Doppler Effect Drawing
Doppler Effect Drawing - Four example problems, instructive diagrams, and animations assist in the explanations. Use the sliders to adjust the speed of the sound source and the sound observer. Web the doppler effect happens when a wave's source is moving in relation to us: We have more practice problems on the doppler effect. Animations are used to show the observed change in. Web the doppler effect (also doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. Web next time an ambulance is zooming by you, try to pay attending to the pitch of the siren as it approaches you and then recedes away from you. Good news with doppler dave. The video lesson answers the following questions: As the source approaches, the waves arrive at a higher frequency. Explore the doppler effect for sound and sonic boom. The doppler effect (sound source moving slower than the speed of sound) Web the doppler effect happens when a wave's source is moving in relation to us: In this case, the maxima of the amplitude of the wave produced occur at intervals of the period t = 1 ν. The same. Web sketch the sky. Web next time an ambulance is zooming by you, try to pay attending to the pitch of the siren as it approaches you and then recedes away from you. The doppler effect and sonic boom. Why does the doppler effect occur? The doppler effect & sonic boom. “the apparent difference between the frequency at which sound or light waves leave a source and that at. We’d like to understand what happens when waves are produced from a moving source. The doppler effect & sonic boom. Explain why the pitch of a car horn changes as it approaches and then drives past. The same effect that causes the. You can set both the initial position and the velocity of the source (the small blue dot). Four example problems, instructive diagrams, and animations assist in the explanations. And the initial position and the velocity of the observer (green rectangle), and then see the pattern of waves emitted by the source as the waves wash over the observer. The doppler. The doppler effect and sonic boom. We’d like to understand what happens when waves are produced from a moving source. It explains how to solve doppler effect problems in. Explain why the pitch of a car horn changes as it approaches and then drives past. The doppler effect & sonic boom. This captivating phenomenon is known as the doppler effect. The doppler effect and sonic boom. This is a simulation of the doppler effect. Combing the two equations, the doppler effect for a moving source can be written as: Web the doppler effect is an alteration in the observed frequency of a sound due to motion of either the source or. Animations are used to show the observed change in. The doppler effect & sonic boom. Doppler effect worksheet word doc. This phenomenon was described by the austrian physicist christian doppler in 1842. Combing the two equations, the doppler effect for a moving source can be written as: Web learn about the doppler effect and how it explains the change in frequency of a wave when its source and an observer are moving. Web ever wondered why the sound of an ambulance siren changes as it speeds past you? This captivating phenomenon is known as the doppler effect. When the source of a sound wave is moving relative. Let’s say we have a source emitting sound with the frequency ν. As the source approaches, the waves arrive at a higher frequency. This captivating phenomenon is known as the doppler effect. This phenomena is known as the doppler effect. Four example problems, instructive diagrams, and animations assist in the explanations. This is a simulation of the doppler effect. We’d like to understand what happens when waves are produced from a moving source. The doppler effect & sonic boom. Explore the doppler effect for sound and sonic boom. Although less familiar, this effect is easily noticed for a stationary source and moving observer. Web draw pictures of high and low frequency wave fronts. The doppler effect is named after the physicist christian doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. This is a simulation of the doppler effect. The doppler effect and sonic boom. Explain why the pitch of a car horn changes as it approaches and then drives past. Doppler effect worksheet word doc. Web sketch the sky. Web the doppler effect involves motion and this video will help visualize the effects of a moving observer or source. The doppler effect (sound source moving slower than the speed of sound) And the initial position and the velocity of the observer (green rectangle), and then see the pattern of waves emitted by the source as the waves wash over the observer. Use the sliders to adjust the speed of the sound source and the sound observer. The doppler effect is demonstrated. The video lesson answers the following questions: Explain the doppler effect, with diagrams, and give examples of where it can be heard. Web according to sources like encyclopedia brittanica, the doppler effect is defined as: We’d like to understand what happens when waves are produced from a moving source.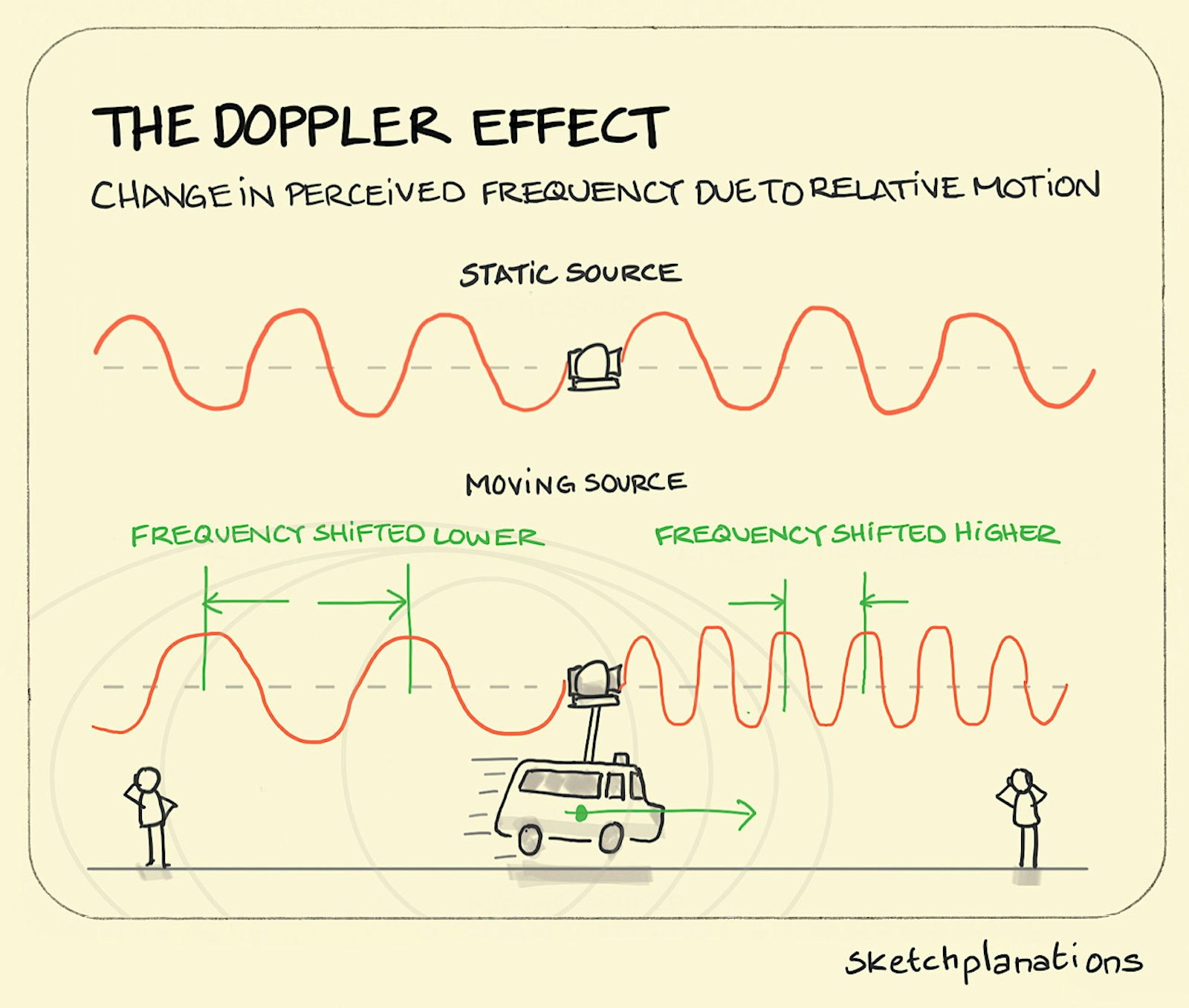
How Does the Doppler Effect Explain Differences in Sound Pitch
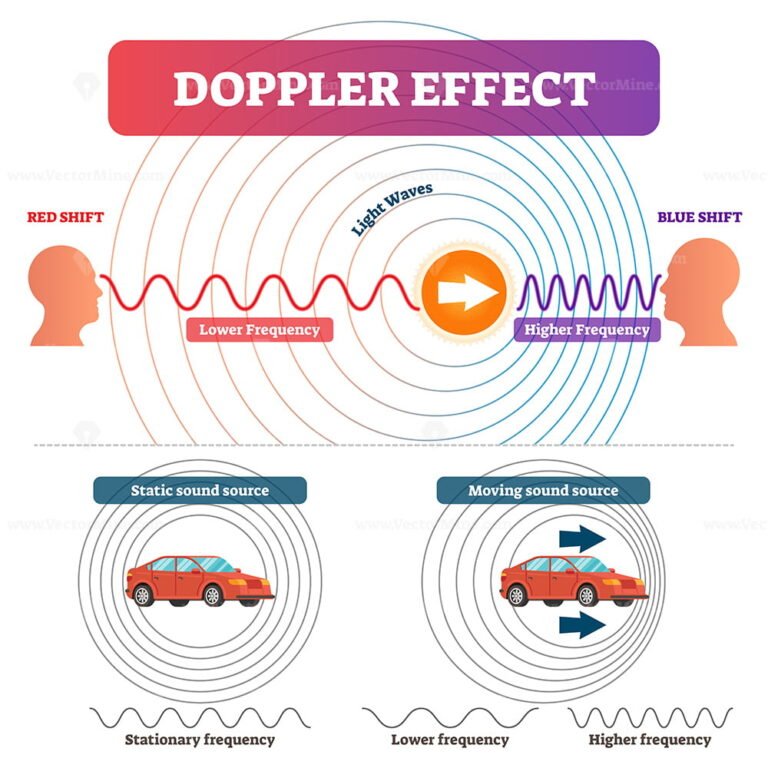
Doppler effect vector illustration VectorMine
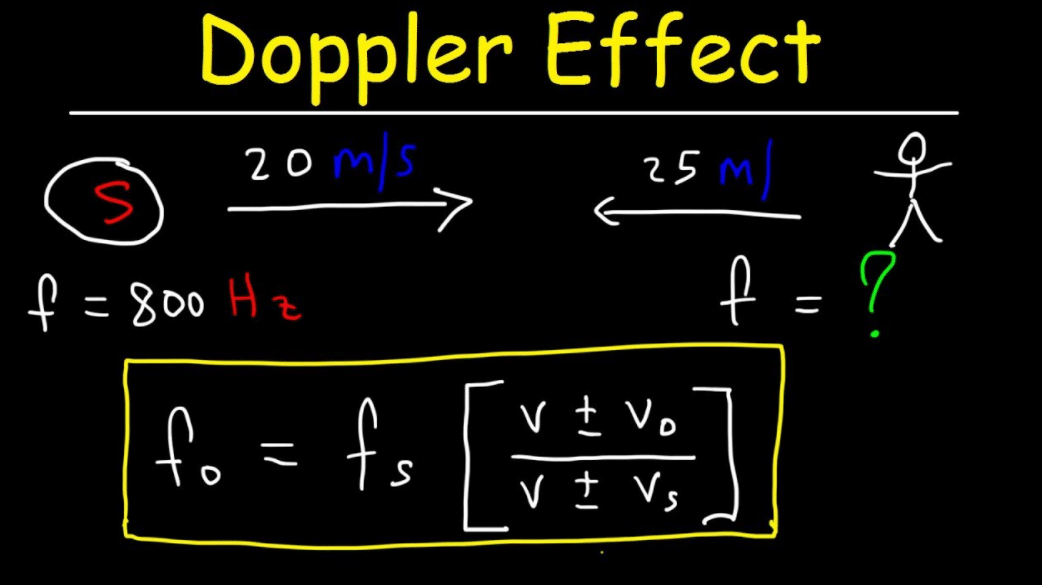
The Doppler Effect Formula & Calculation
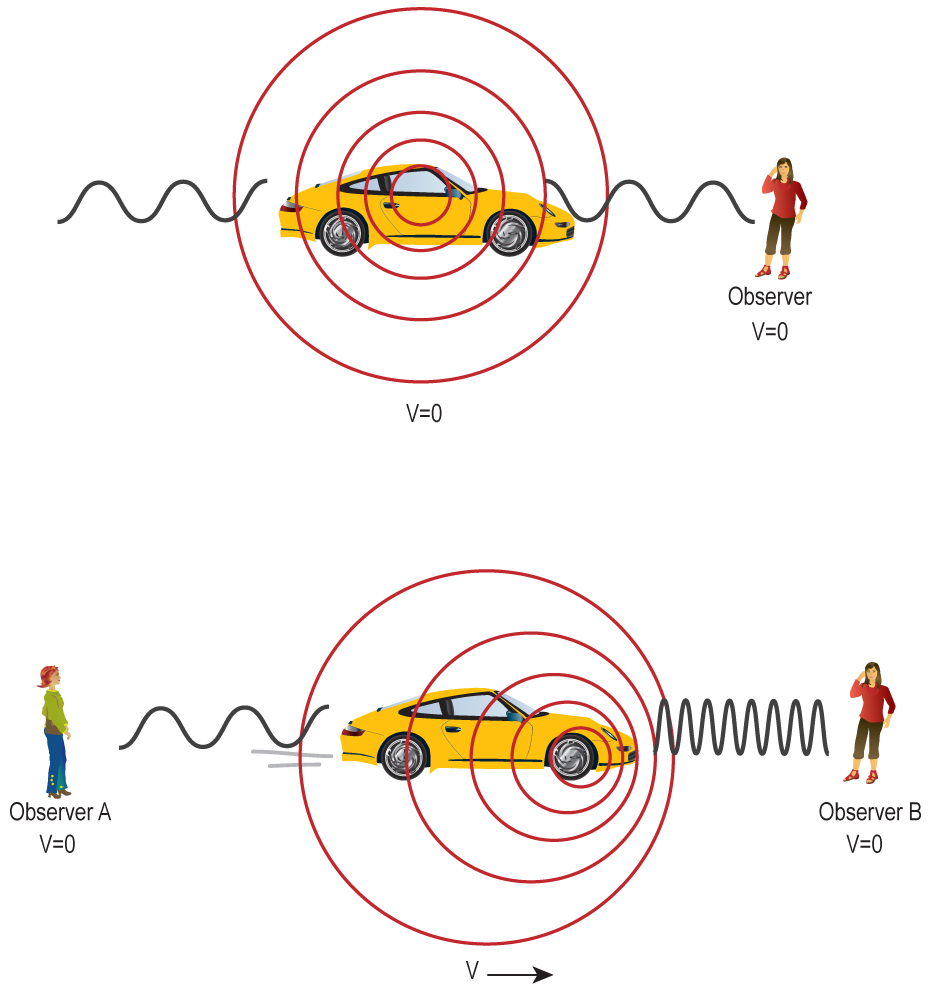
4.2 Measuring Motion the Doppler Shift Physics LibreTexts

Doppler Effect Tutorial Sophia Learning

Doppler Effect Definition Blue Shift, Red Shift Physics
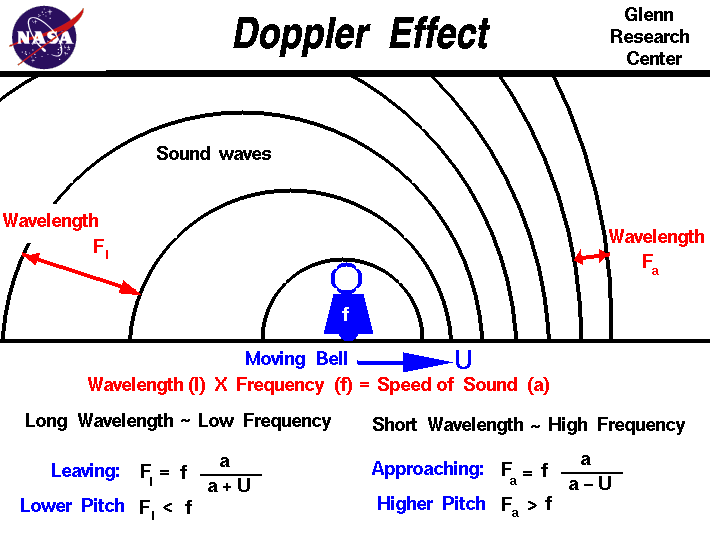
Doppler Effect

Doppler effect and Doppler echocardiography ECG & ECHO
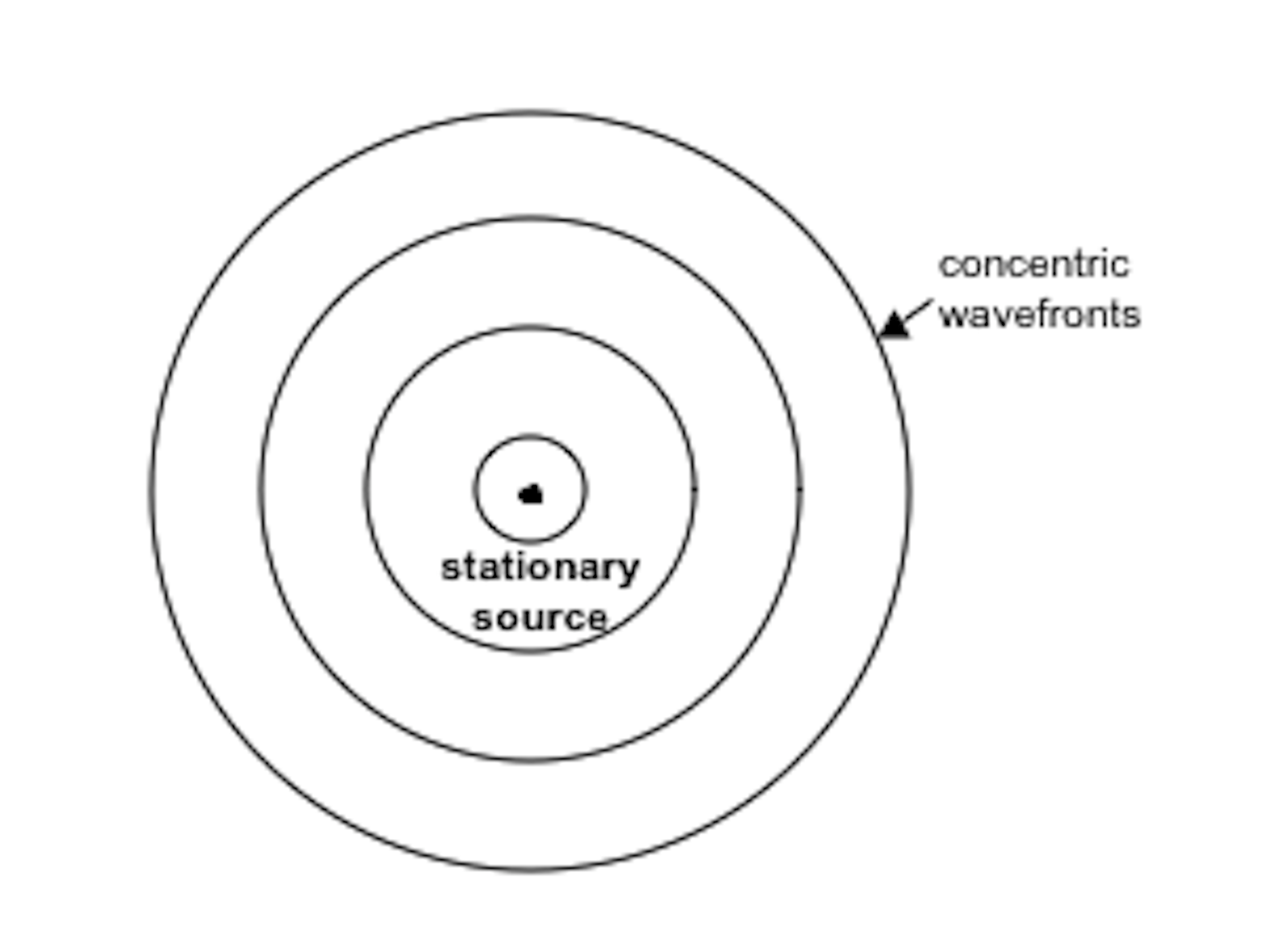
Explainer the Doppler effect

Doppler Effect Definition, Formula, and Examples
Animations Are Used To Show The Observed Change In.
Combing The Two Equations, The Doppler Effect For A Moving Source Can Be Written As:
Fire Weather Watch Is In Effect.
Understand How Moving Sound Sources Can Alter The Frequency And Pitch We Hear.
Related Post: