Draw And Label One Complete Cell Cycle
Draw And Label One Complete Cell Cycle - The life cycle is different from that of animals in that plants alternate between diploid and haploid forms b. Cells go through the process of cytokinesits, or division of cytoplasm, upon the completion of nuclear division. , which divides plant cell division, unltike animal cell division, involves formation. Web human cells exhibit typical eukaryotic cell cycle and take around 24 hours to complete one cycle of growth and division. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Gap 1 (g1), synthesis (s), gap 2 (g2), and mitosis (m). 6 draw and label one complete cell cycle. 7 draw and label one complete cell cycle. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: , which divides plant cell division, unltike animal cell division, involves formation. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The main phases are shown: Web overview of the cell cycle phases. Identify the characteristics of cytokinesis. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. The main phases are shown: During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. Web the cell cycle has two major phases: Web stages of the cell cycle. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated, and the cell divides. 6 draw and label one complete cell cycle. Web the cell cycle. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. Web draw your bead chromosomes in each stage of mitosis. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. Identify the characteristics and stages of mitosis. Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated, and the cell divides. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. 6 draw and label one complete cell cycle. During the mitotic phase, the duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. Cells go through the. When your entire group is ready, let your instructor know. During interphase, cells grow, replicate their dna and organelles, and prepare for division. Identify the characteristics and stages of mitosis. New cells are born through the division of their “parent” cell, producing two “daughter” cells from one single “parent” cell. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a. 6 draw and label one complete cell cycle. The main phases are shown: Cells divide during mitosis (m). Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal growth processes while also preparing for cell division. It is sometimes referred to as the “cell division cycle” for that reason. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. , which divides. The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically. The life cycle is different from that of animals in that plants alternate between diploid and haploid forms b. Web the cell cycle consists of interphase and the mitotic phase. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear. The main phases are shown: There are two distinct phases: 8 what does the production of new cells allow an organism to do? Gap 1 (g1), synthesis (s), gap 2 (g2), and mitosis (m). Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. During interphase, the cell grows and the nuclear dna is duplicated. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. The life cycle is different from that of animals in that plants alternate between diploid and haploid forms b. Web an overview of the cell cycle. Web students label the image of a cell undergoing mitosis and answer questions about the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. But be sure to accurately indicate the relative sizes and colors of each different chromosome pair. The cell cycle is divided into four stages: It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells.
Cell Cycle Diagram Quizlet
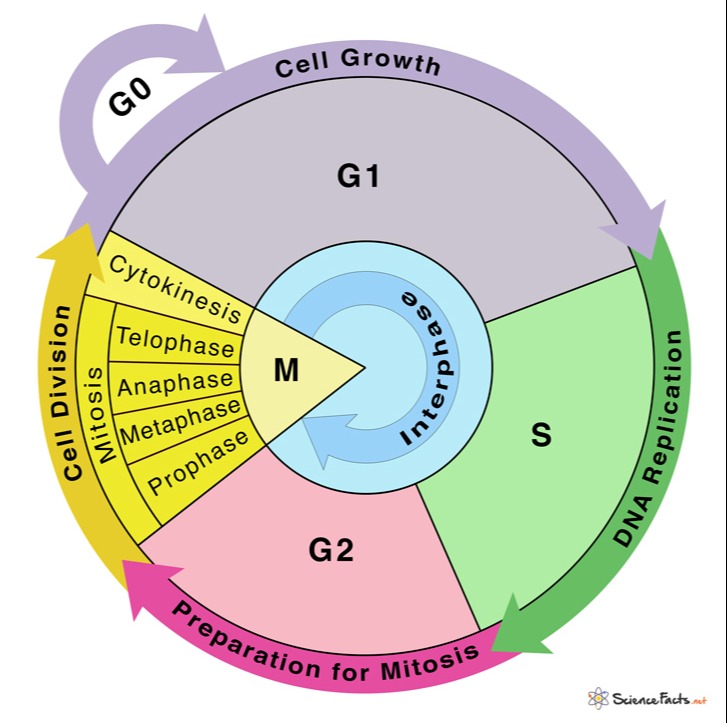
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit

Cell Cycle Phase Definition, Fours phases of Cell cycle Division
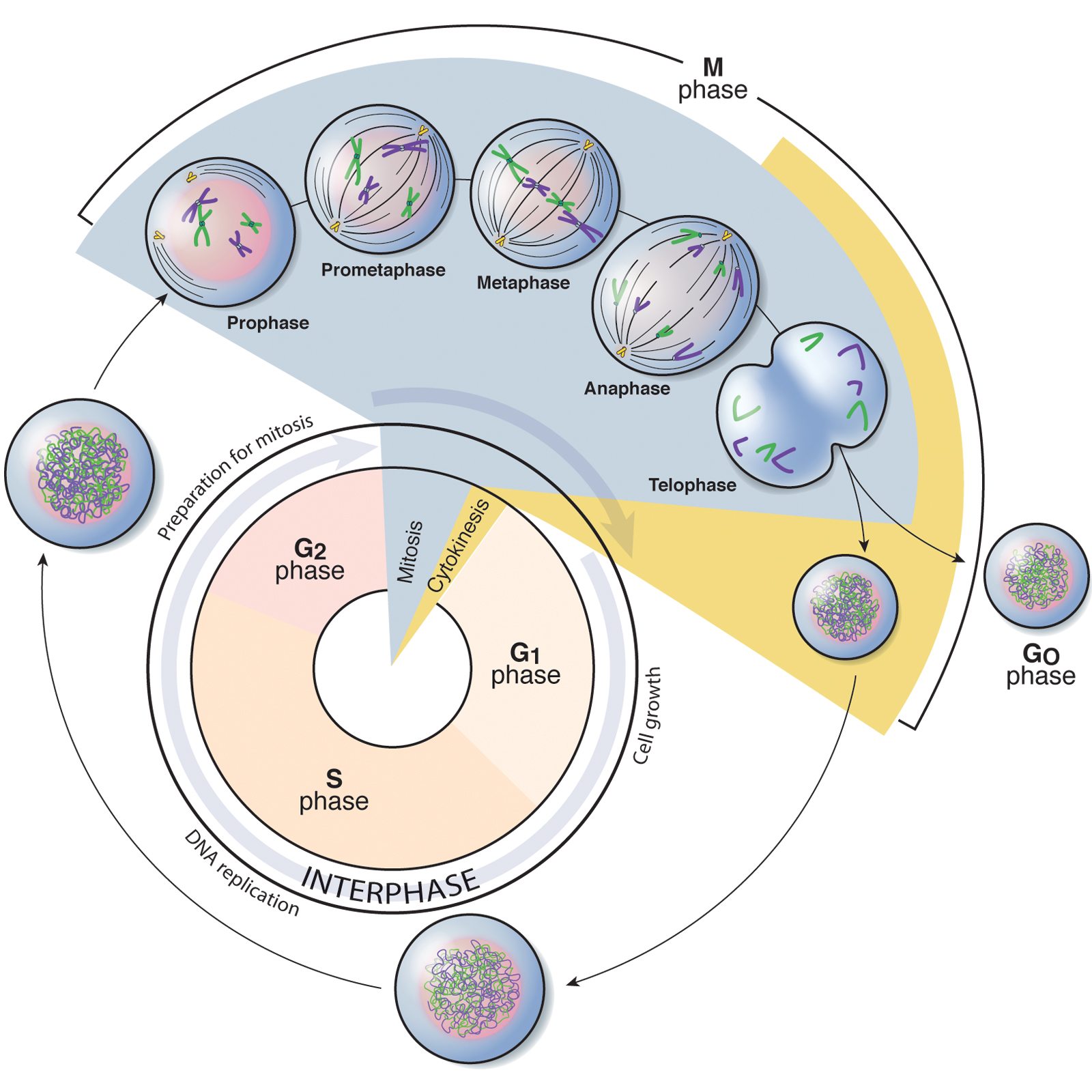
Phases of the cell cycle Battista Illustration
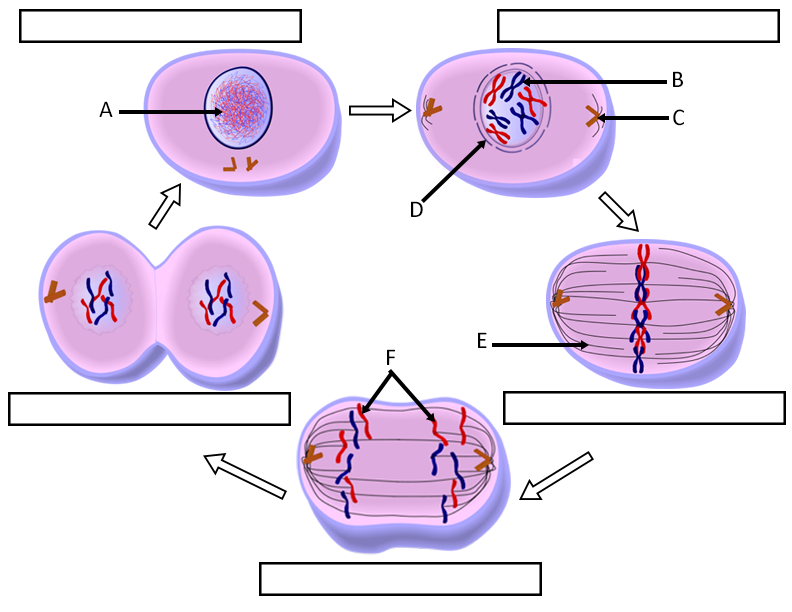
Cell Cycle Labeling

Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes Leverage Edu

The Cell Cycle Biology for Majors I

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
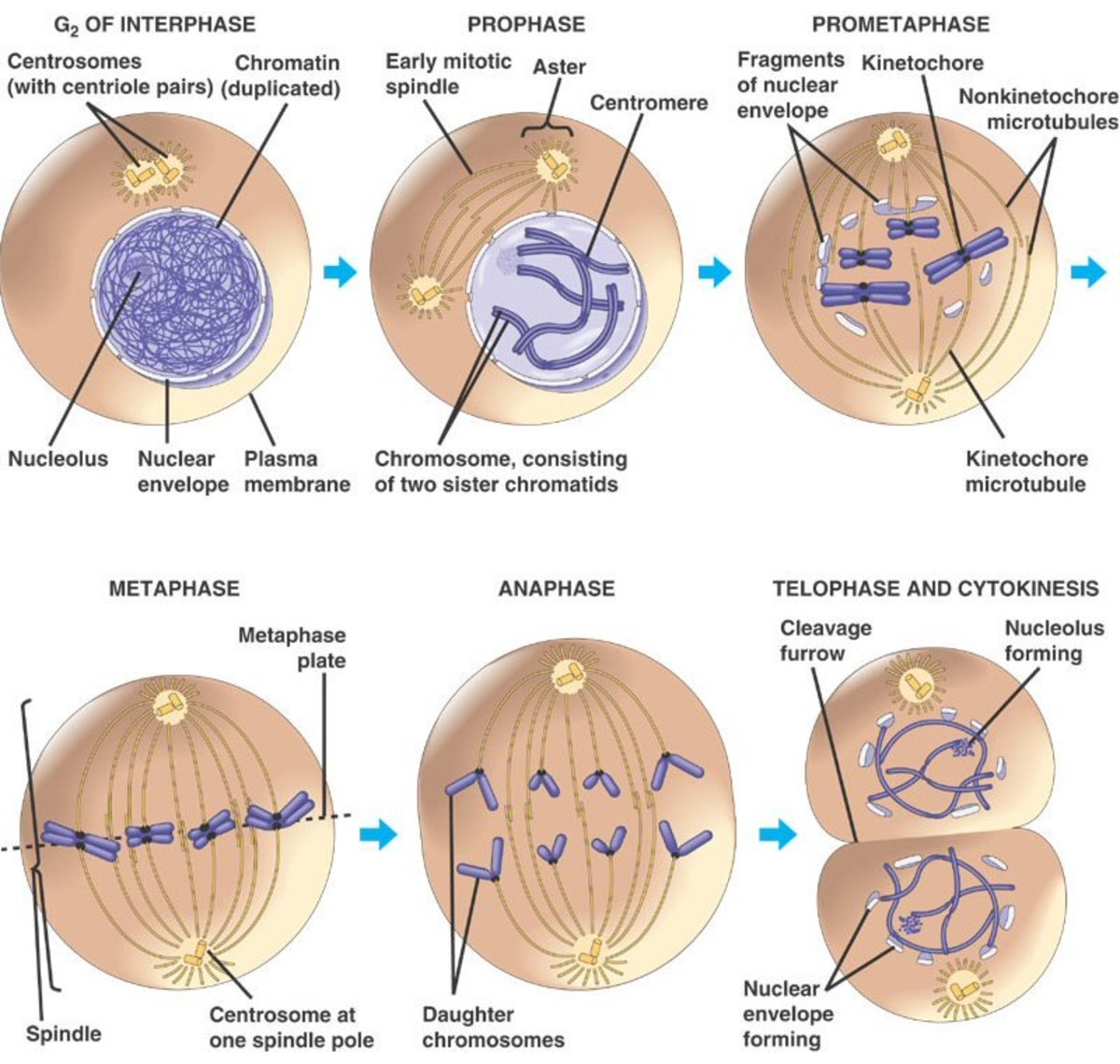
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
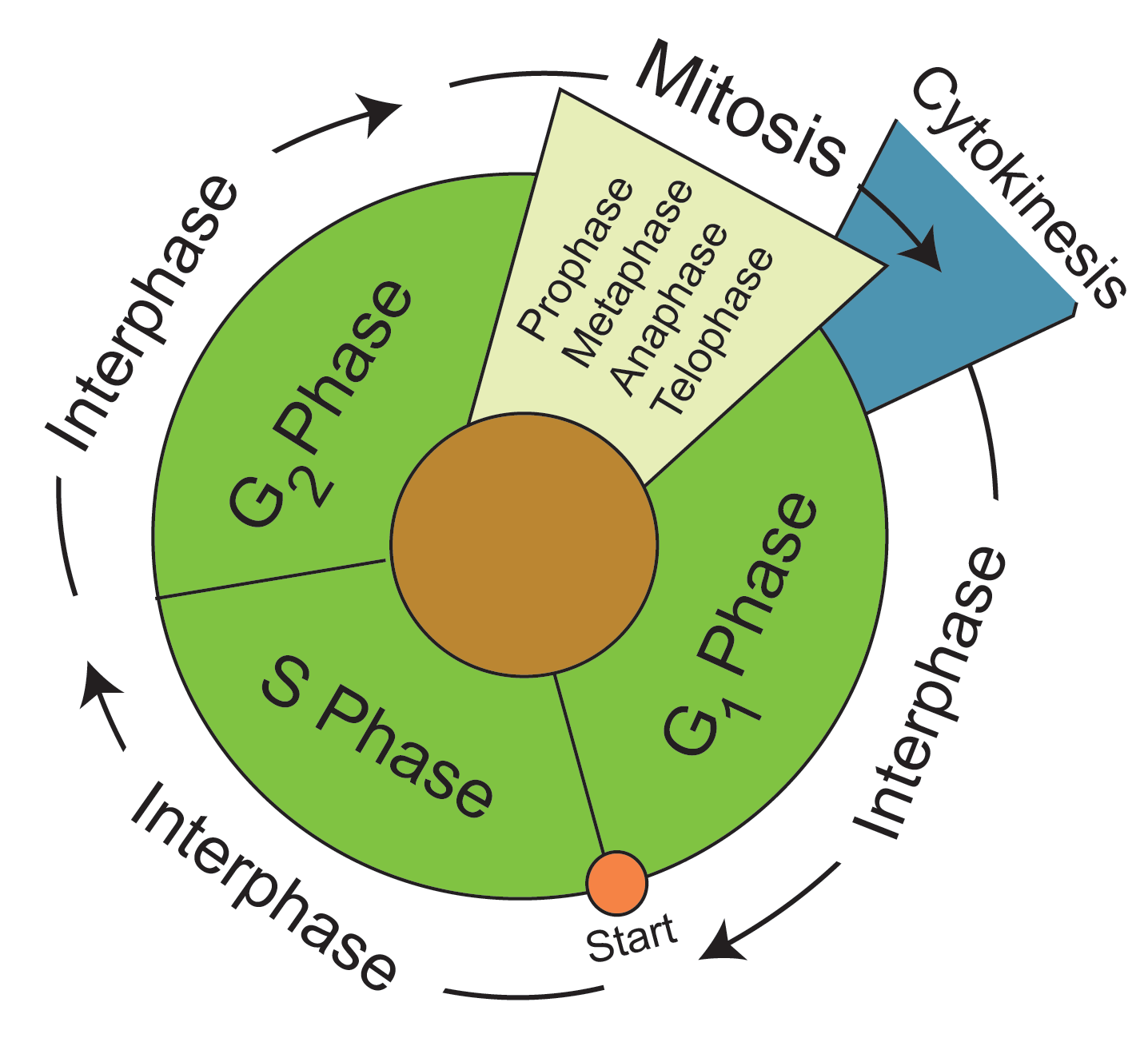
Cell Cycle Phases , Diagram , Types and Comparison
The Two Broad Phases Of The Cell Cycle Are Interphase And Mitosis.
Web The Cell Cycle Is An Orderly Sequence Of Events.
Cells On The Path To Cell Division Proceed Through A Series Of Precisely Timed And Carefully Regulated Stages Of Growth, Dna Replication, And Division That Produce Two Genetically Identical Cells.
During Interphase, Cells Grow, Replicate Their Dna And Organelles, And Prepare For Division.
Related Post: