Cranial Drawer Sign
Cranial Drawer Sign - Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of. Web the key to diagnosis of a ruptured ccl is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called the 'cranial drawer sign'. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. This video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust). 8.3k views 2 years ago. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. In order to feel this, you dog will be placed on his/ her side, and the veterinarian will feel the. Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”. In some cases, however, a crisp endpoint to the cranial drawer motion. 8.3k views 2 years ago. Pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. The drawer test is used in the initial clinical assessment of suspected rupture of the cruciate ligaments in the knee. Web the clinical diagnosis is based on a positive drawer test in which the tibial plateau is. Web this is the positive cranial drawer sign. The resulting instability damages the cartilage and. In some cases, however, a crisp endpoint to the cranial drawer motion. Most dogs with this injury cannot walk normally and they experience pain. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured. Web this movement is known as a positive drawer sign. Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point. Web one of the difficult orthopedic test to learn when you are just starting out as a rehabilitation practitioner or veterinarian is the. Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”. Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Common findings may include pain localized to the stifle, joint effusion. In order to feel this, you dog will be placed on his/. The drawer test is used in the initial clinical assessment of suspected rupture of the cruciate ligaments in the knee. Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. A small bony fragment may be seen at the. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a. Comparing the affected stifle with the normal stifle provides a ready frame of reference. Common findings may include pain localized to the stifle, joint effusion. A small bony fragment may be seen at the. The veterinarian stabilizes the position of the femur with. In order to feel this, you dog will be placed on his/ her side, and the veterinarian. A small bony fragment may be seen at the. Web the clinical diagnosis is based on a positive drawer test in which the tibial plateau is manually displaced cranially with a fixed distal femur. Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion. This video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust). Most dogs with this injury cannot walk normally and they experience pain. In some cases, however, a crisp endpoint to the cranial drawer motion. Common findings may include pain localized to the stifle, joint effusion. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. This video demonstrates how to perform the cranial drawer and tibial compression (tibial thrust). Web the diagnosis of cclr is typically based on the presence of the “cranial drawer sign”. A presumptive diagnosis of a cranial cruciate ligament injury is based on the physical. Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point. The cranial drawer sign is pathognomonic for rupture of the cranial cruciate ligament (crcl). A presumptive diagnosis of a cranial cruciate ligament injury is based on the physical exam. Web diagnosis of cranial. 8.3k views 2 years ago. Web the key to diagnosis of a ruptured ccl is the demonstration of an abnormal knee motion called the 'cranial drawer sign'. Comparing the affected stifle with the normal stifle provides a ready frame of reference. The drawer test is used in the initial clinical assessment of suspected rupture of the cruciate ligaments in the knee. Anesthesia may be necessary to move the limb to the extent needed because pain from a ruptured. The resulting instability damages the cartilage and. Web diagnosing cranial cruciate ligament pathology is easy when a supportive history, signalment, gait evaluation, and radiographic appearance are combined with. Web a positive cranial drawer sign can be elicited, and radiographs show joint effusion and cranial dislocation of the tibia (fig. Web if it is suspected that your dog has a cranial cruciate ligament tear or rupture, your veterinarian will perform a physical exam to determine whether or not this type of. A small bony fragment may be seen at the. Web the cranial drawer sign is definitive for diagnosing ccl rupture. Web the loss of these normal findings indicates periarticular fibrosis, joint effusion or both. Web the ability to move the tibia forward (cranially) with respect to a fixed femur is a positive cranial drawer sign indicative of a ccl rupture. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the. Web on an orthopedic examination, muscle mass asymmetry, joint effusion, tissue warmth, painful flexion and extension of the stifle joint and decreased joint range of motion point. Lameness may resolve in patients weighing.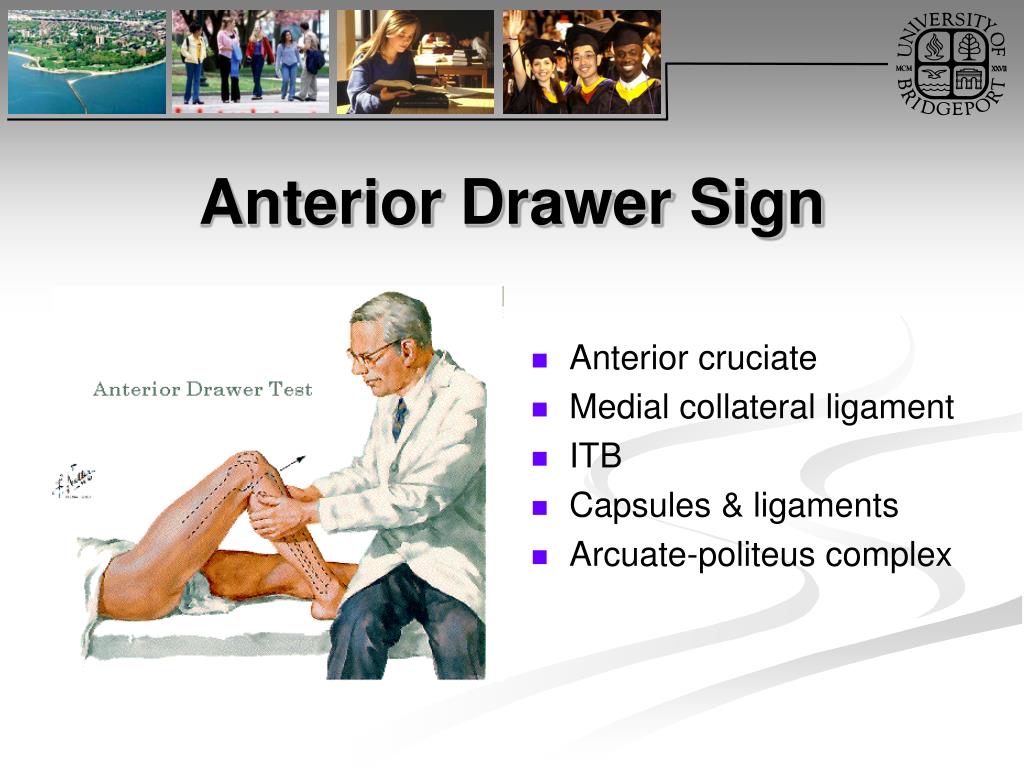
PPT Knee Orthopaedic Tests PowerPoint Presentation, free download
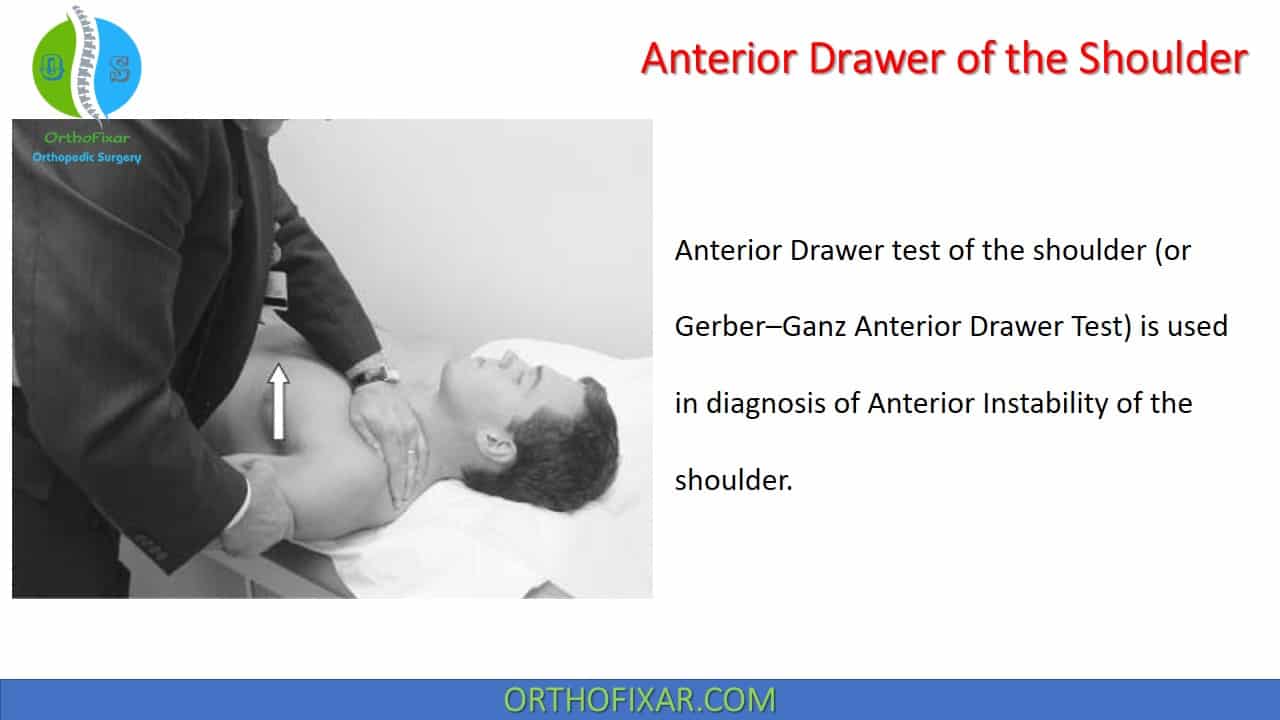
Anterior Drawer Test Shoulder

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior

PPT Joints of the Lower Limb PowerPoint Presentation, free download
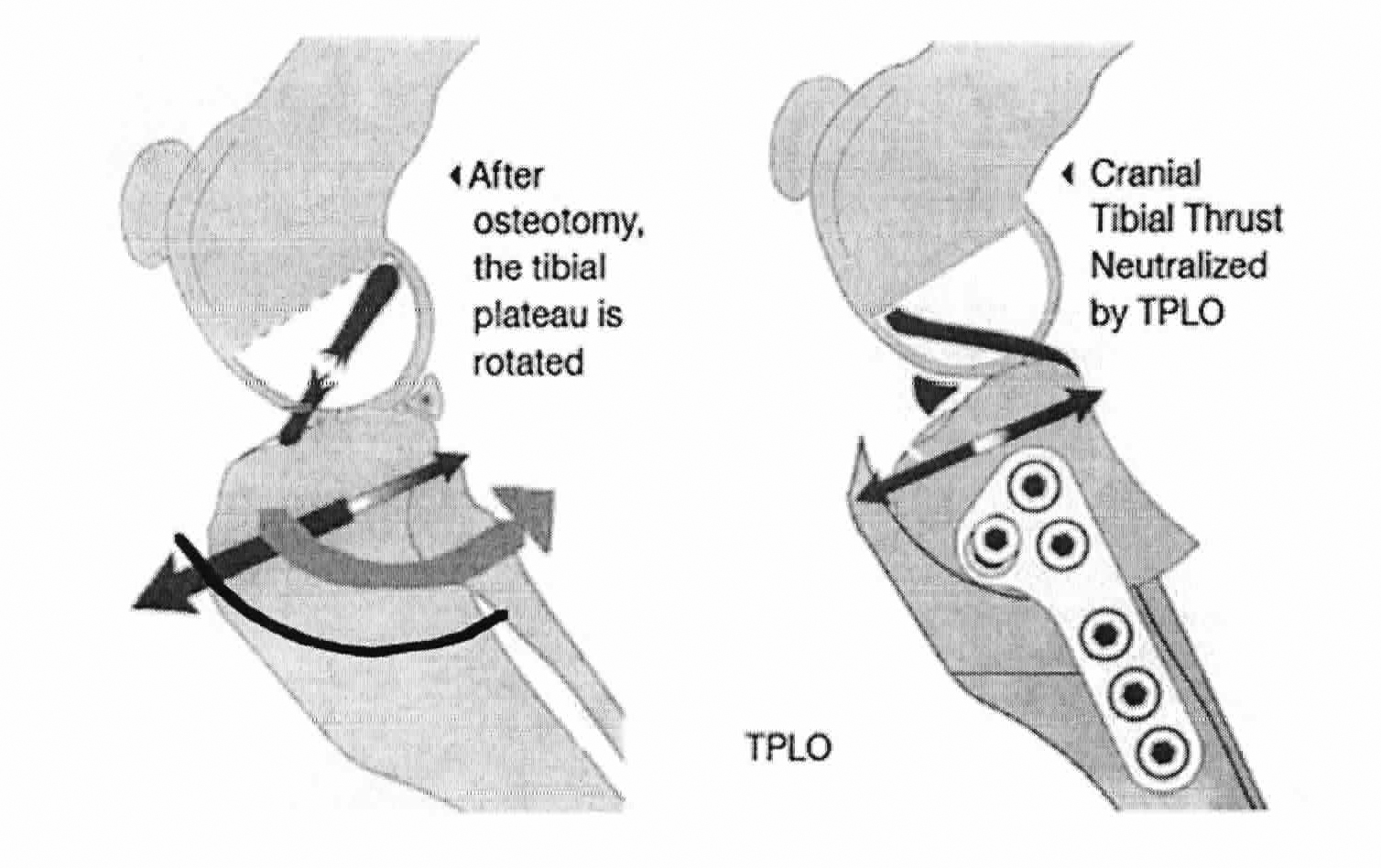
Tibial Plateau Leveling Osteotomy

Medicine Notes, Emergency Medicine, Physical Therapy Education, Nurse

Cranial drawer test/sign for diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube
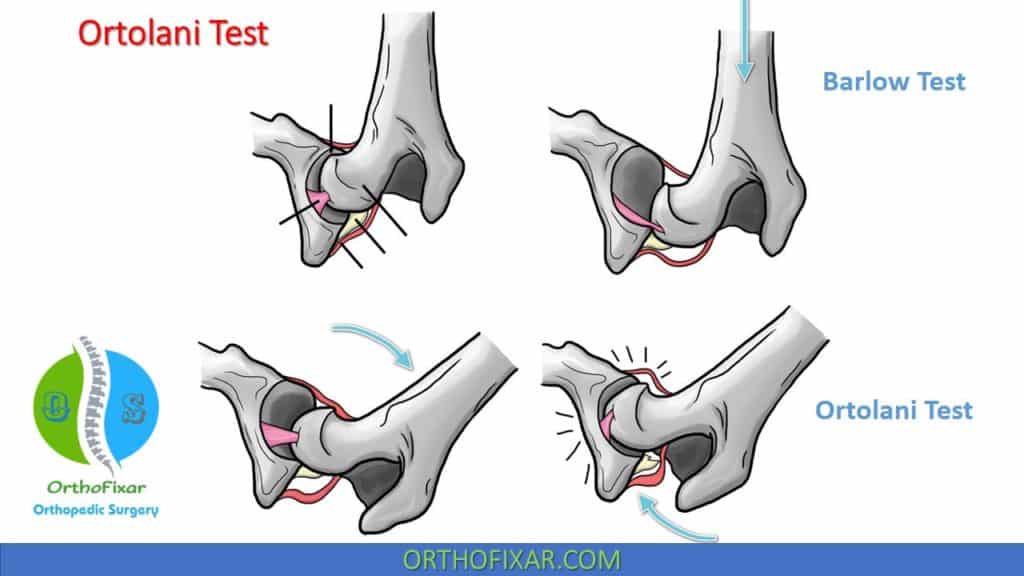
Ortolani Test OrthoFixar 2023
Web This Is The Positive Cranial Drawer Sign.
Web The Clinical Diagnosis Is Based On A Positive Drawer Test In Which The Tibial Plateau Is Manually Displaced Cranially With A Fixed Distal Femur.
In Order To Feel This, You Dog Will Be Placed On His/ Her Side, And The Veterinarian Will Feel The.
Web The Diagnosis Of Cclr Is Typically Based On The Presence Of The “Cranial Drawer Sign”.
Related Post: