embedded in the bilayer. Web phospholipids are a very important class of lipids containing phosphorous bound in a diester linkage. 1k views 2 years ago a level biology. Web phospholipids [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic head containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic tails derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Image modified from openstax biology. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. Each phospholipid is amphipathic, with two hydrophobic tails and a hydrophilic head. Web the parts of a phospholipid molecule. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. When you go to the dentist to get a tooth pulled, you really do not want to feel any pain. Infant respiratory distress syndrome (irds) Some phospholipids like lecithin’s may also play an important role in transport of ions across the membranes.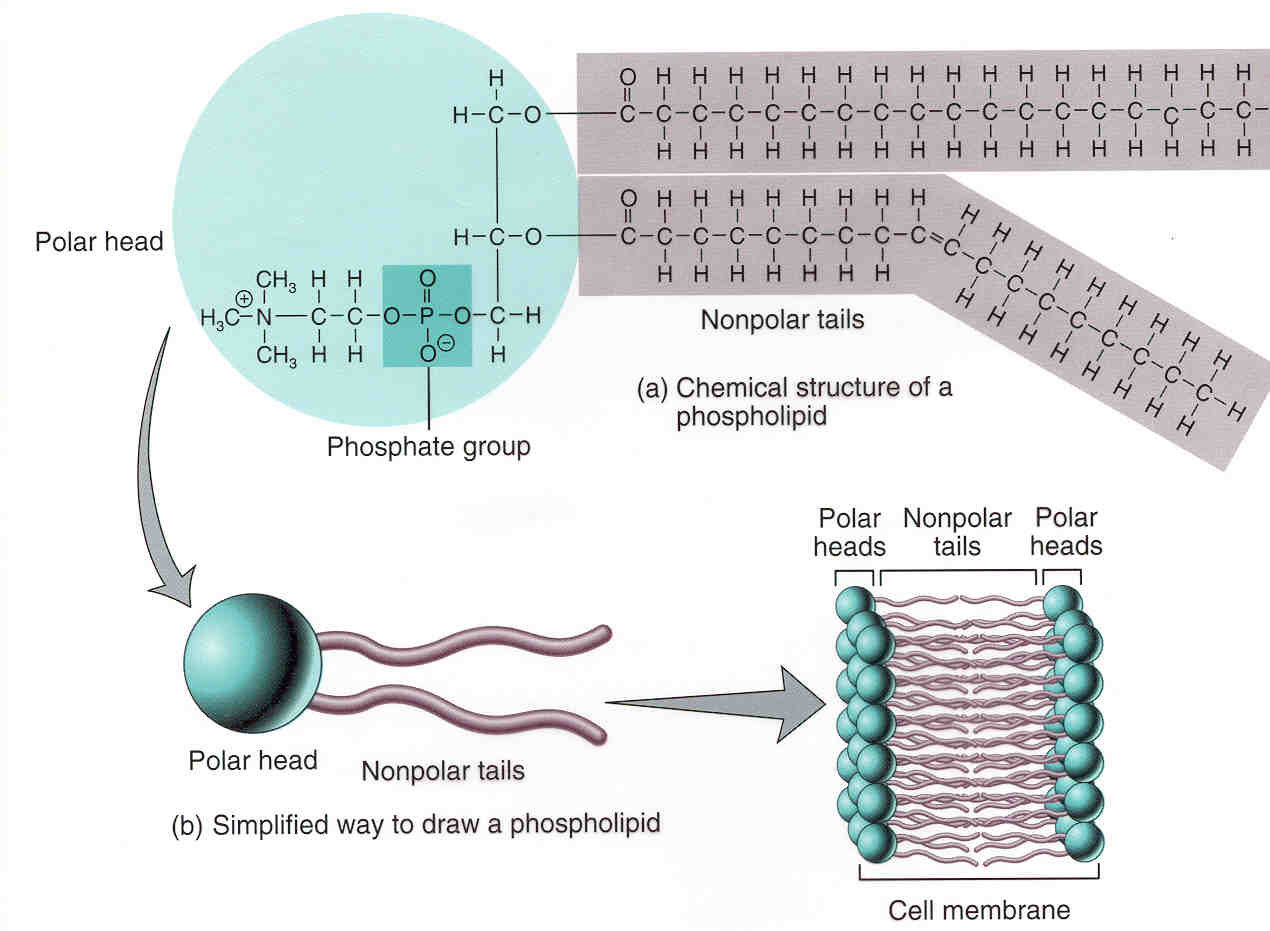
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction, Structure and Functions

3.5C Phospholipids Biology LibreTexts

Components and Structure OpenStax Biology 2e

Phospholipid or phosphatides lipids head and tail structure outline

Phospholipid Molecule Structure
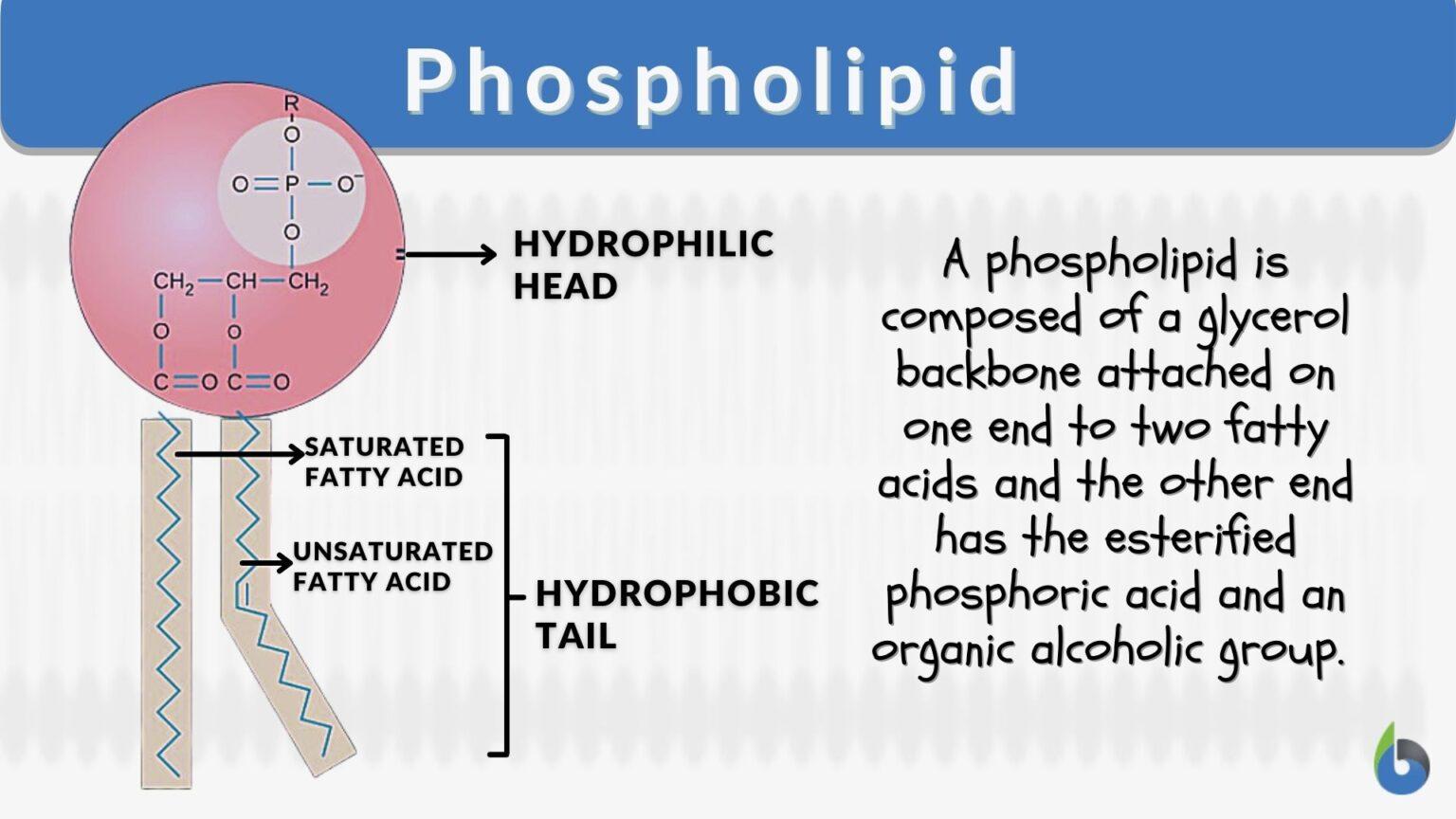
Phospholipid Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
/phospholipid_molecule-58adc6f95f9b58a3c9d1143f.jpg)
How Phospholipids Help Hold a Cell Together

Lipids · Microbiology

How to Draw a Phospholipid Bilayer YouTube
14.3 Phospholipids in Cell Membranes Chemistry LibreTexts
Web Phospholipids Are Lipids Containing Phosphorus.
The Phospholipids Are Very Important Structural Components Of All Cell Membranes Including Those Of The Cell Organelles.
Web In Contrast, The Interior Of The Cell Membrane Is Hydrophobic And Will Not Interact With Water.
Explain How The Phospholipid Molecules Form The Bilayer Of The Cell Membrane.
Related Post: