Codon Drawing
Codon Drawing - Web this index considers both the supply and the demand of a codon by computing for each codon a weight which is based on the tai and the relative frequency of the relevant codon in all the mrnas. Most importantly, the position of the start codon determines the reading frame, or how the mrna sequence is divided up into groups of three nucleotides inside the ribosome. What is evolution and how does it work? Draw a picture of the completed protein coded for by this strand of dna (abbreviations are fine). In the genetic code, groups of three mrna nucleotides stand for one amino acid. A large and a small subunit. Web a codon chart, often referred to as a codon table, is an essential scientific reference tool that provides a systematic representation of the relationship between sequences of three nucleotides, known as codons, and the amino acids they encode. Conservation of codons means that a purified mrna encoding the globin protein in horses could be transferred to a tulip cell, and the tulip would synthesize horse globin. Web one codon is a start codon that indicates where to start translation. Here are some features of codons: Uga, uaa, and uag are stop codons. So you've seen our dna vs rna and protein synthesis videos, but now you may be wondering how to use. It can measure translation efficiency. Web one codon is a start codon that indicates where to start translation. You can see this in the image below: The start codon specifies the amino acid methionine, so most polypeptides begin with this amino acid. Web a ribosome is made up of two basic pieces: How to read a codon chart. Learn about codons, the start and stop codon definitions, codon examples. Which amino acid does codon 2 in the drawing stand for? Uga, uaa, and uag are stop codons. Three other “stop” codons signal the end of a polypeptide. Image showing how each gene is made up codons (aka the a, t, g, and c bases). You can see this in the image below: As shown in the diagram below, the same sequence of nucleotides can encode. Three stop codons mark the end of a protein. How to read a codon chart. Walter suza & donald lee. Web this lesson outlines the basic steps of how dna forms protein and how to read a codon chart. The start codon specifies the amino acid methionine, so most polypeptides begin with this amino acid. A large and a small subunit. Codons are made up of any triplet combination of the four nitrogenous bases adenine (a), guanine. Strands and directions of synthesis. The ribosome moves forward on the mrna, codon by codon, as it is read and translated into a polypeptide (protein chain). Most codons specify an amino acid. Web author yash solanki. Three mrna nucleotides are called a codon. Web draw a complete picture of all the trna molecules that will match up with the codons from the previous question. Web this lesson outlines the basic steps of how dna forms protein and how to read a codon chart. Web a ribosome is made up of two basic. During translation, the two subunits come together around a mrna molecule, forming a complete ribosome. Three stop codons mark the end of a protein. Web there are dozens of different analyses available, including comparisons of gc content at different codon positions, measures of codon usage bias, amino acid usage, and a markov model method for hgt detection (fig. A large. What is evolution and how does it work? You can see this in the image below: Most codons specify an amino acid. So you've seen our dna vs rna and protein synthesis videos, but now you may be wondering how to use. Web a codon is a segment (or piece) of double stranded dna that is three nucleotides long. Include all appropriate amino acids in your picture, and do not mix up their order! Web this index considers both the supply and the demand of a codon by computing for each codon a weight which is based on the tai and the relative frequency of the relevant codon in all the mrnas. Three other “stop” codons signal the end. Web a codon chart, often referred to as a codon table, is an essential scientific reference tool that provides a systematic representation of the relationship between sequences of three nucleotides, known as codons, and the amino acids they encode. Three other “stop” codons signal the end of a polypeptide. Web the start codon is critical because it determines where translation. Walter suza & donald lee. Web cells use this same coding system to translate messenger rna nucleotide sequences into the amino acid sequences of proteins. How to read a codon chart. The start codon specifies the amino acid methionine, so most polypeptides begin with this amino acid. So you've seen our dna vs rna and protein synthesis videos, but now you may be wondering how to use. What does a codon code for? Three mrna nucleotides are called a codon. Here are some features of codons: Web a codon is a segment (or piece) of double stranded dna that is three nucleotides long. One start codon, aug, marks the beginning of a protein and also encodes the amino acid methionine. Strands and directions of synthesis. You can see this in the image below: Most importantly, the position of the start codon determines the reading frame, or how the mrna sequence is divided up into groups of three nucleotides inside the ribosome. It calls for a specific amino acid to be brought. Web there are dozens of different analyses available, including comparisons of gc content at different codon positions, measures of codon usage bias, amino acid usage, and a markov model method for hgt detection (fig. In the genetic code, groups of three mrna nucleotides stand for one amino acid.
RNA Codons Chart For Amino Acids Sequences. The Codon Circle
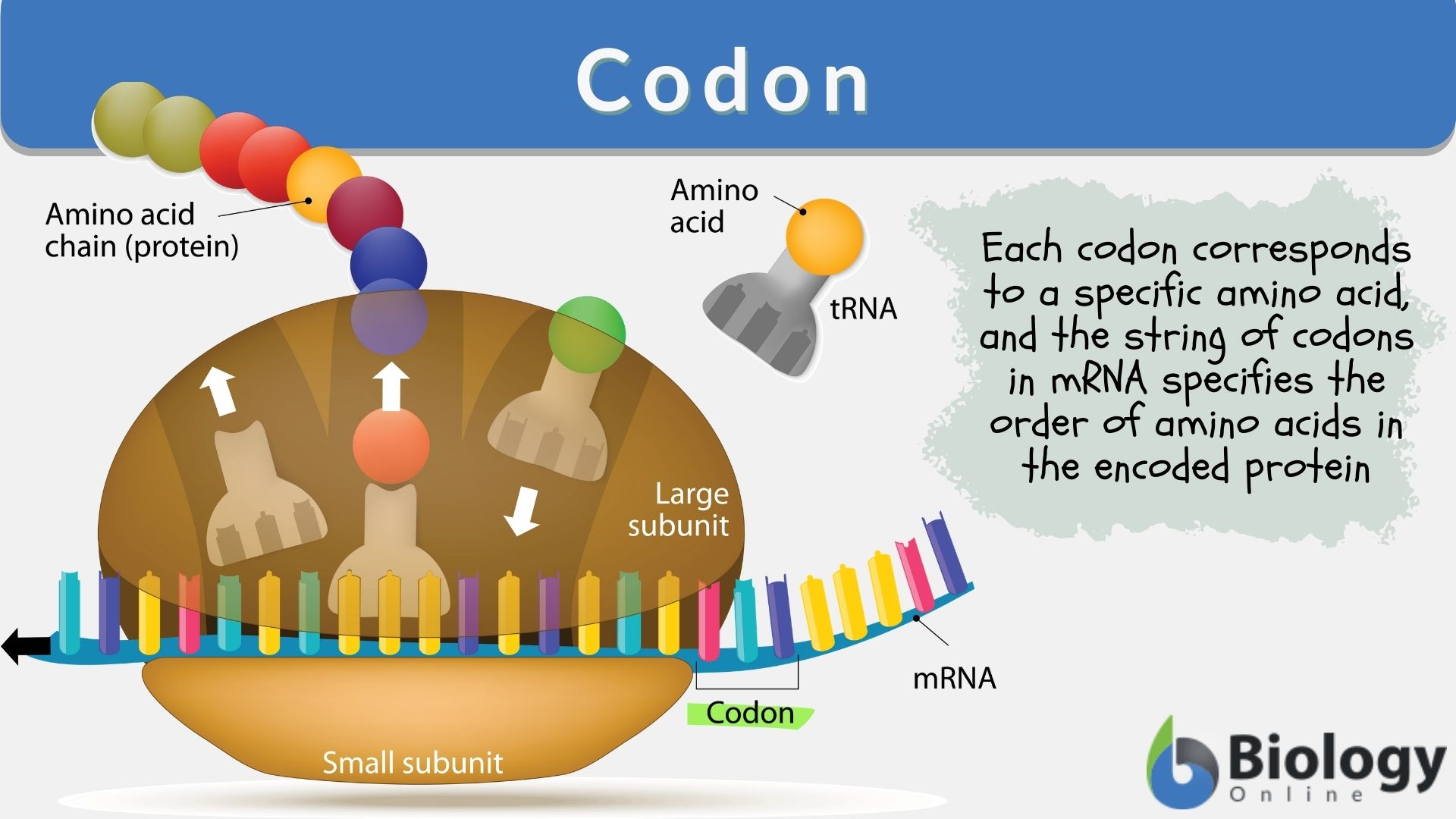
Codon Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
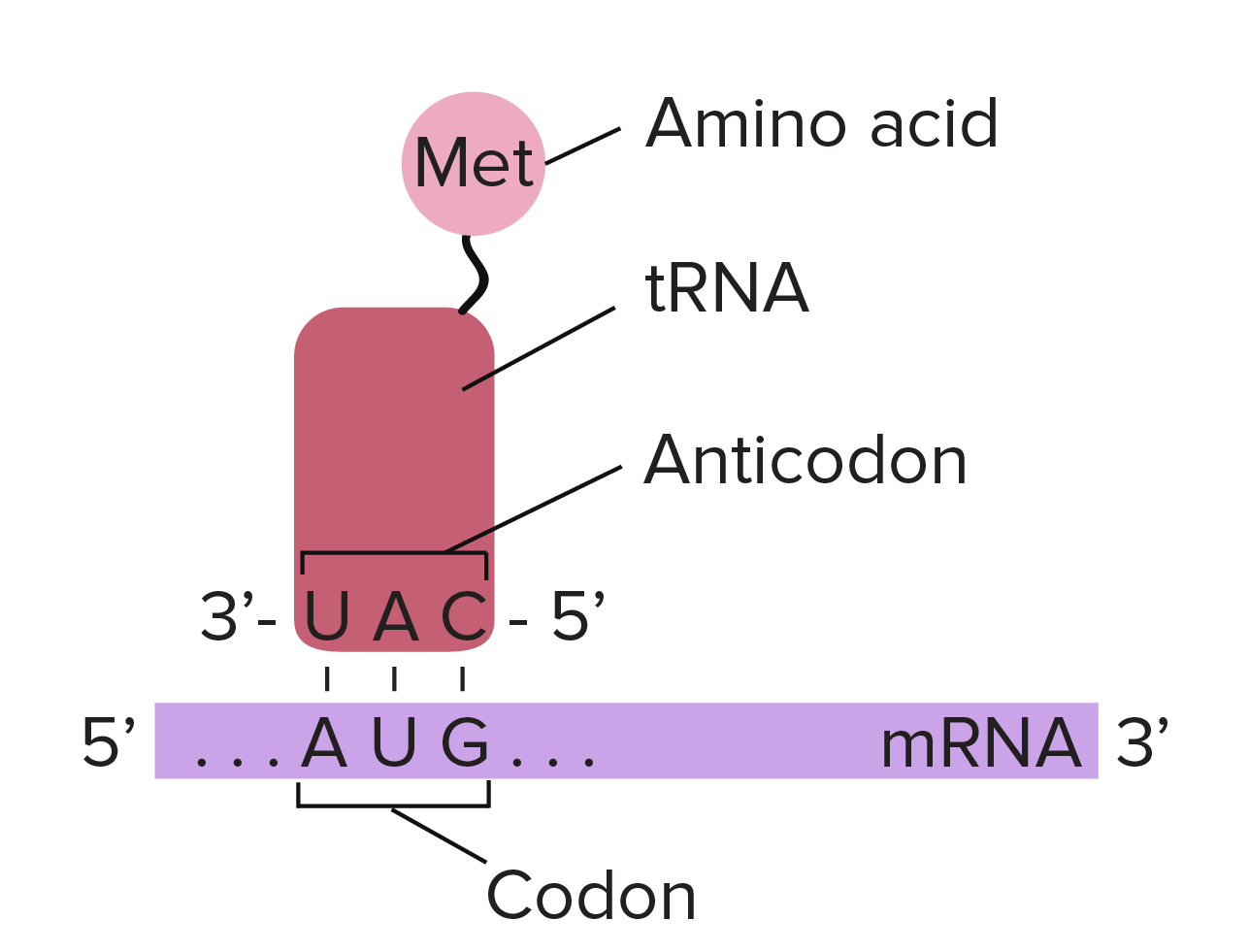
translation PMG Biology
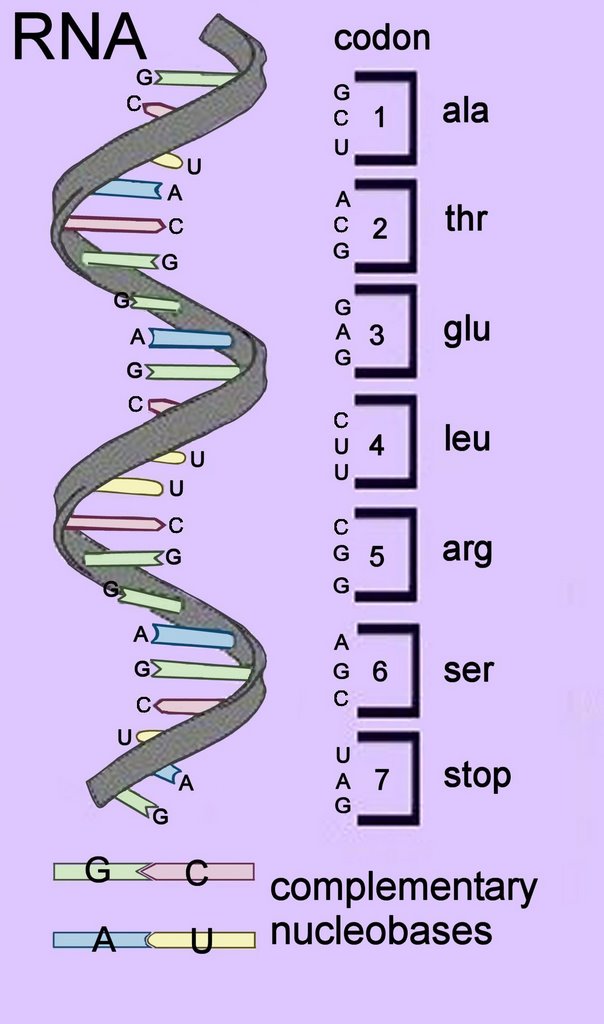
Molecular Biology codon

Sketch of the codonspecific elongation model (COSEM). Ribosomes attach
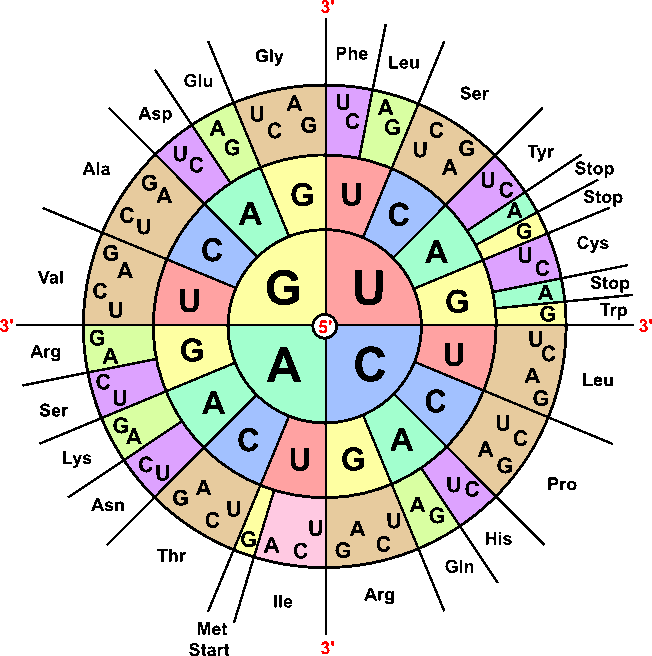
How does DNA code for proteins? + Example

Protein Synthesis The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Codons — Definition & Role in Translation Expii
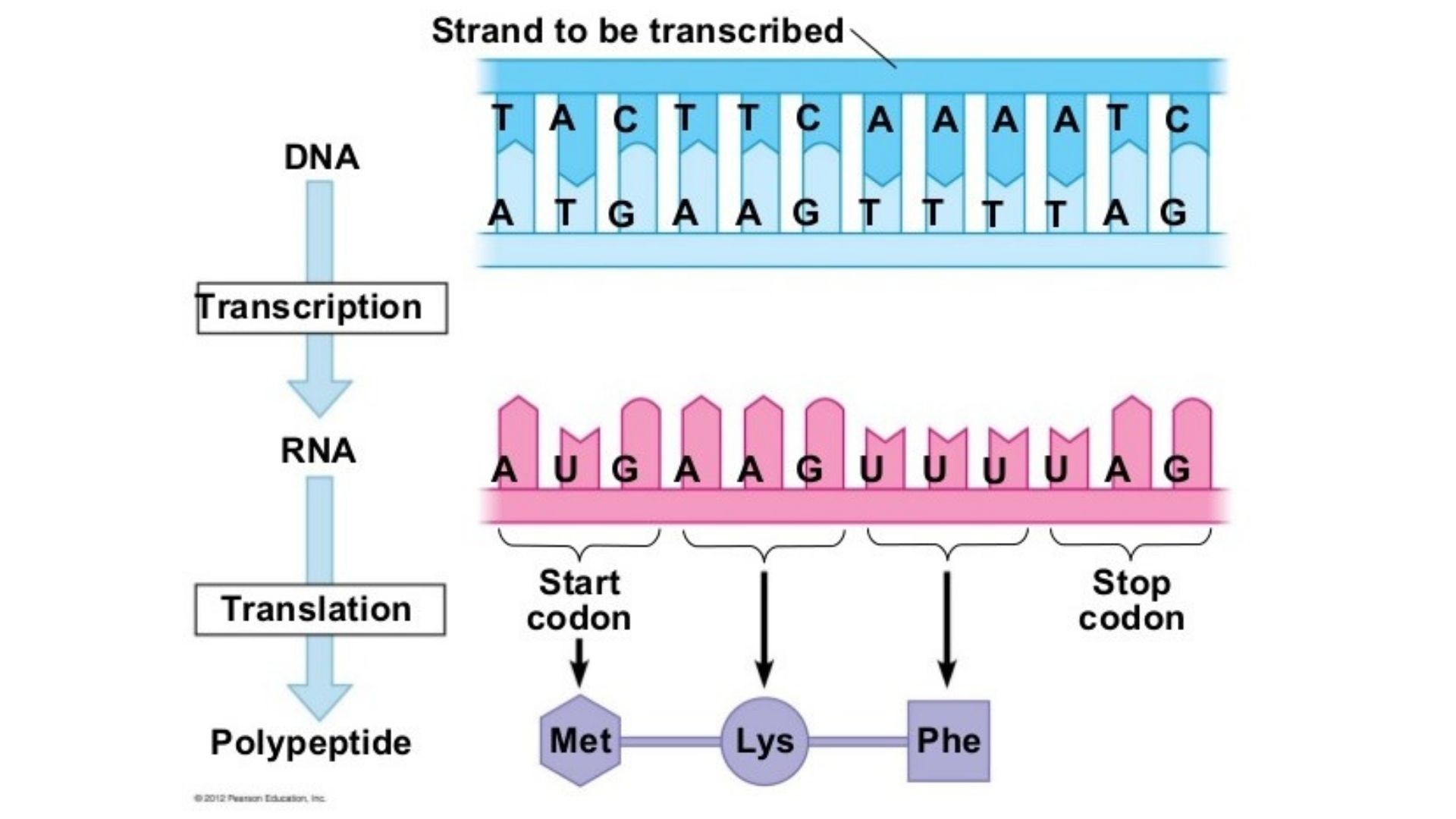
Mrna Amino Acid Table Start Codon Elcho Table
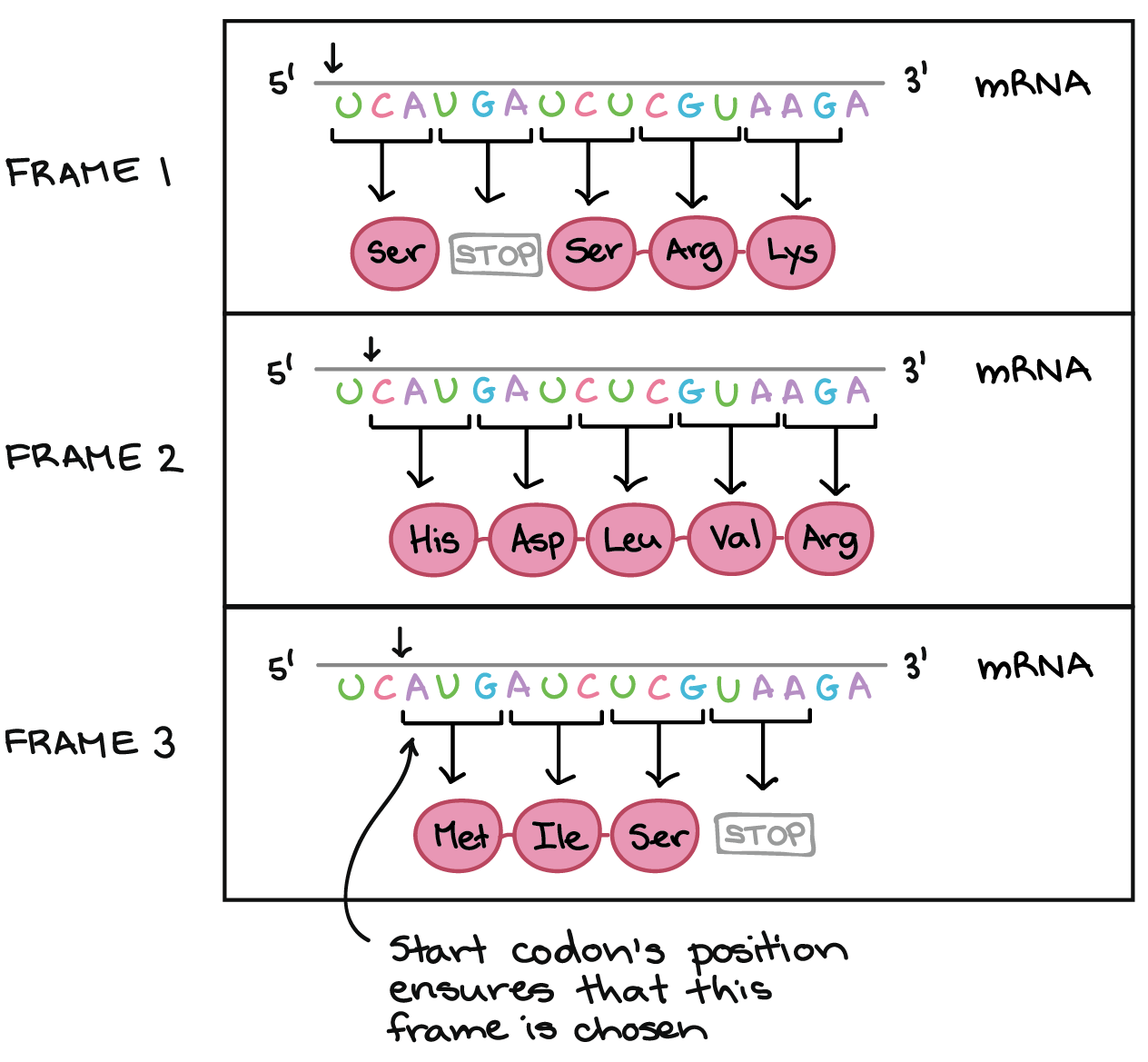
A Codon Consists of a Sequence of How Many Nucleotides
Uga, Uaa, And Uag Are Stop Codons.
Web A Ribosome Is Made Up Of Two Basic Pieces:
Web One Codon Is A Start Codon That Indicates Where To Start Translation.
Web Codon, In Genetics, Any Of 64 Different Sequences Of Three Adjacent Nucleotides In Dna That Either Encodes Information For The Production Of A Specific Amino Acid Or Serves As A Stop Signal To Terminate Translation (Protein Synthesis).
Related Post: