Carbohydrates Structure Drawing
Carbohydrates Structure Drawing - Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. We will cover the chemistry of carbohydrates more completely in chapter 10, but the following is a quick overview. Carbohydrates can be represented by the formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. It explains how to convert the fischer. Web which enzyme hydrolyzes each carbohydrate? Draw the mirror image of a carbohydrate molecule. The glyconavi is a tool for carbohydrate researchers. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Carbohydrate is a group of organic compounds occurring in living tissues and foods in the form of starch, cellulose, and sugars. Web sugars rather carbohydrates are precisely defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones with one chiral carbon atom at least. In a fischer projection drawing, the four bonds to a chiral carbon make a cross with the carbon atom at the intersection of the horizontal and vertical lines. Web sugars can be drawn in the straight chain form as either fisher projections or perspective structural formulas. There also must be at least three carbons. 783 views 2 months ago. Describe. Draw the mirror image of a carbohydrate molecule. Web sugars can be drawn in the straight chain form as either fisher projections or perspective structural formulas. And these are chains of carbon atoms that feature an aldehyde or a ketone functional group. A carbohydrate is a type of molecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Classification of carbohydrates and its. Web which enzyme hydrolyzes each carbohydrate? In other words, these are organic molecules that incorporate multiple water. Web drawing and visualisation of molecular structures are some of the most common tasks carried out in structural glycobiology, typically using various software. 783 views 2 months ago. Web sugars rather carbohydrates are precisely defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones with one. The ratio of oxygen and hydrogen in carbohydrates is the same as in water i.e. And these are chains of carbon atoms that feature an aldehyde or a ketone functional group. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. 783 views 2 months ago. Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of. In other words, these are organic molecules that incorporate multiple water. It explains how to convert the fischer. In a fischer projection drawing, the four bonds to a chiral carbon make a cross with the carbon atom at the intersection of the horizontal and vertical lines. Carbohydrate is a group of organic compounds occurring in living tissues and foods in. The ratio of oxygen and hydrogen in carbohydrates is the same as in water i.e. Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Web sugars can be drawn in the straight chain form as either fisher projections or perspective structural formulas. Draw the structure of a hypothetical reducing disaccharide composed of. Web drawing and visualisation of molecular structures are some of the. Draw the mirror image of a carbohydrate molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Web carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen — with the hydrogen and oxygen occurring in a 2:1 ratio. In a fischer projection drawing, the four bonds to a chiral carbon make a cross with the. Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of the monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Web sugars rather carbohydrates are precisely defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones with one chiral carbon atom at least. Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Web draw and name the common, simple carbohydrates using structural formulas and fischer projection formulas. In a fischer projection drawing, the. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources. There also must be at least three carbons. In this video gaurav bhateja sir will share very important tricks to draw carbohydrate structure in a very easy way. This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. 805k views 5 years ago new organic chemistry playlist. Hazel takes you through the basics of carbohydrates, including their uses, how to draw the structure of alpha and beta glucose, the difference between monosaccharides. Alternatively, a text box option provides a way to draw. In other words, these are organic molecules that incorporate multiple water. Hazel takes you through the basics of carbohydrates, including their uses, how to draw the structure of alpha and beta glucose, the difference between monosaccharides. Web carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (ch 2 o)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. Carbohydrates can be represented by the formula (ch 2 o) n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. Distinguish between monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Identify several major functions of carbohydrates. What structural characteristics are necessary if a disaccharide is to be a reducing sugar? We will cover the chemistry of carbohydrates more completely in chapter 10, but the following is a quick overview. Web carbohydrates are literally “hydrates of carbon.” this name derives from the generalized formula of simple monosaccharides, which can be written in the form of c x (h 2 o) x, where x is a digit typically between 3 and 8. Web which enzyme hydrolyzes each carbohydrate? Web drawing and visualisation of molecular structures are some of the most common tasks carried out in structural glycobiology, typically using various software. In this perspective article, we outline developments in the computational tools for the sketching, visualisation and modelling of glycans. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. Web the term 'carbohydrate', which literally means 'hydrated carbons', broadly refers to monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides (shorter polymers) and polysaccharides (longer polymers). This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into carbohydrates. Discuss the structural, chemical, and biochemical properties of the monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides.
General carbohydrates molecular structures Vector Image

Structure And Function Of Carbohydrates Alevel Biology

Carbohydrates Structure, Function, Types & Role In Biology
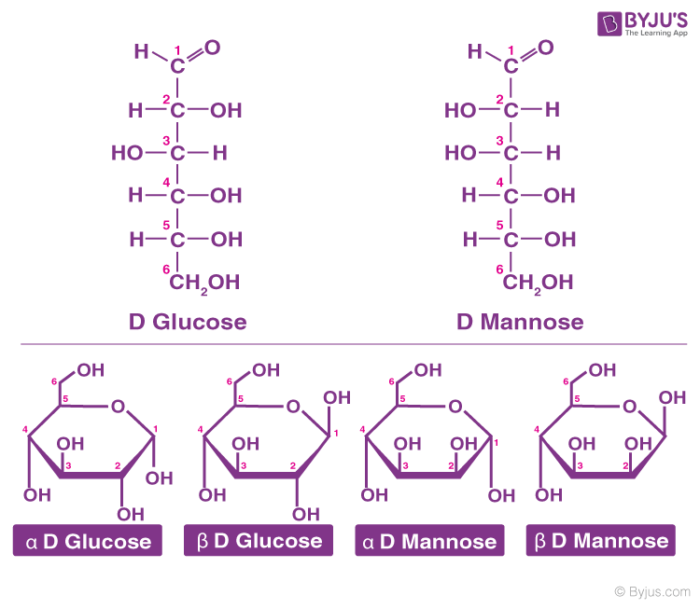
Carbohydrate Structure
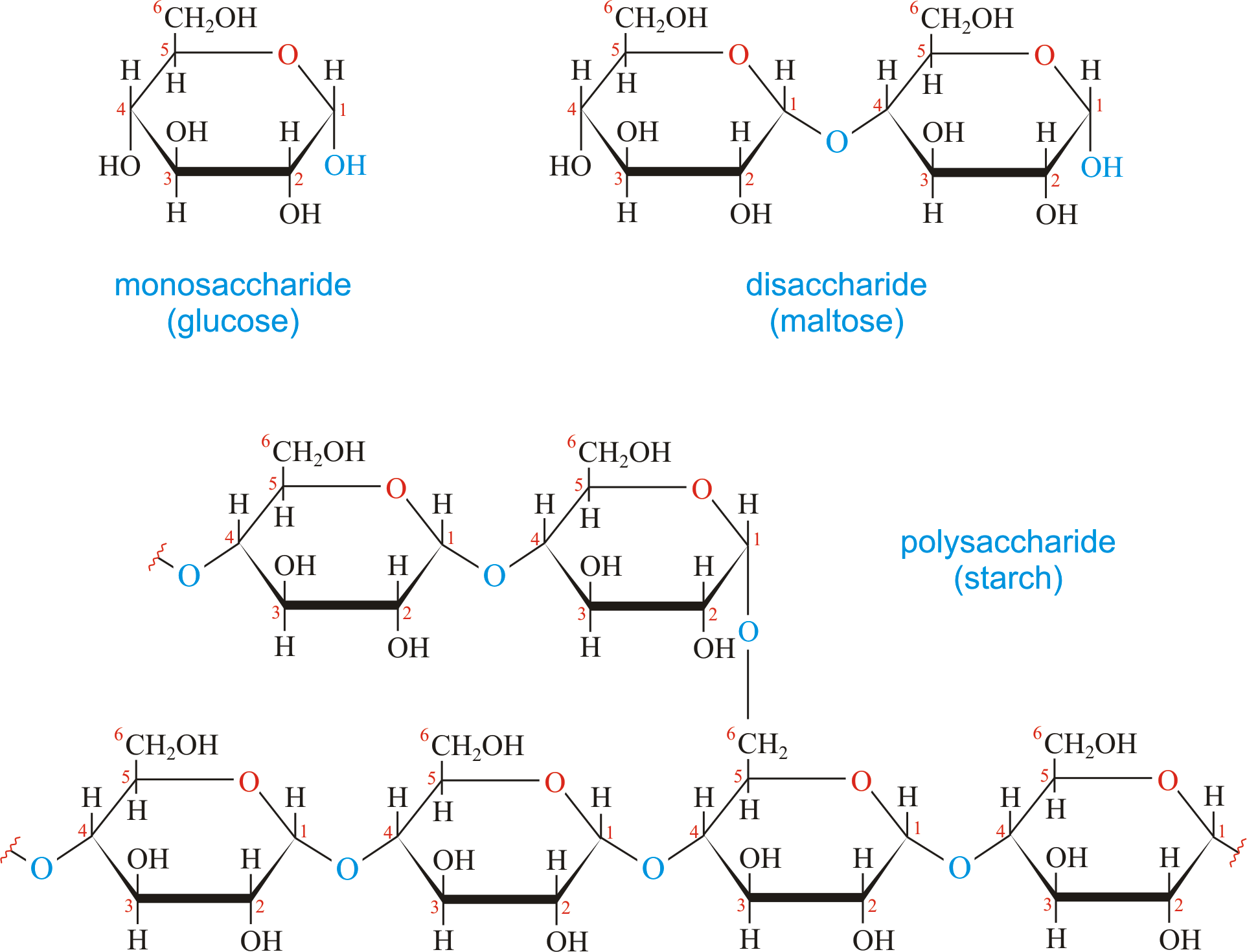
Carbohydrate Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary

Classification of Carbohydrates with Types, Formula and Structure

Carbohydrates Definition Structure Types Examples
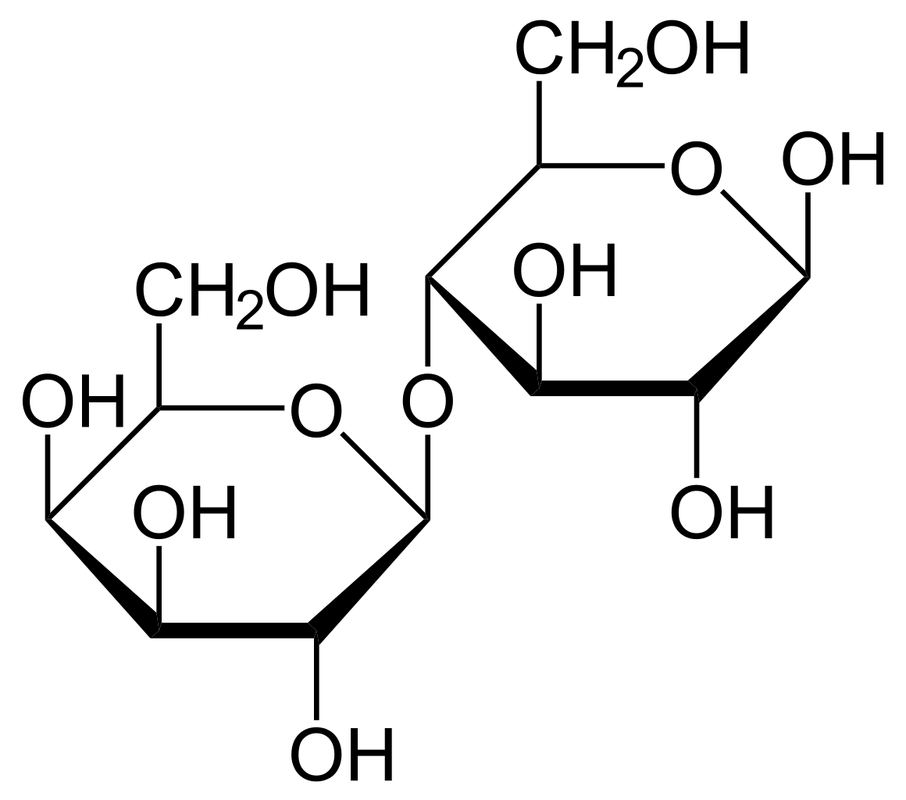
Lab 2e Structure and Properties of Carbohydrates Toby Guenthner
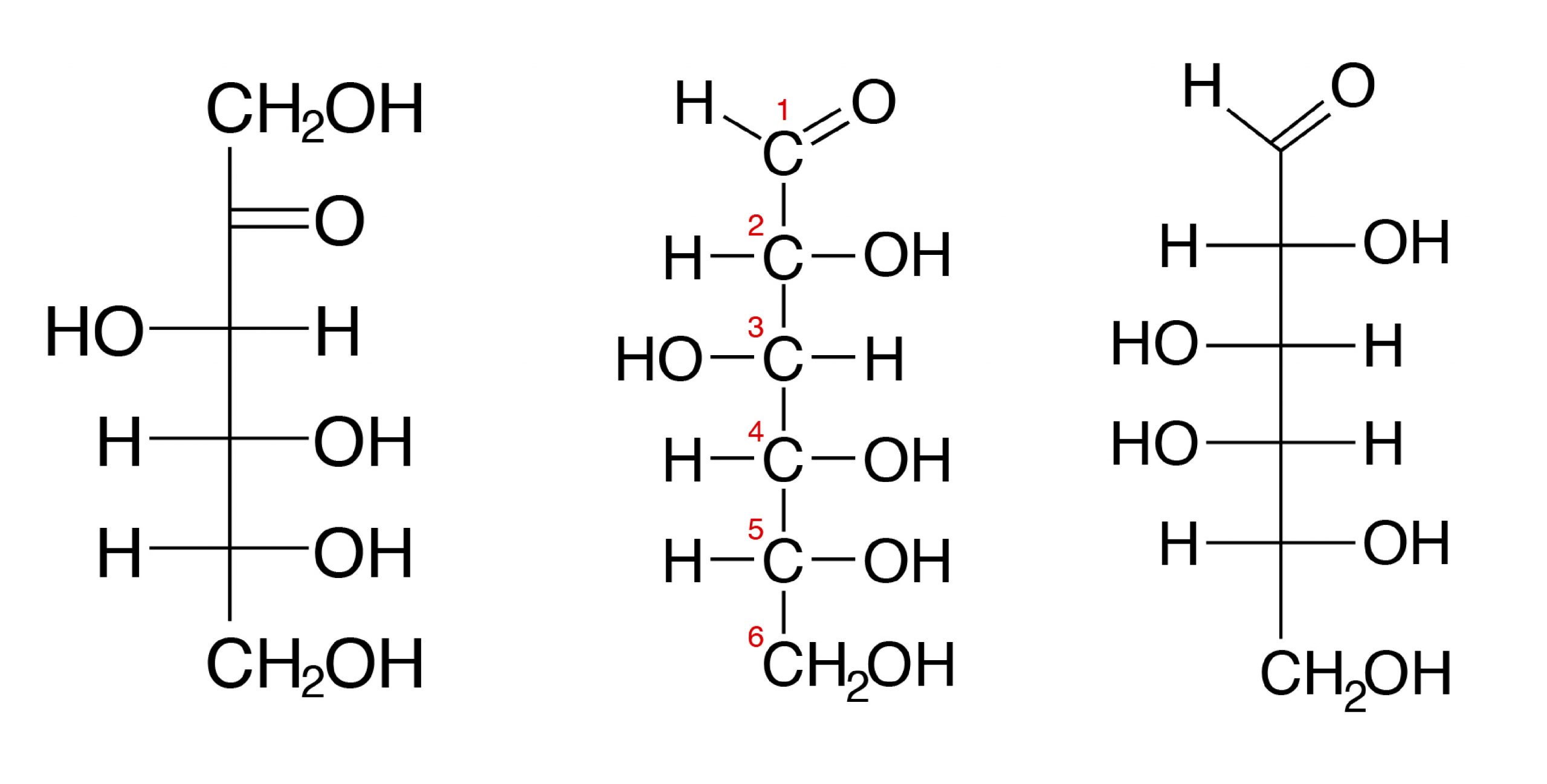
Basic Carbohydrate Chemical Structure
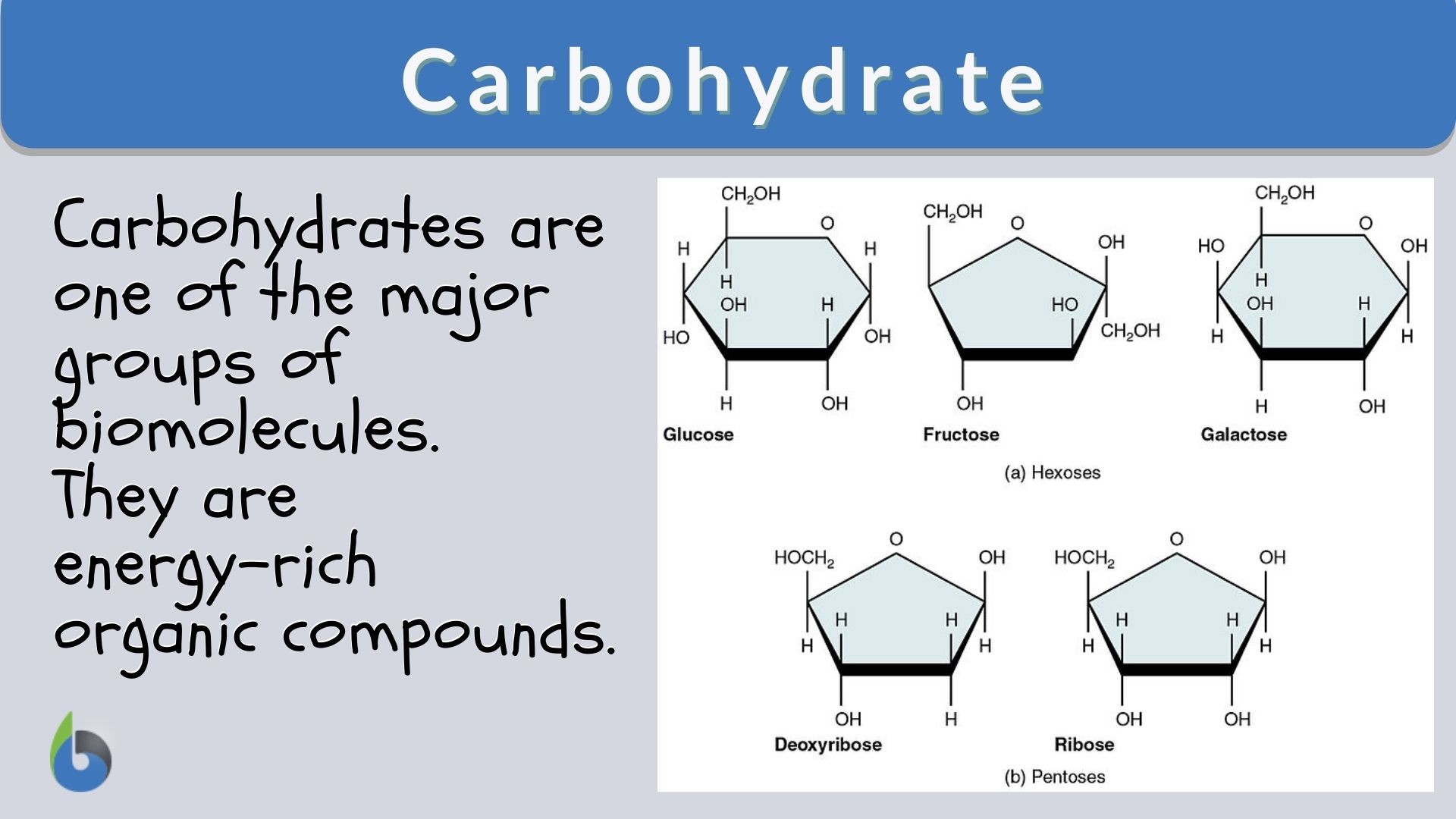
Carbohydrate Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
In A Fischer Projection Drawing, The Four Bonds To A Chiral Carbon Make A Cross With The Carbon Atom At The Intersection Of The Horizontal And Vertical Lines.
When Drawing Fischer Projections, The Aldehyde Group Is Written At The Top, And The H And Oh Groups That Are Attached To Each Chiral Carbon Are Written To The Right Or Left.
Draw The Mirror Image Of A Carbohydrate Molecule.
Carbohydrates Are One Of The Four Main Classes Of Macromolecules That Make Up All Cells And Are An Essential Part Of Our Diet;
Related Post: