Cytokinesis Drawing
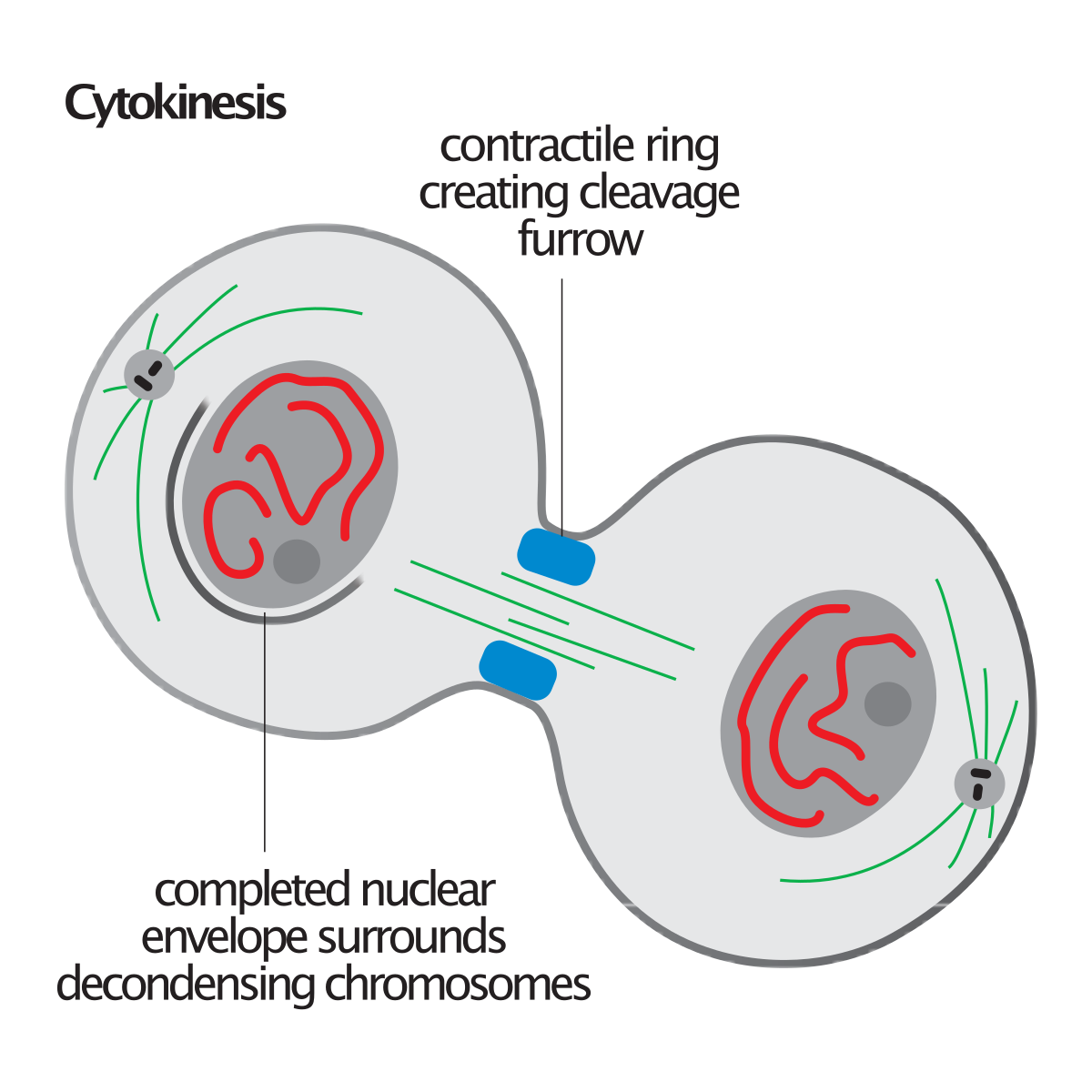
Cytokinesis Drawing - Cytokinesis, or “cell motion,” is the second main stage of the mitotic phase during which cell division is completed via the physical separation of the cytoplasmic components into two daughter cells. Web in cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell is split in two, making two new cells. The primary purpose of cytokinesis is to ensure that one nucleus ends up in each daughter cell after division. Cytokinesis is a physical process of cell division, that normally takes place after mitosis. Review setting up your microscope. Web cytokinesis is the process following the division of the nucleus, the cytoplasm and plasma membrane are divided, resulting in two cells, each with its own nucleus and cytoplasm surrounded by a plasma membrane. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. Mitosis in a whitefish embryo. Web this illustration is one of more than one hundred drawings from flemming's \cell substance, nucleus, and cell division.\ flemming repeatedly observed the different forms of chromosomes leading. Cytokinesis usually begins just as mitosis is ending, with a little overlap. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. This process is known as cytokinesis (also called cytodieresis), and is shown here for a plant (vegetal) cell. Web cytokinesis is the final step of the cell division process of a eukaryotic cell when the parent cell cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells. It occurs in both plant cells and animal cells. Cytokinesis. Francis leroy, biocosmos / science photo library. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: During interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. Diagram showing the stage of cell division that involves the splitting of the cell cytoplasm between two daughter cells. Web usually the cell will divide after mitosis in a process. Web explain how the cytoplasmic content is divided during cytokinesis. Web cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase, and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis. Estimating relative time spent in each stage of mitosis. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: Cytokinesis typically overlaps with anaphase and/or telophase. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. Web explain how the cytoplasmic content is divided during cytokinesis. Identify the characteristics of cytokinesis. Web cytokinesis illustration ciliate undergoing cytokinesis, with the cleavage furrow being clearly visible. Walk through the process of mitotic cell division to understand the foundation of growth. The cell cycle and mitosis: Cytokinesis (/ ˌ s aɪ t oʊ k ɪ ˈ n iː s ɪ s /) is the part of the cell division process and part of mitosis during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytokinesis usually begins just as mitosis is ending, with a little overlap. The. Web cytokinesis is the final step of the cell division process of a eukaryotic cell when the parent cell cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells. Diagram showing the stage of cell division that involves the splitting of the cell cytoplasm between two daughter cells. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: (more) see all videos for. Estimating relative time spent in each stage of mitosis. Cytokinesis usually begins just as mitosis is ending, with a little overlap. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. It occurs concurrently with two types of nuclear division called. Cytokinesis is the physical division of the cell cytoplasm, the cell membrane, and cell organelles in. Web cytokinesis is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: The process of cell division begins with cell growth and nuclear doubling and ends with cytokinesis, the physical separation of the two identical daughter cells. Division is not complete. Cytokinesis usually begins just as mitosis is ending, with a little overlap. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: Web cytokinesis is the final step of the cell division process of a eukaryotic cell when the parent cell cytoplasm divides to form two daughter cells. Identify the characteristics of cytokinesis. The position of the cell plate is. Mitosis in a whitefish embryo. Cytokinesis is the final process in eukaryotic cell division, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles, and cellular membrane. Web usually the cell will divide after mitosis in a process called cytokinesis in which the cytoplasm is divided and two daughter cells are formed. Cytokinesis, or “cell motion,” is the second main stage of the mitotic phase. Estimating relative time spent in each stage of mitosis. (more) see all videos for this article. Cytokinesis (/ ˌ s aɪ t oʊ k ɪ ˈ n iː s ɪ s /) is the part of the cell division process and part of mitosis during which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell divides into two daughter cells. Web in cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell is split in two, making two new cells. It occurs in tandem with two types of nuclear divisions: Mitosis in a whitefish embryo. College of the redwoods via asccc open educational resources initiative. All phases of mitosis, as well as the flanking periods of. Cytokinesis usually begins just as mitosis is ending, with a little overlap. Web cytokinesis is the final physical cell division that follows telophase, and is therefore sometimes considered a sixth phase of mitosis. Cytokinesis is a physical process of cell division, that normally takes place after mitosis. During interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web cytokinesis illustration ciliate undergoing cytokinesis, with the cleavage furrow being clearly visible. Francis leroy, biocosmos / science photo library. Web usually the cell will divide after mitosis in a process called cytokinesis in which the cytoplasm is divided and two daughter cells are formed.
What is Cytokinesis? (with pictures)

What is Cytokinesis? (with pictures)
Cell Cycle Regulation Cyclins and CDKs PraxiLabs
Cytokinesis Drawing at Explore collection of
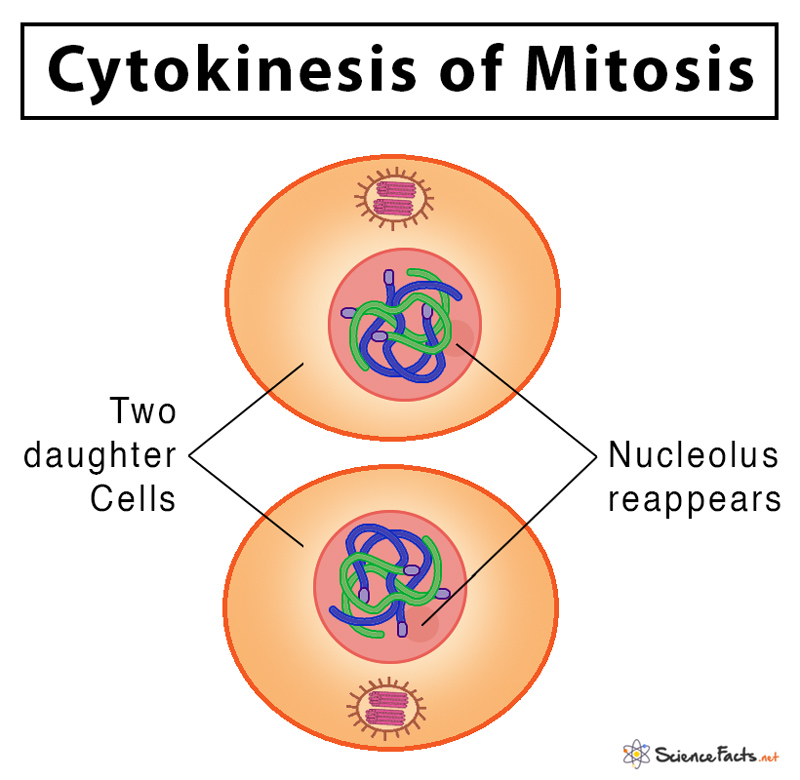
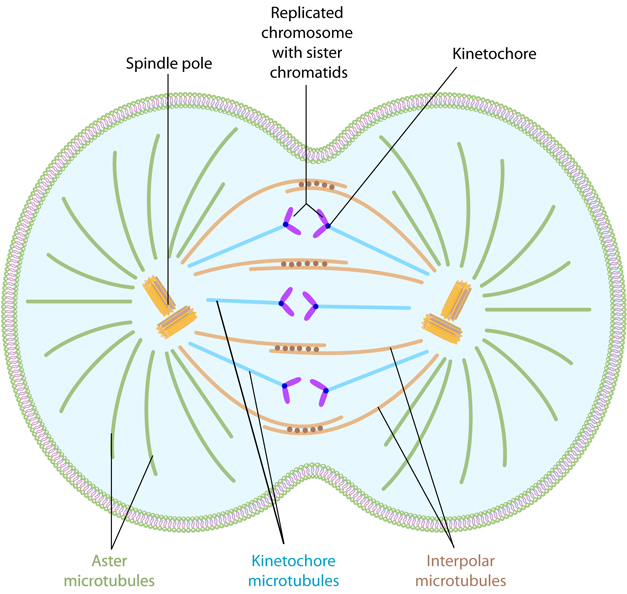
Mitosis Definition, Stages, & Purpose, with Diagram
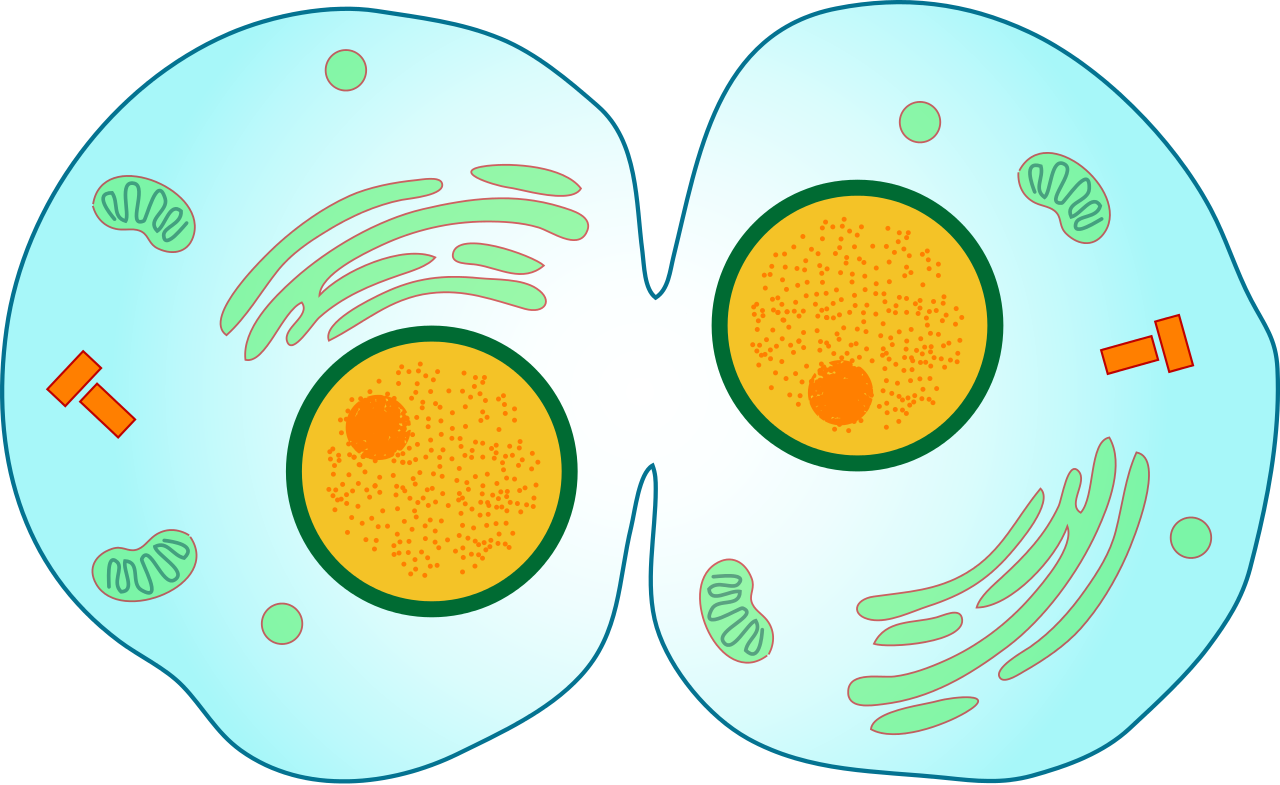
Cytokinesis Drawing at Explore collection of
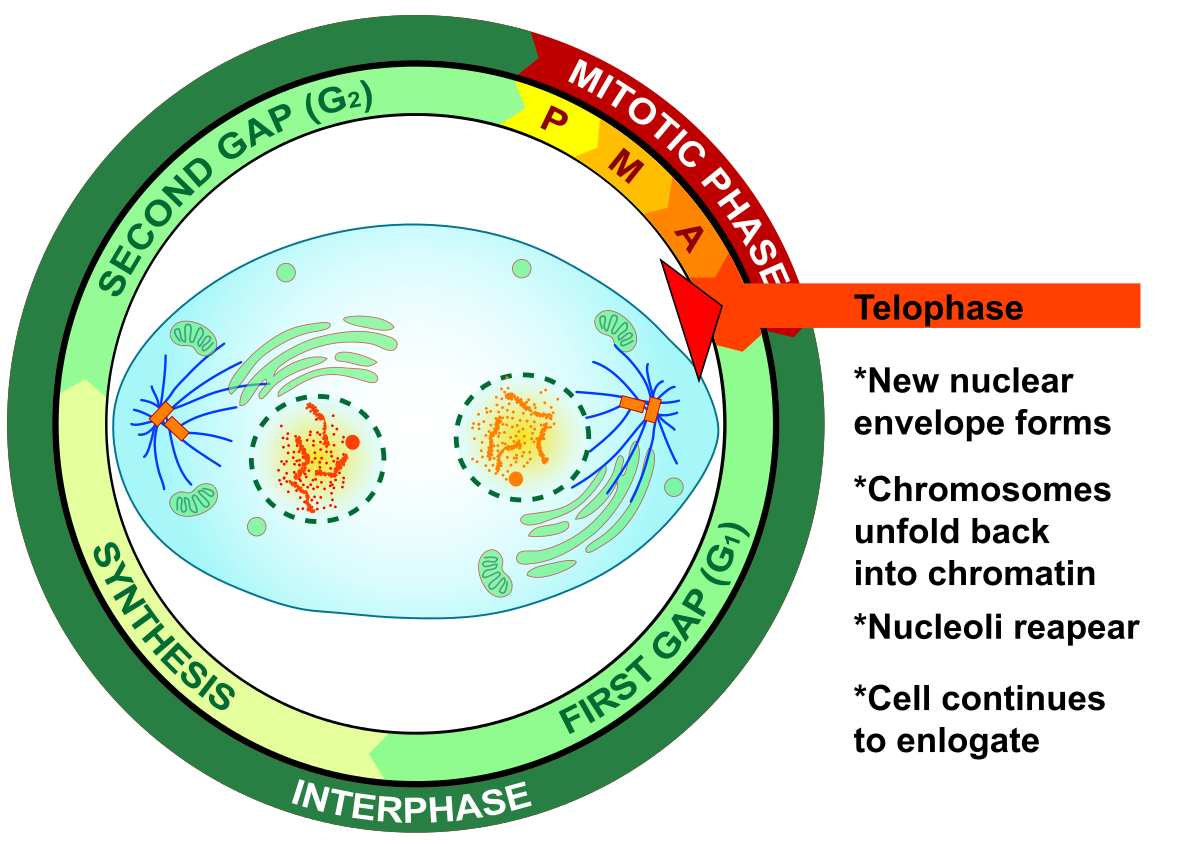
Cytokinesis Drawing at Explore collection of

Biology 2e, The Cell, Cell Reproduction, The Cell Cycle OpenEd CUNY
EduPic Cell Drawings
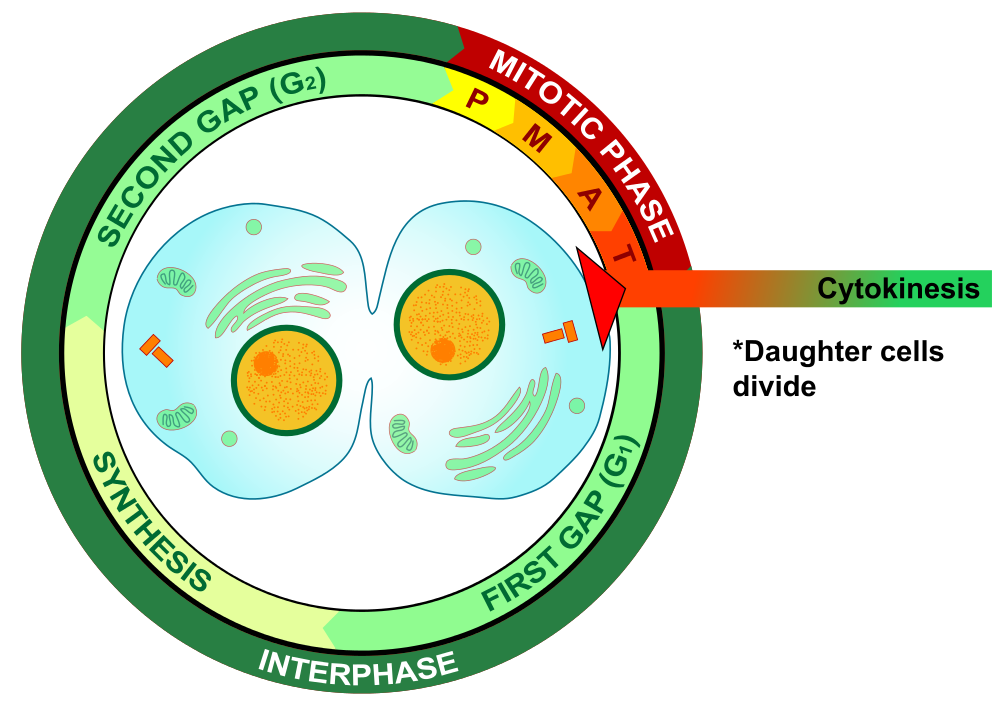
4.13 Mitosis and Cytokinesis Human Biology
Cells Are The Building Blocks Of Most Organisms.
The Cell Cycle And Mitosis:
Cytokinesis, Or “Cell Motion,” Is The Second Main Stage Of The Mitotic Phase During Which Cell Division Is Completed Via The Physical Separation Of The Cytoplasmic Components Into Two Daughter Cells.
Identify The Characteristics Of Cytokinesis.
Related Post: