Chromatin Drawing
Chromatin Drawing - Replication involves dna duplicating itself. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). Web chromatin can be defined as highly condensed chromosomes at metaphase stage, and very diffuse structures in course of interphase. Cutting edge microscopy techniques to image chromatin organization with super resolution; Web as dna repair, replication, and transcription involve active reorganization of chromatin, live visualization of chromatin motions will elucidate new functional mechanisms of these nuclear processes. Web the complex of dna plus histones and other structural proteins is called chromatin. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. Computational imaging tools to interpret chromatin structure and dynamics; As a result, chromatin can be packaged into a much smaller volume than dna. Web various genome‐wide mapping techniques have begun to reveal that, despite the tremendous complexity, chromatin organization is governed by simple principles. Web electron micrographs indicate that the dna in metaphase chromosomes is organized into large loops attached to a protein scaffold (figure 4.13), but we currently understand neither the detailed structure of this highly condensed chromatin nor. H1, h2a, h2b, h3 and h4. Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into. Web electron micrographs indicate that the dna in metaphase chromosomes is organized into large loops attached to a protein scaffold (figure 4.13), but we currently understand neither the detailed structure of this highly condensed chromatin nor. Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein found in eukaryotic cells. Web updated on february 15, 2020. Rather each chromosome occupies a spatially. The major structures in dna compaction: Rather each chromosome occupies a spatially limited, roughly elliptical domain which is known as a chromosome territory (ct). These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: Here we look at classic experiments that led to our understanding that genes are composed of dna. Web begin to move them towards opposite poles of the cell. These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus. In s phase, the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the dna in its nucleus. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of. Chromatin is a mass of genetic material composed of dna and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division. Its prime function lies in the packaging of dna molecules in a very long denser compact shape withholds the strands from becoming tangled and plays a role in strengthening the dna during cell division. Difference between chromosomes and chromatin.. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. Do cells always grow before they divide? Web as dna repair, replication, and transcription involve active reorganization of chromatin, live visualization of chromatin motions will elucidate new functional mechanisms of these nuclear processes. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: The sex cells of a. Histones are small and positively charged proteins and are of 5 major types: Difference between chromosomes and chromatin. In s phase, the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the dna in its nucleus. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Web chromatin is defined as a complex of rna, dna, and protein observed in eukaryotic cells. In s phase, the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the dna in its nucleus. Phase, also called the first gap phase, the cell grows physically larger, copies organelles, and makes the molecular building blocks it will need in later steps. Computational imaging tools to interpret chromatin structure and dynamics; In this stage, the chromatin coils and condenses into chromosomes.. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). Difference between chromosomes and chromatin. H1, h2a, h2b, h3 and h4. Web electron micrographs indicate that the dna in metaphase chromosomes is organized into large loops attached to a protein scaffold (figure 4.13), but we currently understand neither the detailed structure of. Web as dna repair, replication, and transcription involve active reorganization of chromatin, live visualization of chromatin motions will elucidate new functional mechanisms of these nuclear processes. Tools to physically manipulate chromatin; Difference between chromosomes and chromatin. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web in the g1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes. Many of the proteins — namely, histones — package the massive amount of dna in a genome into a highly compact form that can fit in the cell nucleus. For example, humans are diploid (2n) and have 46 chromosomes in their normal body cells. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Chromatin refers to a mixture of dna and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms. The sex cells of a human are haploid (n), containing only one. Different species have different numbers of chromosomes. These 46 chromosomes are organized into 23 pairs: Do cells always grow before they divide? Web in the g1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. Chromatin is located in the nucleus of our cells. In the s phase, the cell's dna is replicated. The g2 phase is another growth phase, after which the cell is ready for mitosis. Rather each chromosome occupies a spatially limited, roughly elliptical domain which is known as a chromosome territory (ct). Chromatin is a mass of genetic material composed of dna and proteins that condense to form chromosomes during eukaryotic cell division. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase).
Everything to Know about Chromatin In Plant Cell Garden Bagan
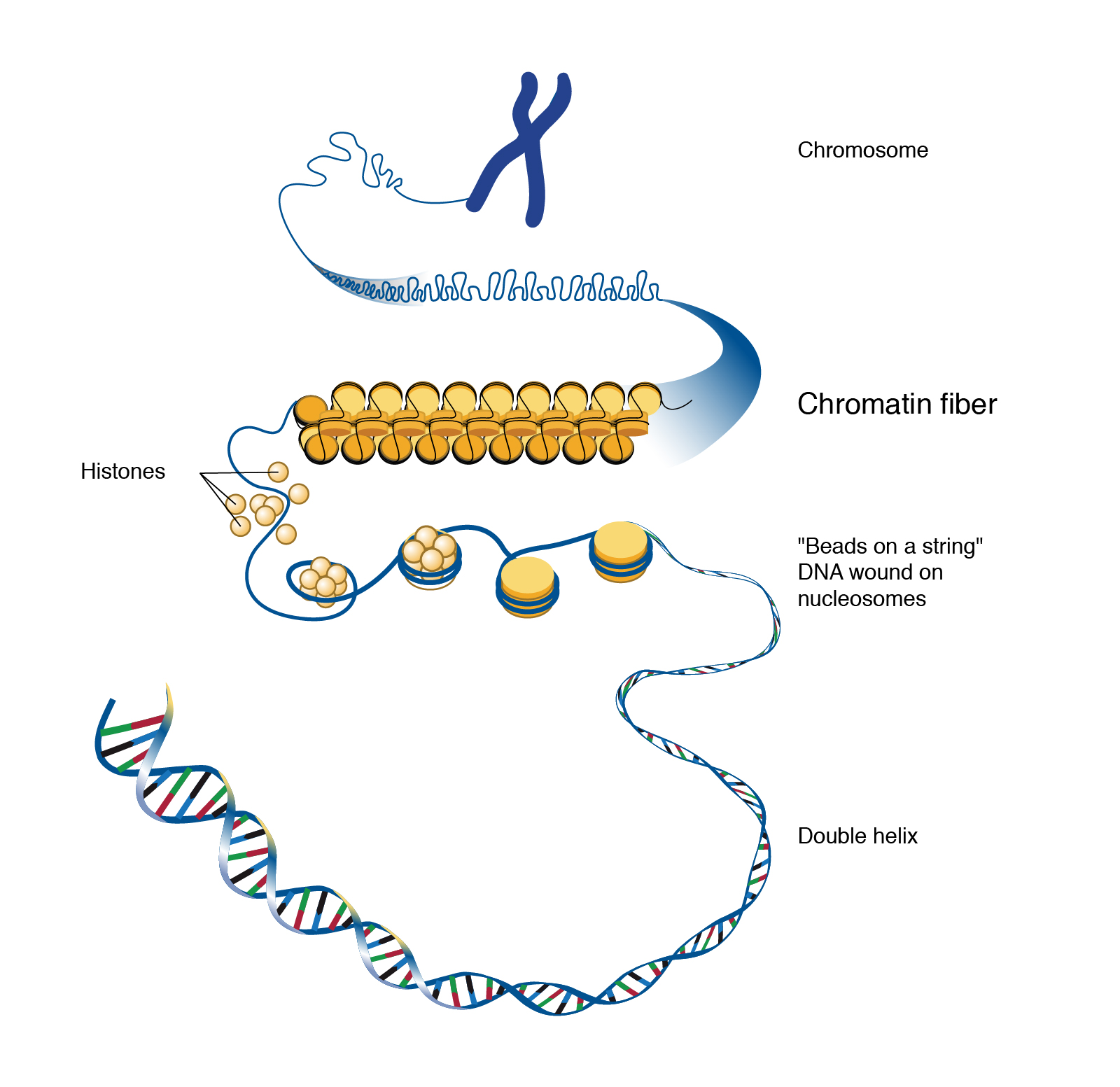
Chromatin
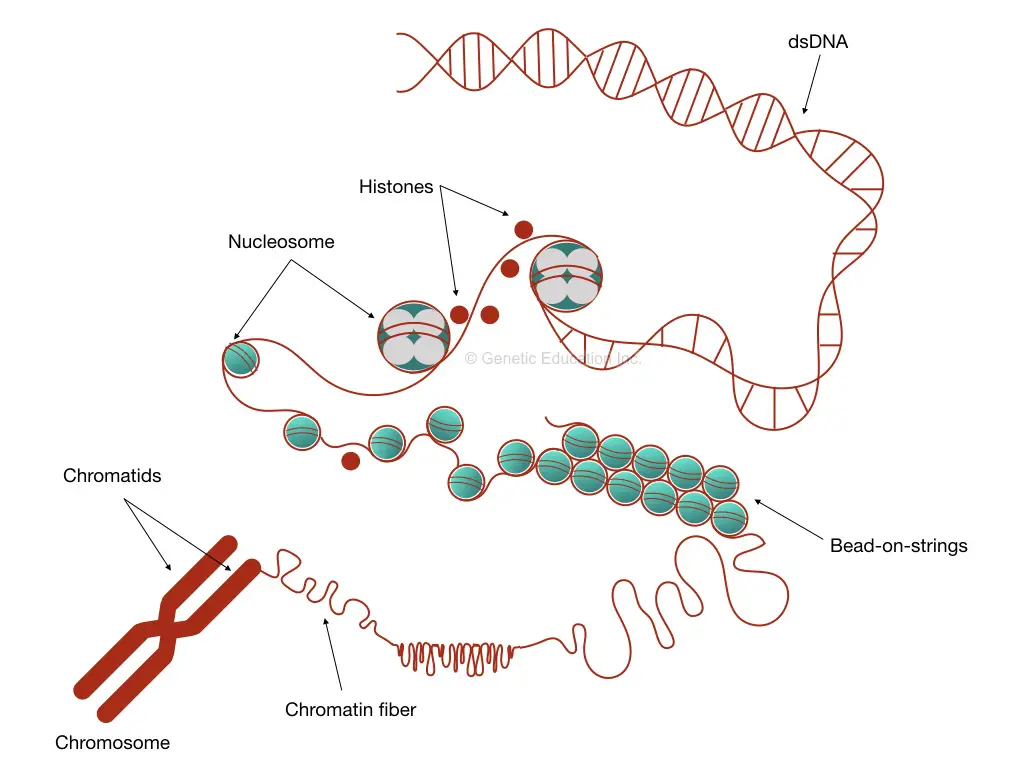
Inside Chromatin Definition, Structure, and Function Education
Chromatin Drawing Mitosis, HD Png Download kindpng
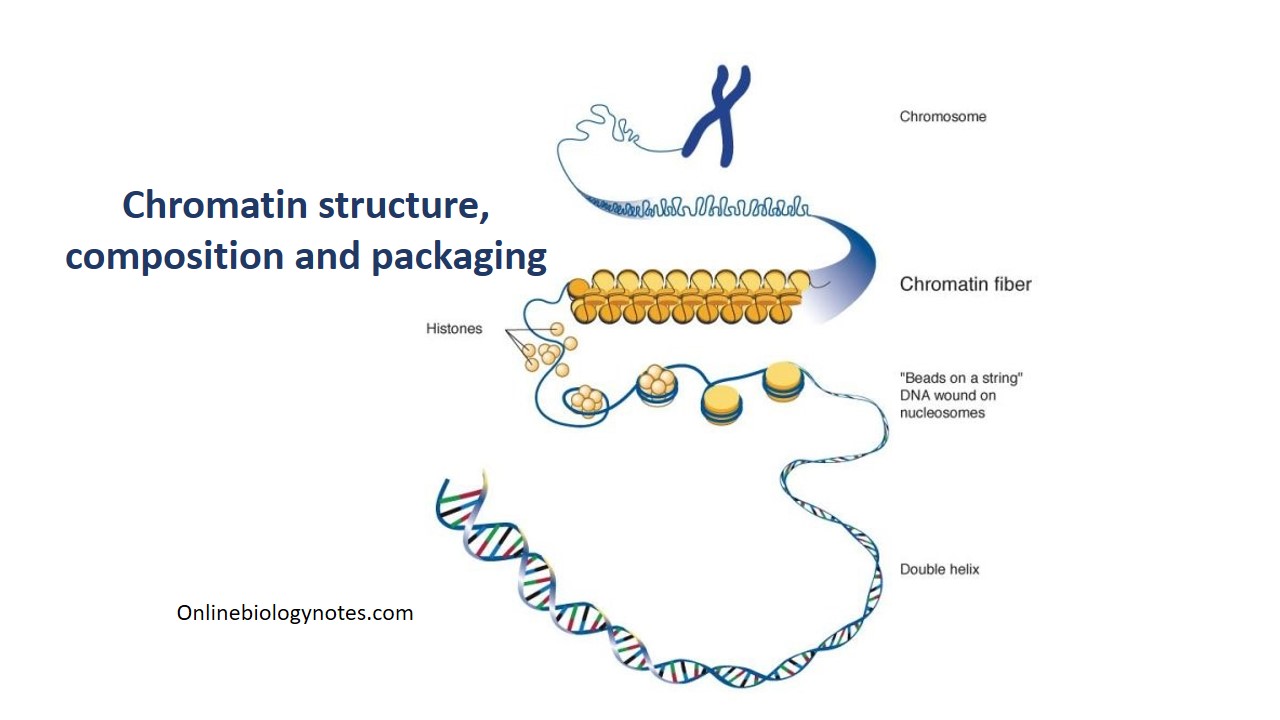
Chromatin Is the Complex of and Found Within Eukaryotic Chromosomes.
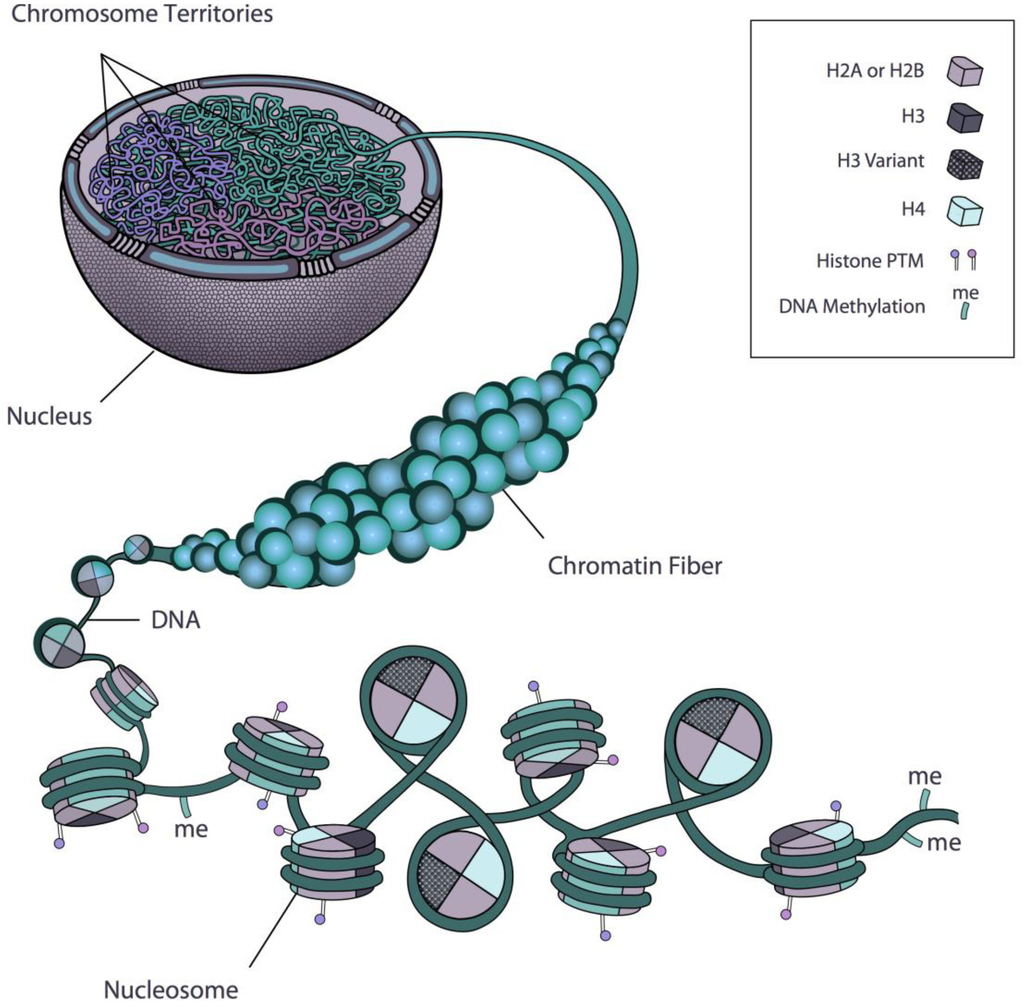
Nucleosome Histone Chromatin

Chromatin structure Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock

What are chromatin? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL

What are chromatin? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
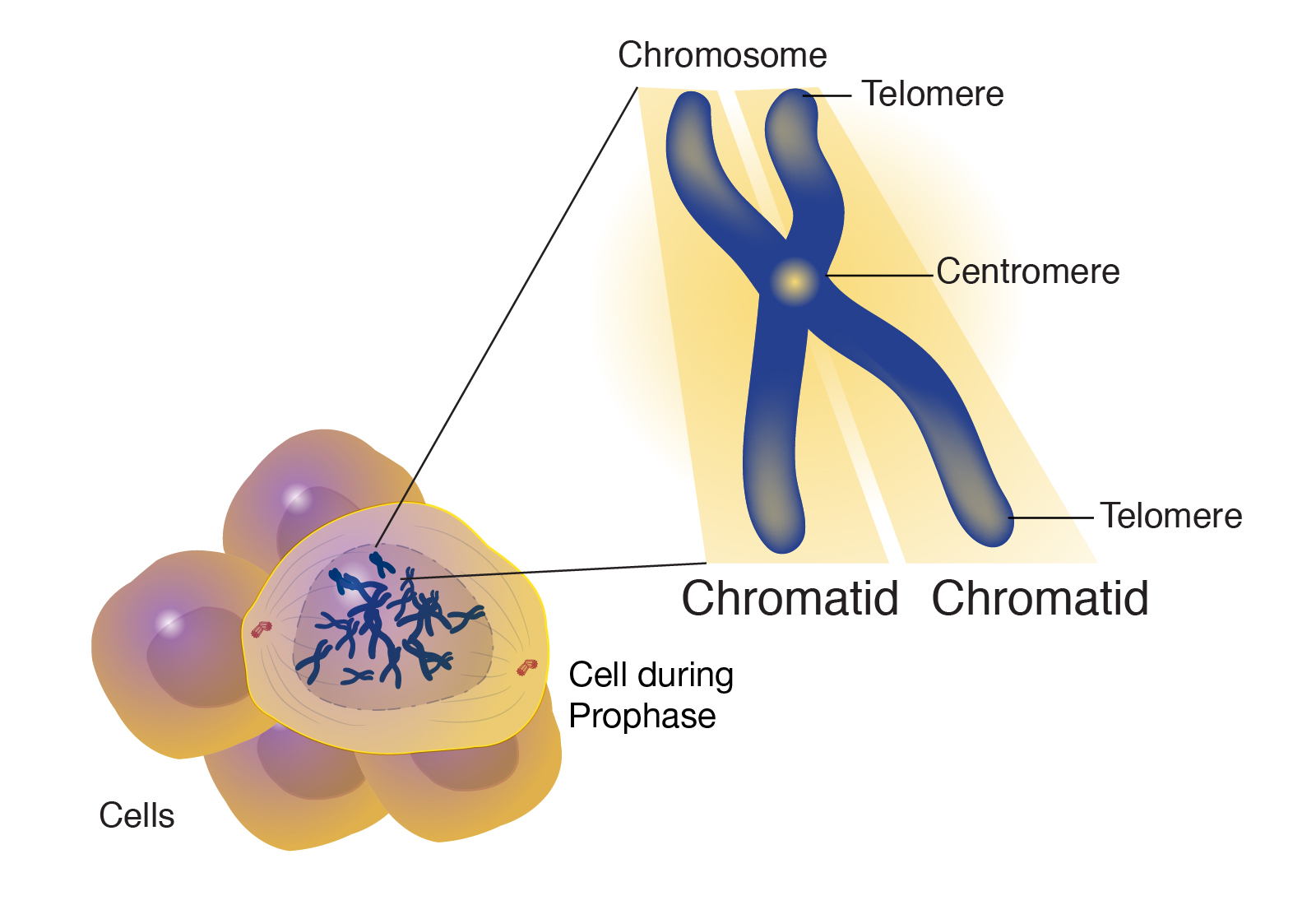
Chromatin And Chromosomes
To Model The Prophase Stage Of Mitosis, Leave The Chromosomes Where They Are In Your Cell Drawing.
Web Courses On Khan Academy Are Always 100% Free.
In S Phase, The Cell Synthesizes A Complete Copy Of The Dna In Its Nucleus.
Web The Complex Of Dna Plus Histones And Other Structural Proteins Is Called Chromatin.
Related Post: