Bone Cell Drawing
Bone Cell Drawing - Web the skeletal system. Web between the rings of matrix, the bone cells (osteocytes) are located in spaces called lacunae. The strength, shape and stability of the human body are dependent on the musculoskeletal system. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue: It occupies a small chamber called a lacuna, which is contained in the calcified matrix of bone. Web structure of osteocytes. ( a) preosteocyte enlarges its secretory territory, thus reducing its appositional growth rate, and starts to radiate processes towards the osteoid. Diseases and disorders of bone cells. This is concerned with bone formation and is found in the growing surface where the bony matrix is deposited. Osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Osteoblasts are like construction crews that build new bone cells. Web between the rings of matrix, the bone cells (osteocytes) are located in spaces called lacunae. Paget’s disease of the bone. Web as shown in figure \(\pageindex{3}\), bone tissues are composed of four different types of bone cells: Osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [ 1, 2 ]. Identify the anatomical features of a bone. Each cell type has a unique function and is. Web in this review, we discuss the current data about the structure and functions of bone cells and the factors that influence bone remodeling. The strength, shape and stability of the human body are dependent on the musculoskeletal system. You might see them called. Bone is a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: Distinguish among the four cell types in bone. Web although bone cells compose a small amount of the bone volume, they are crucial to the function of bones. Osteoblasts are like construction crews that build new bone cells. Describe the histology of bone tissue. Osteoprogenitor cells are the 'stem' cells of bone, and are the source of new osteoblasts. Describe the histology of bone tissue. Explore the cellular structure of bone, including the bone matrix and the cells that form it. Schematic drawing showing the asynchronous and asymmetric pattern of cytoplasmic processes formation during osteocyte differentiation (preosteocytes = black; By the end of this. Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells and osteoclasts (figure 10.3.5). By the end of this section, you will be able to: Types of cell found in bone. Web the skeletal system. Diseases and disorders of bone cells. Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor (or osteogenic) cells. They are also important in that they help rebuild bones in the event that they break. In compact bone, the haversian systems are packed tightly together to form what appears to be a solid mass. There are three main types of bone cells: Web what do osteoblasts do? By the end of this section, you will be able to: Small channels ( canaliculi) radiate from the lacunae to the osteonic (haversian) canal to provide passageways through the hard matrix. Identify the anatomical features of a bone. Describe the microscopic and gross anatomical structures of bones. ( a) preosteocyte enlarges its secretory territory, thus reducing its appositional growth rate,. Web although bone cells compose a small amount of the bone volume, they are crucial to the function of bones. Bone consists of four types of cells: Describe the histology of bone tissue, including the function of bone cells and matrix. You might see them called osteogenic cells. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Growing new bones (bone formation). Describe the histology of bone tissue. Describe the microscopic and gross anatomical structures of bones. Osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells and osteoclasts (figure 10.3.5). Four types of cells are found within bone tissue: Describe the histology of bone tissue, including the function of bone cells and matrix. Web by the end of this section, you will be able to: Osteocyte, a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone. They strengthen your existing bones and help form new bone tissue. Web in this review, we discuss the current data about the structure and functions of bone cells and the factors that influence bone remodeling. Growing new bones (bone formation). Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts (figure 6.11). Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor (or osteogenic) cells. Identify the anatomical features of a bone. Human anatomy (lange et al.) 5: Define and list examples of bone markings. Web by the end of this section, you will be able to: Osteocyte, a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, and osteogenic cells. Bone consists of four types of cells: Explore the skeletal system with our interactive 3d anatomy models. Osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts [ 1, 2 ]. In compact bone, the haversian systems are packed tightly together to form what appears to be a solid mass. They are derived from osteoprogenitor cells and are responsible for building new bones as one grows.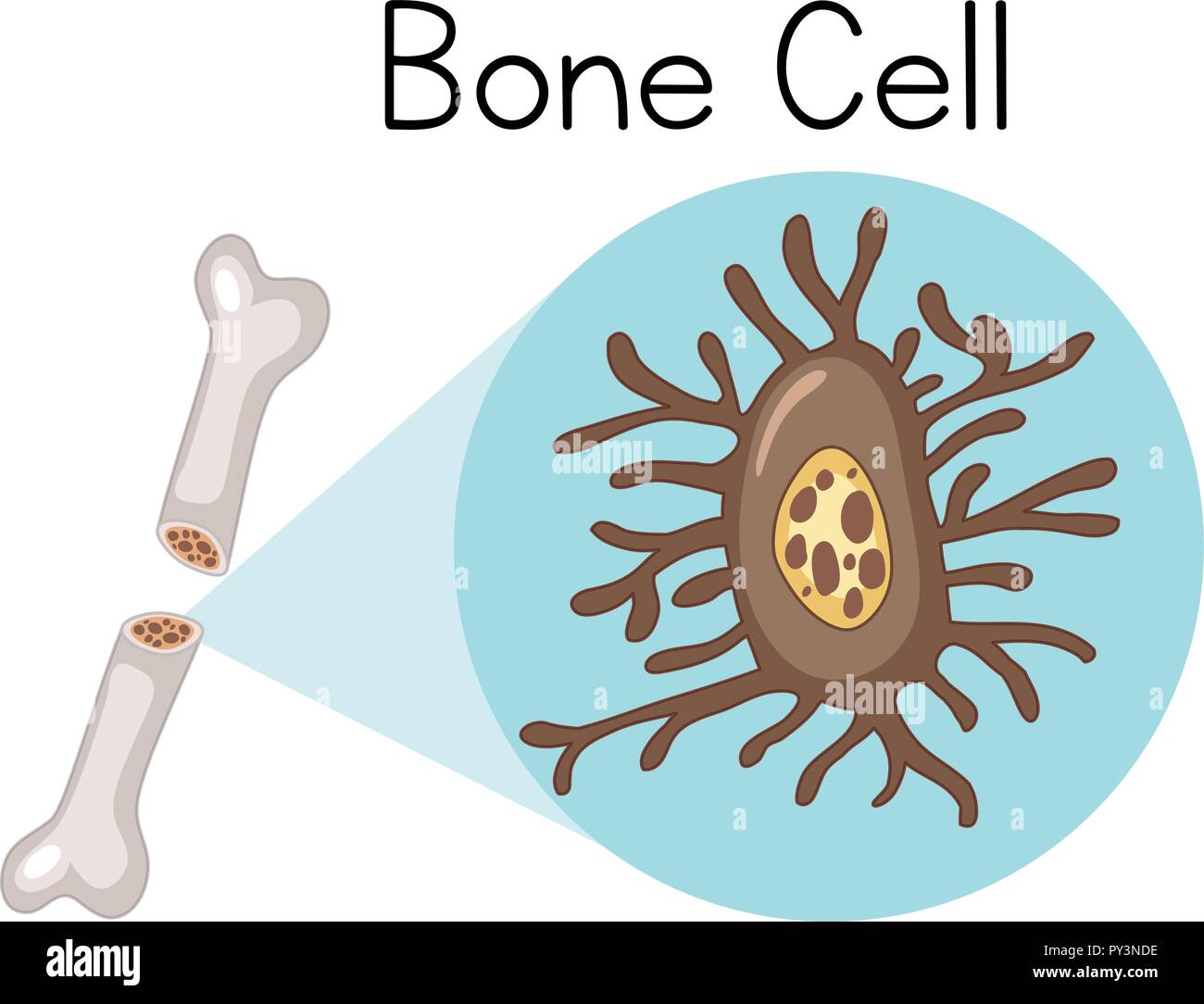
Bone Cell Structure And Function

Bone cells human anatomy organs
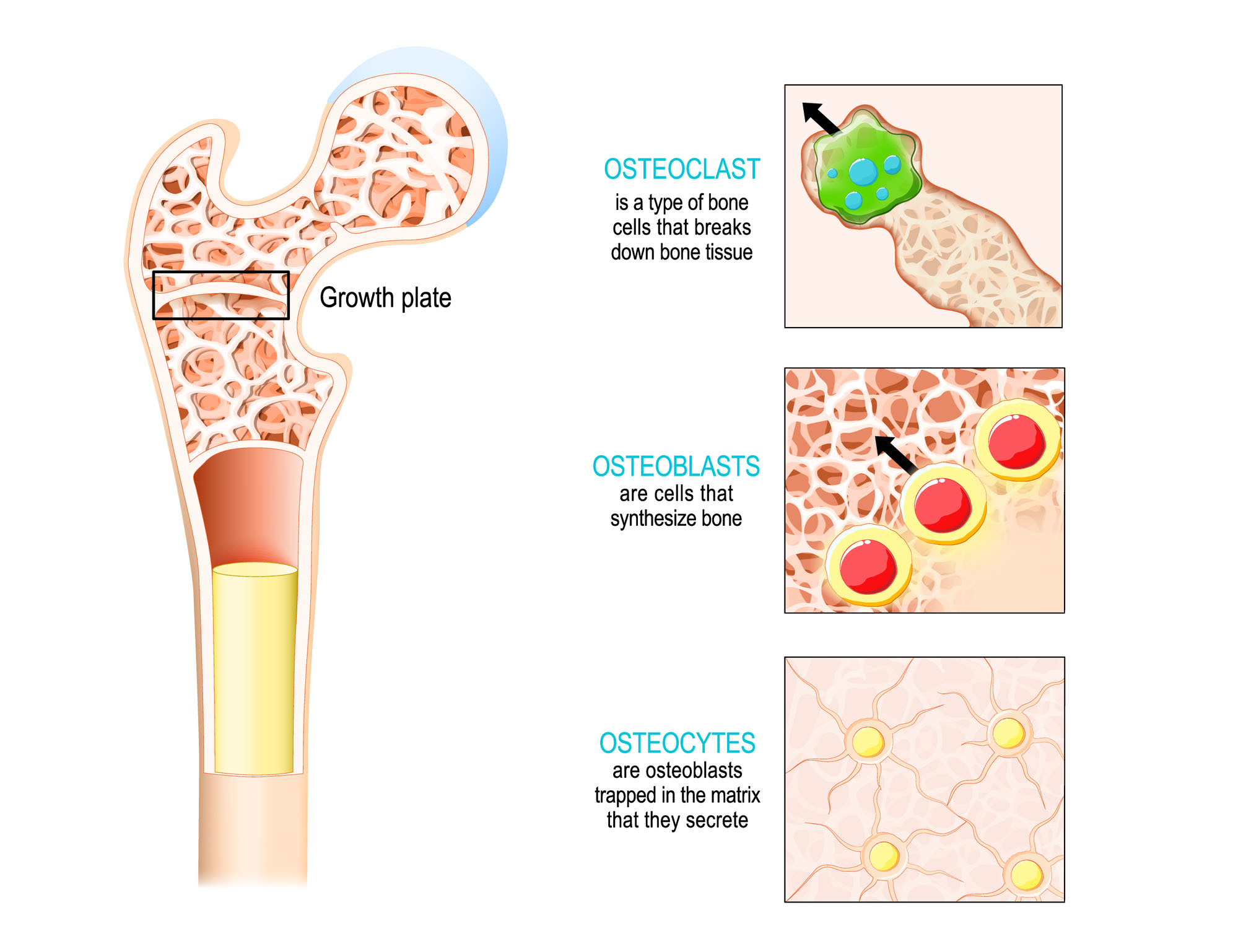
2a3 Bone Structure HumanBio

Human bone cells anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image

Human bone cells anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
.jpg)
Bone Anatomy and Function
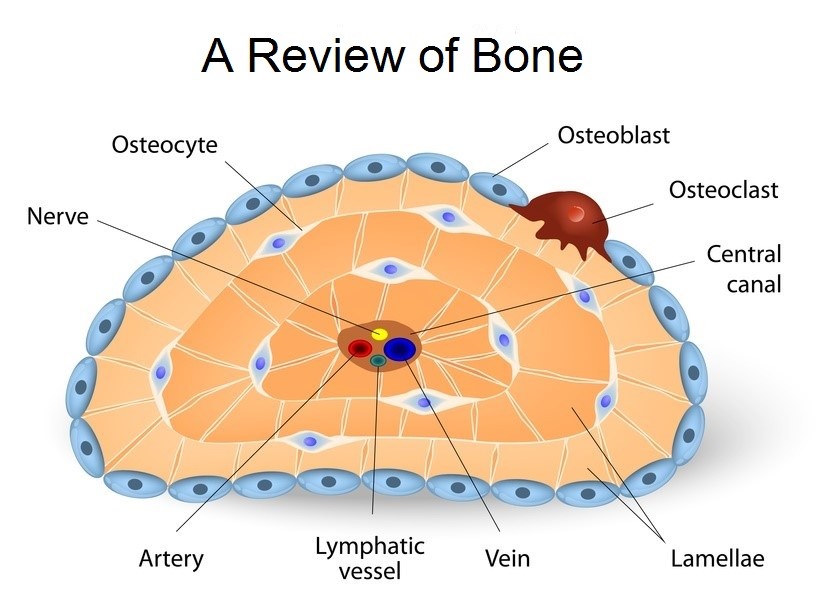
Bone Cells Structure Images Galleries With A Bite!

Human bone cell types vector illustration infographic Osteoblast

Cross section of a bone. Cells are the basic entities that keep the
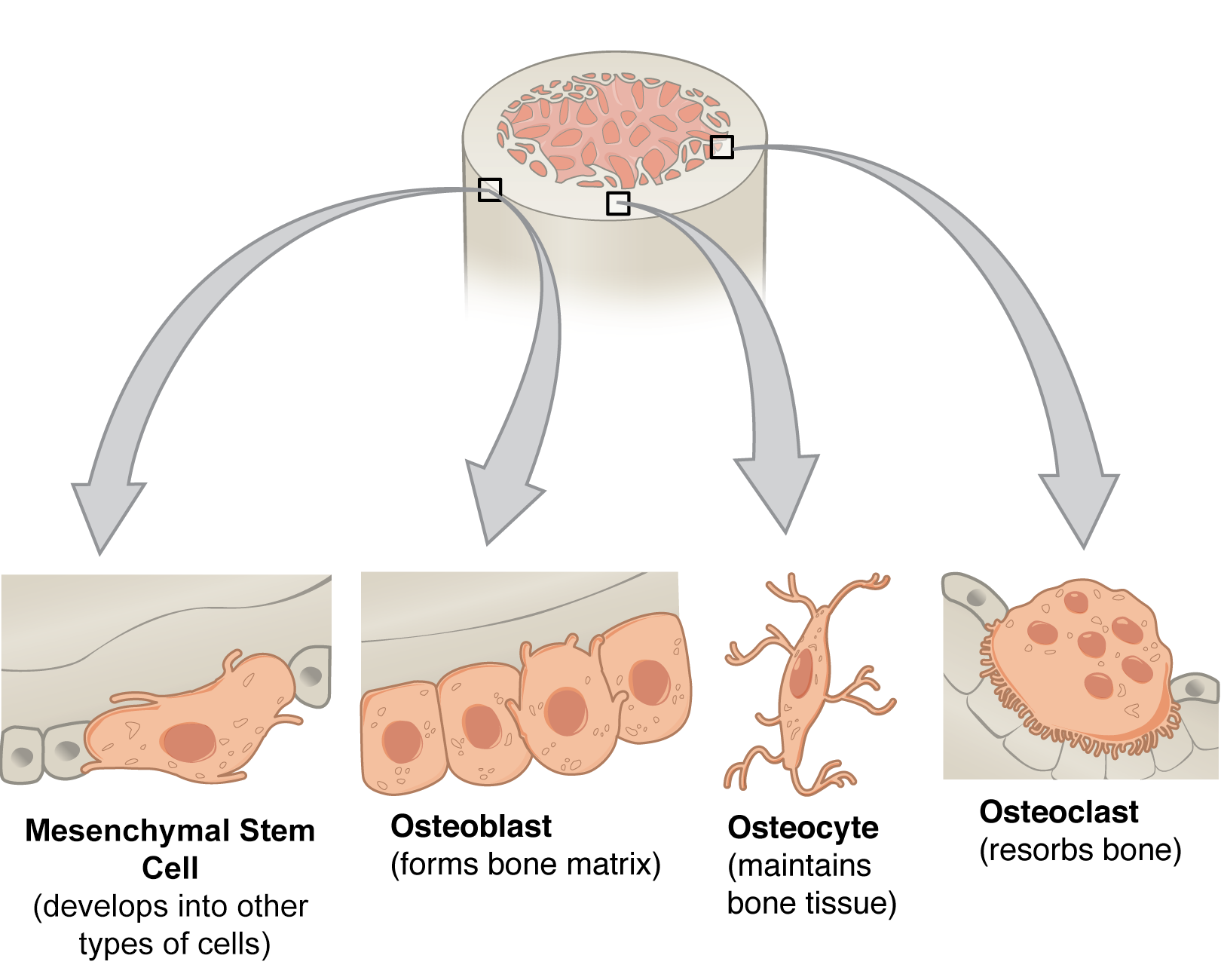
Bone Composition Part 1 Bone Cells Biogennix
Four Types Of Cells Are Found Within Bone Tissue.
Bone Is A Modified Form Of Connective Tissue Which Is Made Of Extracellular Matrix, Cells And Fibers.
Osteoblasts, Osteocytes, Osteogenic Cells And Osteoclasts (Figure 10.3.5).
Web Although Bone Cells Compose A Small Amount Of The Bone Volume, They Are Crucial To The Function Of Bones.
Related Post: